PASCO OS-8500 INTRODUCTORY OPTICS SYSTEM User Manual
Page 33
012-02744K
Introductory Optics System
®
27
Experiment 11: Image Formation from Cylindrical Mirrors
EQUIPMENT NEEDED:
-Optics Bench
-Light Source
-Ray Table and Base
-Component Holder (2)
-Slit Plate
-Ray Optics Mirror
-Parallel Ray Lens.
Figure 11.2 Virtual Object
Introduction
Ray tracing techniques can be used to locate the image formed by reflection from any mirror of known
shape. Simply think of the object as a collection of point sources of light. For a given point source, light
rays diverging from it are reflected from the mirror according to the Law of Reflection. If the reflected
rays intersect at a point, a real image is formed at that point. If the reflected rays do not intersect, but
would if they were extended back beyond the mirror, a virtual image is formed which appears to be
located at the point where the extended rays cross.
In this experiment, you will use the Ray Table to study the properties of image formation from cylindri-
cal surfaces. The properties you will observe have important analogs in image formation from spherical
mirrors.
Procedure
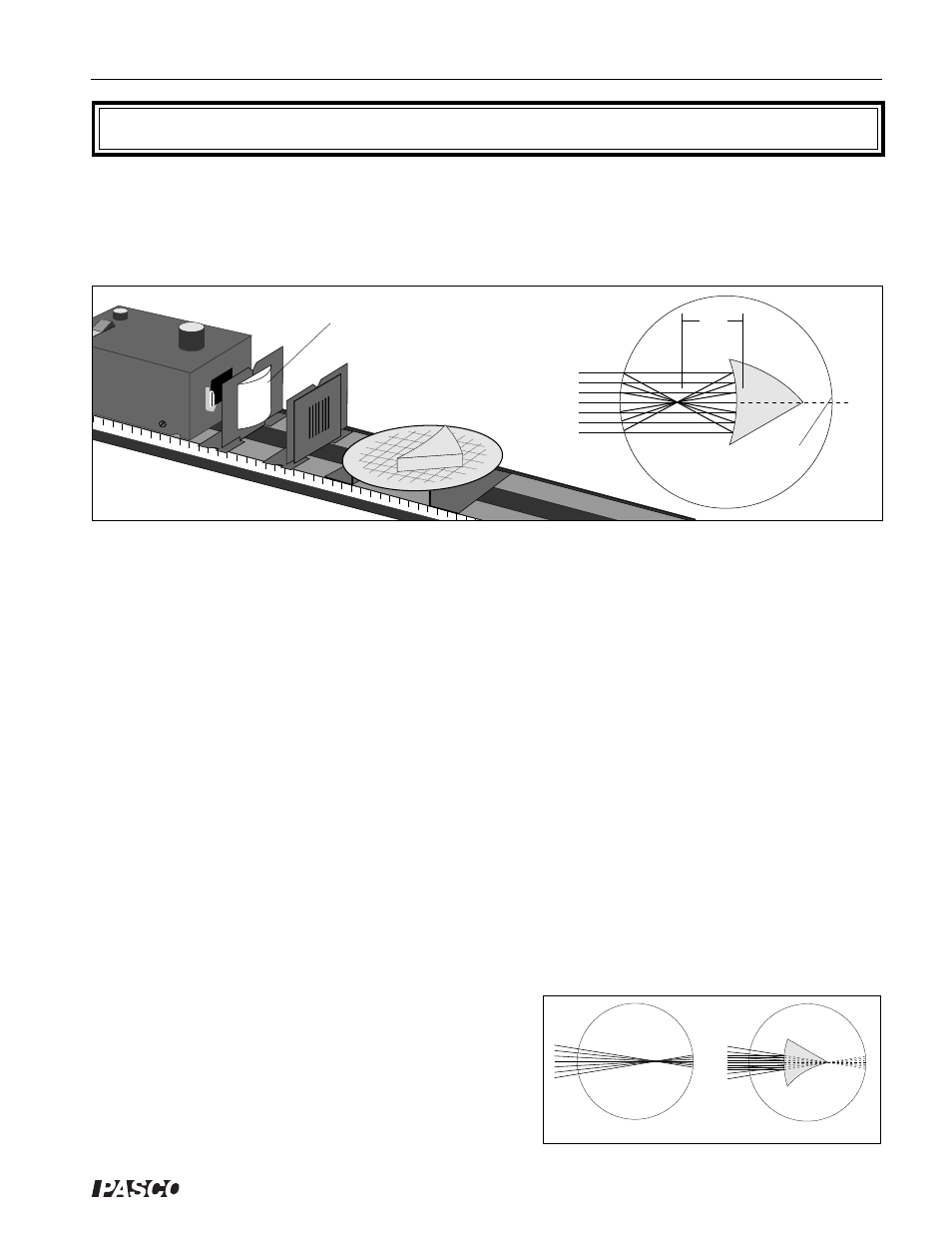
Set up the equipment as shown in Figure 11.1. Position the Ray Optics Mirror on the Ray Table so the rays are
all reflected from the concave surface of the mirror.
Focal Point
Adjust the position of the Parallel Ray Lens to obtain parallel rays on the Ray Table. Adjust the mirror on the
Ray Table so the incident rays are parallel to the optical axis of the mirror.
➀ Measure F.L., the focal length of the concave cylindrical mirror.
F.L. = _______________________________________.
➁ Use ray tracing techniques to measure the focal length of
the convex cylindrical mirror. (Check your textbook if
you have doubts about the sign conventions.)
F.L. = _______________________________________.
Position the Light Source and the Parallel Ray Lens so the
rays cross at a point on the Ray Table, as shown in Figure
11.2a. (A blank, white sheet of paper placed over the Ray
Table will help to see the rays.) Since rays diverge from
this point of intersection, it can be used as an object.
Figure 11.1 Equipment Setup
Parallel Ray
Lens
Optical Axis of
Mirror
F.L.
(a)
(b)
