2 × 12a digital dual microdlynx, Non-isolated dc-dc power modules, Datasheet – GE Industrial Solutions 2 × 12A Digital Dual Output MicroDLynx User Manual
Page 18: Digital feature descriptions
GE
Datasheet
2 × 12A Digital Dual MicroDlynx
TM
: Non-Isolated DC-DC Power Modules
4.5Vdc –14.4Vdc input; 0.51Vdc to 5.5Vdc output; 2 × 12AOutput Current
February 14, 2014
©2014 General Electric Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 18
Digital Feature Descriptions
PMBus Interface Capability
The 2 × 12A Digital Dual MicroDlynx
TM
power modules have
a PMBus interface that supports both communication and
control. The PMBus Power Management Protocol
Specification can be obtained from
www.pmbus.org.
The
modules support a subset of version 1.1 of the specification
(see Table 6 for a list of the specific commands supported).
Most module parameters can be programmed using PMBus
and stored as defaults for later use.
All communication over the module PMBus interface must
support the Packet Error Checking (PEC) scheme. The PMBus
master must generate the correct PEC byte for all
transactions, and check the PEC byte returned by the
module.
The module also supports the SMBALERT# response
protocol whereby the module can alert the bus master if it
wants to talk. For more information on the SMBus alert
response protocol, see the System Management Bus
(SMBus) specification.
The module has non-volatile memory that is used to store
configuration settings. Not all settings programmed into the
device are automatically saved into this non-volatile
memory, only those specifically identified as capable of
being stored can be saved (see Table 6 for which command
parameters can be saved to non-volatile storage).
PMBus Data Format
For commands that set thresholds, voltages or report such
quantities, the module supports the “Linear” data format
among the three data formats supported by PMBus. The
Linear Data Format is a two byte value with an 11-bit, two’s
complement mantissa and a 5-bit, two’s complement
exponent. The format of the two data bytes is shown below:
Data Byte High
7 6 5 4 3
2 1 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Data Byte Low
Exponent
MSB
Mantissa
MSB
The value is of the number is then given by
Value = Mantissa x 2
Exponent
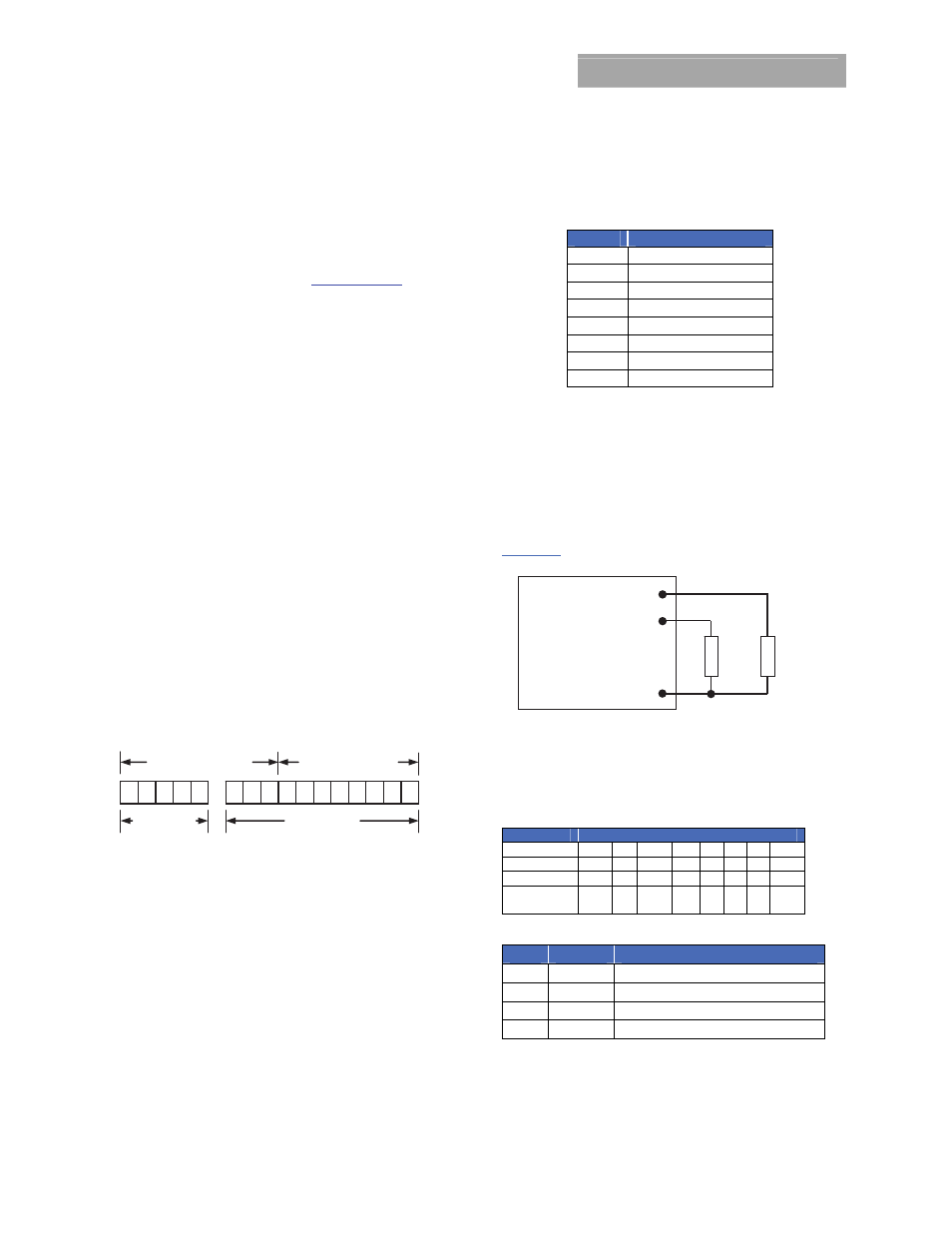
PMBus Addressing
The power module can be addressed through the PMBus
using a device address. The module has 64 possible
addresses (0 to 63 in decimal) which can be set using
resistors connected from the ADDR0 and ADDR1 pins to
SIG_GND. Note that some of these addresses (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 12, 40, 44, 45, 55 in decimal) are reserved
according to the SMBus specifications and may not be
useable. The address is set in the form of two octal (0 to 7)
digits, with each pin setting one digit. The ADDR1 pin sets
the high order digit and ADDR0 sets the low order digit. The
resistor values suggested for each digit are shown in Table 4
(1% tolerance resistors are recommended). Note that if
either address resistor value is outside the range specified in
Table 4, the module will respond to address 127.
Table 4
Digit
Resistor Value (KΩ)
0 11
1 18.7
2 27.4
3 38.3
4 53.6
5 82.5
6 127
7 187
The user must know which I
2
C addresses are reserved in a
system for special functions and set the address of the
module to avoid interfering with other system operations.
Both 100kHz and 400kHz bus speeds are supported by the
module. Connection for the PMBus interface should follow
the High Power DC specifications given in section 3.1.3 in the
SMBus specification V2.0 for the 400kHz bus speed or the
Low Power DC specifications in section 3.1.2. The complete
SMBus specification is available from the SMBus web site,
smbus.org.
ADDR0
SIG_GND
R
ADDR0
R
ADDR1
ADDR1
Figure 48. Circuit showing connection of resistors used to
set the PMBus address of the module.
PAGE
Both the outputs of the module can be configured,
controlled and monitored through only one physical address
Format
Unsigned Binary
Bit Position
7 6 5 4 3 2
1 0
Access
r/w r r
r
r
r
r r/w
Function
PA X X X X X X P0
Default
Value
0 X X X X X
X 0
PAGE Command Truth Table
PA
P0
Logic Results
0 0 All Commands address first output
0 1
All Commands address second output
1 0
Illegal input, Ignore write
1 1
All Commands address both outputs
If PAGE=11, then any read commands affect the first
channel. Any value to ready-only registers is ignored.
