Table 5. option pin settings – Rainbow Electronics MAX17480 User Manual
Page 37
MAX17480
AMD 2-/3-Output Mobile Serial
VID Controller
______________________________________________________________________________________
37
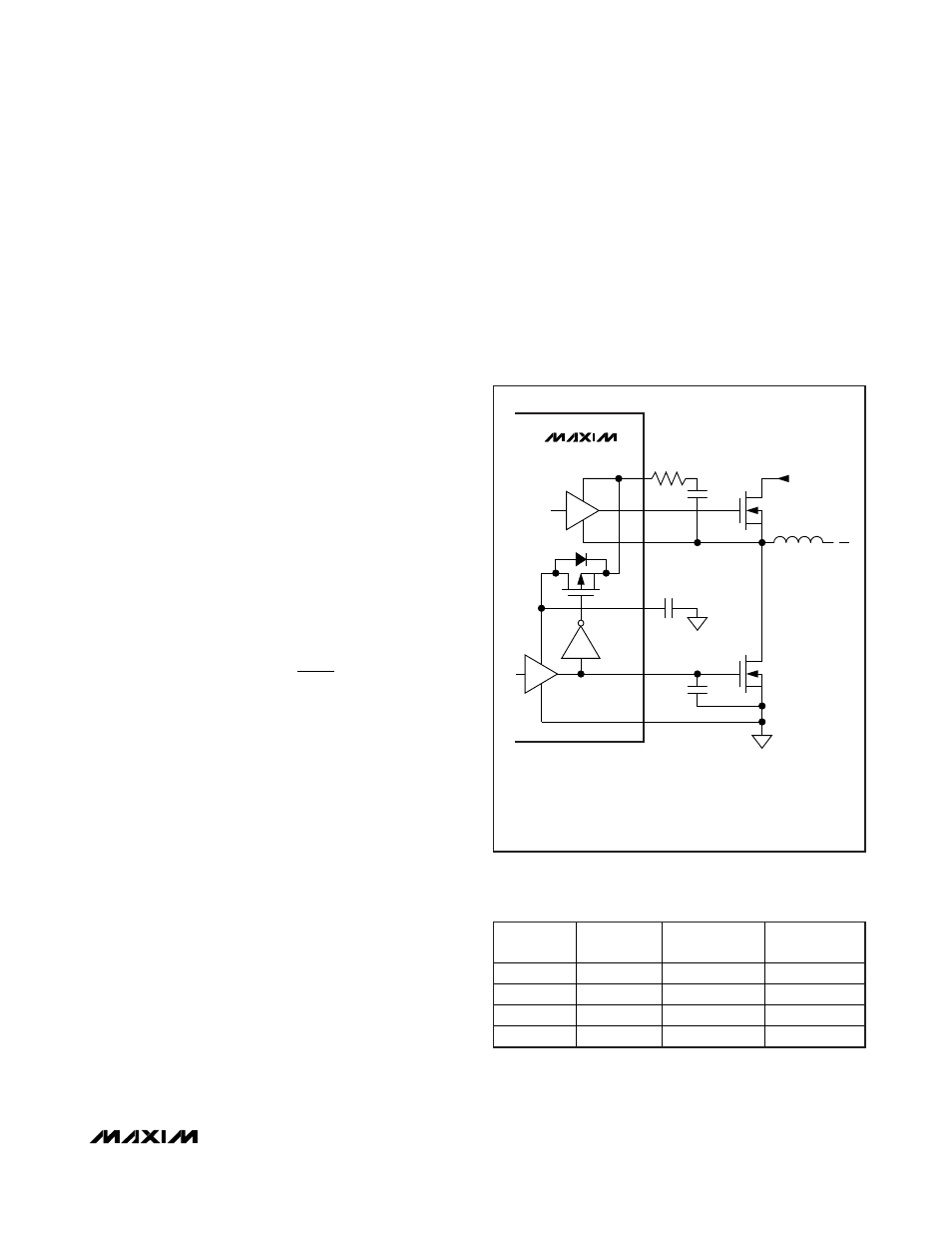
Adaptive dead-time circuits monitor the DL and DH dri-
vers and prevent either FET from turning on until the
other is fully off. The adaptive driver dead time allows
operation without shoot-through with a wide range of
MOSFETs, minimizing delays and maintaining efficiency.
There must be a low-resistance, low-inductance path
from the DL and DH drivers to the MOSFET gates
for the adaptive dead-time circuits to work properly;
otherwise, the sense circuitry in the MAX17480 inter-
prets the MOSFET gates as “off” while charge actually
remains. Use very short, wide traces (50 mils to 100
mils wide if the MOSFET is 1in from the driver).
The internal pulldown transistor that drives DL low is
robust, with a 0.25
Ω (typ) on-resistance. This helps pre-
vent DL from being pulled up due to capacitive coupling
from the drain to the gate of the low-side MOSFETs
when the inductor node (LX) quickly switches from
ground to V
IN
. Applications with high input voltages and
long inductive driver traces could require rising LX
edges that do not pull up the low-side MOSFET’s gate,
causing shoot-through currents. The capacitive coupling
between LX and DL created by the MOSFET’s gate-to-
drain capacitance (C
RSS
), gate-to-source capacitance
(C
ISS
- C
RSS
), and additional board parasitics should not
exceed the following minimum threshold:
Typically, adding a 4700pF capacitor between DL and
power ground (C
NL
in Figure 11), close to the low-side
MOSFETs, greatly reduces coupling. Do not exceed
22nF of total gate capacitance to prevent excessive
turn-off delays.
Alternatively, shoot-through currents can be caused by
a combination of fast high-side MOSFETs and slow low-
side MOSFETs. If the turn-off delay time of the low-side
MOSFET is too long, the high-side MOSFETs can turn
on before the low-side MOSFETs have actually turned
off. Adding a resistor less than 5
Ω in series with BST
slows down the high-side MOSFET turn-on time, elimi-
nating the shoot-through currents without degrading the
turn-off time (R
BST
in Figure 11). Slowing down the
high-side MOSFET also reduces the LX node rise time,
thereby reducing EMI and high-frequency coupling
responsible for switching noise.
Offset and Address Change
for Core SMPSs (OPTION)
The +12.5mV offset and the address change features
of the MAX17480 can be selectively enabled and dis-
abled by the OPTION pin setting. When the offset is
enabled, setting the PSI_L bit to 0 disables the offset,
reducing power consumption in the low-power state.
See the
Core SMPS Offset
section for a detailed
description of this feature.
In addition, the address of the core SMPSs can be
exchanged, allowing for flexible layout of the MAX17480
with respect to the CPU placement on the same or
opposite sides of the PCB. Table 5 shows the OPTION
pin voltage levels and the features that are enabled.
V
V
C
C
GS TH
IN
RSS
ISS
(
)
>
⎛
⎝
⎜
⎞
⎠
⎟
MAX17480
N
H
N
L
(R
BST
)*
(R
BST
)* OPTIONAL—THE RESISTOR LOWERS EMI BY DECREASING
THE SWITCHING NODE RISE TIME.
(C
NL
)* OPTIONAL—THE CAPACITOR REDUCES LX-TO-DL CAPACITIVE
BST
INPUT (V
IN
)
L
DH
LX
V
DD
DL
PGND
C
BST
(C
NL
)*
C
BYP
COUPLING THAT CAN CAUSE SHOOT-THROUGH CURRENTS.
Figure 11. Gate-Drive Circuit
OPTION
OFFSET
ENABLES
SMPS1
ADDRESS
SMPS2
ADDRESS
V
CC
0
BIT 1 (VDD0)
BIT 2 (VDD1)
3.3V
0
BIT 2 (VDD1)
BIT 1 (VDD0)
2V
1
BIT 1 (VDD0)
BIT 2 (VDD1)
GND
1
BIT 2 (VDD1)
BIT 1 (VDD0)
Table 5. OPTION Pin Settings
Note: VDD0 refers to CORE0 and VDD1 refers to CORE1 for
the AMD CPU.
