I/o configurations, Port structure – Rainbow Electronics T89C5115 User Manual
Page 6
6
T89C5115
4128A–8051–04/02
I/O Configurations
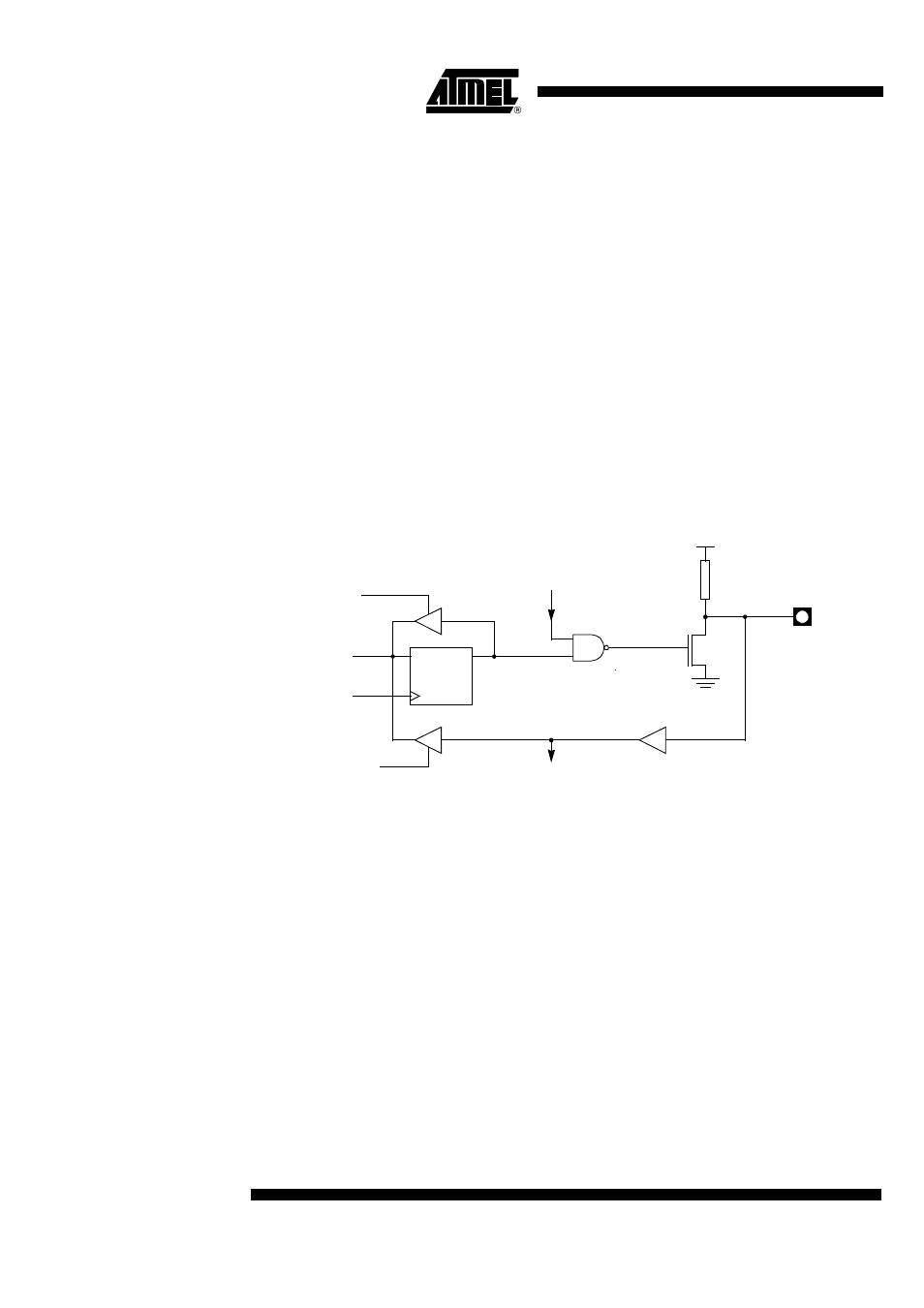
Each Port SFR operates via type-D latches, as illustrated in Figure 1 for Ports 3 and 4. A
CPU "write to latch" signal initiates transfer of internal bus data into the type-D latch. A
CPU "read latch" signal transfers the latched Q output onto the internal bus. Similarly, a
"read pin" signal transfers the logical level of the Port pin. Some Port data instructions
activate the "read latch" signal while others activate the "read pin" signal. Latch instruc-
tions are referred to as Read-Modify-Write instructions. Each I/O line may be
independently programmed as input or output.
Port Structure
Figure 1 shows the structure of Ports, which have internal pull-ups. An external source
can pull the pin low. Each Port pin can be configured either for general-purpose I/O or
for its alternate input output function.
To use a pin for general-purpose output, set or clear the corresponding bit in the Px reg-
ister (x = 1 to 4). To use a pin for general-purpose input, set the bit in the Px register.
This turns off the output FET drive.
To configure a pin for its alternate function, set the bit in the Px register. When the latch
is set, the "alternate output function" signal controls the output level (see Figure 1). The
operation of Ports is discussed further in "quasi-Bidirectional Port Operation" paragraph.
Figure 1. Ports Structure
Note:
The internal pull-up can be disabled on P1 when analog function is selected.
D
CL
Q
LATCH
INTERNAL
WRITE
TO
LATCH
READ
PIN
READ
LATCH
P1.x
ALTERNATE
OUTPUT
FUNCTION
VCC
INTERNAL
PULL-UP (1)
ALTERNATE
INPUT
FUNCTION
BUS
P2.x
P3.x
P4.x
