Rainbow Electronics MAX17480 User Manual
Page 29
MAX17480
AMD 2-/3-Output Mobile Serial
VID Controller
______________________________________________________________________________________
29
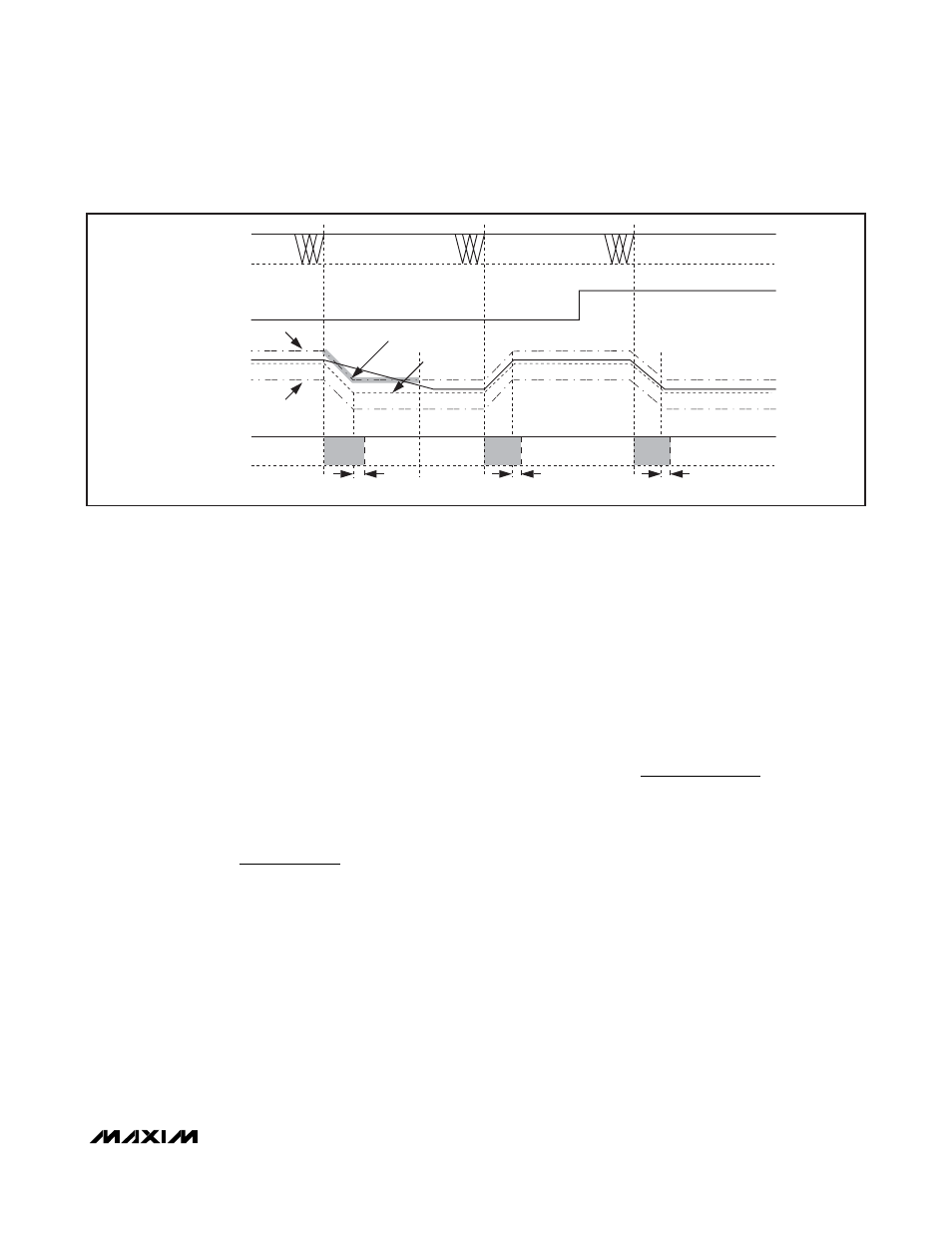
of a downward VID transition, the upper PWRGD thresh-
old is enabled only after the output reaches the lower
VID code setting. Figure 6 shows VID transition timing.
The MAX17480 automatically controls the current to the
minimum level required to complete the transition in the
calculated time. The slew-rate controller uses an inter-
nal capacitor and current source programmed by
R
TIME
to transition the output voltage. The total transi-
tion time depends on R
TIME
, the voltage difference, and
the accuracy of the slew-rate controller (C
SLEW
accuracy). The slew rate is not dependent on the total
output capacitance, as long as the surge current is less
than the current limit set by ILIM12 for the core SMPSs
and ILIM3 for the NB SMPS. For all dynamic positive
VID transitions or negative VID transitions in forced-
PWM mode (PSI_L set to 1), the transition time (t
TRAN
)
is given by:
where dV
TARGET
/dt = 6.25mV/µs
× 143kΩ/R
TIME
is the
slew rate, V
OLD
is the original output voltage, and V
NEW
is the new target voltage. See the Slew-Rate Accuracy
in the
Electrical Characteristics
table for slew-rate limits.
The output voltage tracks the slewed target voltage,
making the transitions relatively smooth. The average
inductor current per phase required to make an output
voltage transition is:
where dV
TARGET
/dt is the required slew rate and C
OUT
is the total output capacitance of each phase.
If the SMPS is in a pulse-skipping mode (PSI_L set to
0), the discharge rate of the output voltage during
downward transitions is then dependent on the load
current and total output capacitance for loads less than
a minimum current, and dependent on the R
TIME
pro-
grammed slew rate for heavier loads. The critical load
current (I
LOAD(CRIT)
) where the transition time is depen-
dent on the load is:
For load currents less than I
LOAD(CRIT)
, the transition
time is:
For soft-start, the controller uses a fixed slew rate of
1mV/µs. In shutdown, the outputs are discharged using
a 20
Ω switch through the CSN_ pins for the core
SMPSs and through the OUT3 pin for the NB SMPS.
Forced-PWM Operation
After exiting the boot mode and if the PSI_L bit is set to
1, the MAX17480 operates with the low-noise, forced-
PWM control scheme. Forced-PWM operation disables
the zero-crossing comparator, forcing the low-side
gate-drive waveforms to constantly be the complement
of the high-side gate-drive waveforms. This keeps the
switching frequency constant and allows the inductor
current to reverse under light loads, providing fast,
accurate negative output-voltage transitions by quickly
discharging the output capacitors.
Forced-PWM operation comes at a cost: the no-load +5V
bias supply current remains between 50mA to 70mA,
t
C
dV
I
TRAN
OUT
TARGET
LOAD
≅
×
I
C
dV
dt
LOAD CRIT
OUT
TARGET
(
)
/
≅
×
(
)
I
C
dV
dt
L
OUT
TARGET
≅
×
(
)
/
t
V
V
dV
dt
TRAN
NEW
OLD
TARGET
=
−
⎡⎣
⎤⎦
(
)
/
SMPS VOLTAGE
(SMPS TARGET)
PWRGD
SMPS LOAD
LIGHT LOAD
HEAVY LOAD
SVC/SVD
BUS IDLE
BUS IDLE
BUS IDLE
PWRGD UPPER THRESHOLD
PWRGD LOWER
THRESHOLD
SMPS TARGET
UPPER THRESHOLD BLANKED
BLANK
HIGH-Z
BLANK
HIGH-Z
BLANK
HIGH-Z
20
µ
s
20
µ
s
20
µ
s
Figure 6. VID Transition Timing
