PASCO OS-8500 INTRODUCTORY OPTICS SYSTEM User Manual
Page 35
012-02744K
Introductory Optics System
®
29
EQUIPMENT NEEDED:
-Optics Bench, Light Source
-Component Holder (3)
-50 mm F. L. Spherical Mirror
-Viewing Screen
-Crossed Arrow Target.
Experiment 12: Image Formation from Spherical Mirrors
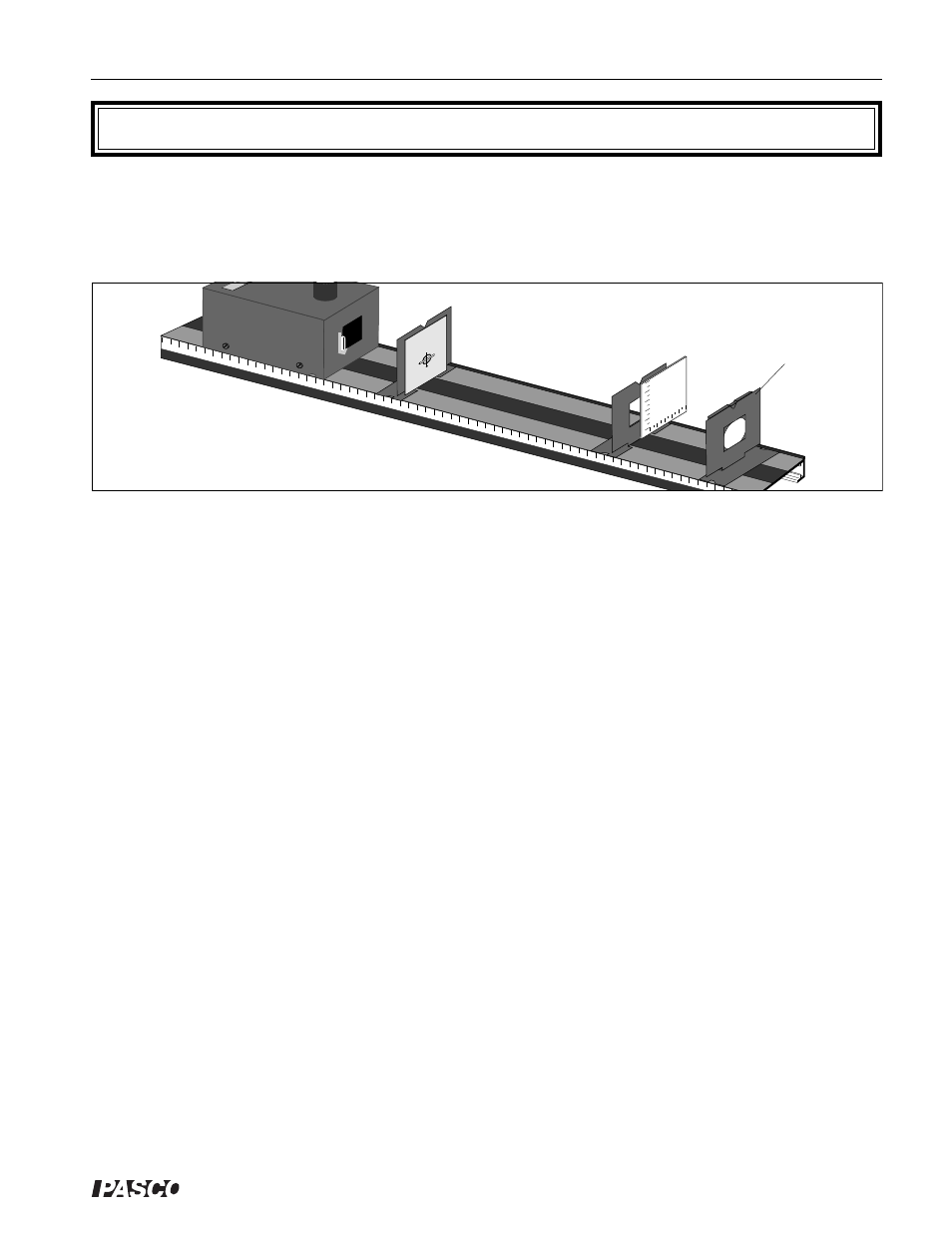
Figure 12.1 Equipment Setup
Introduction
If you cut a thin strip along any diameter of a spherical mirror, the result is a close approximation to a
thin cylindrical mirror. With this in mind, it's not surprising that images formed with spherical mirrors
exhibit many of the same properties as those formed with cylindrical mirrors. In this experiment, you
will investigate some of these properties.
Procedure
Focal Length
Set up the equipment as shown in Figure 12.1, with the concave side of the mirror facing the Light
Source. The Viewing Screen should cover only half the hole in the Component Holder so that light from
the filament reaches the mirror.
To verify the focal length of the mirror, position the mirror on the optical bench as far from the Crossed
Arrow Target as possible. Vary the position of the Viewing Screen to find where the image of the target
is focused.
➀ What is your measured focal length for the concave spherical mirror?
F.L. = ________________________________________________.
➁ How might you determine the focal length more accurately? _______________________.
Image Location, Magnification, and Inversion
In Experiment 7, you tested the validity of the Fundamental Lens Equation: 1/d
o
+ 1/d
i
= 1/f, for which
the magnification of the image is given by the equation: m = -d
i
/d
o
.
In this experiment you will test the validity of this same equation for image formation in a spherical
mirror.
Set the distance between the concave mirror and the Crossed Arrow Target to the values shown in Table
12.1. At each position, place the Viewing Screen so the image of the target is in sharp focus. Use your
data to fill in Table 12.1. Perform the calculations shown in the table to determine if the Fundamental
Lens Equation is also valid for real images formed from a spherical mirror.
➂ Are your results in complete agreement with the Fundamental Lens Equation? If not, to what do you
attribute the discrepancies? _______________________________________.
Spherical Mirror
