Displaying taws data, Hazard avoidance – Garmin G1000 Mooney M20TN User Manual
Page 329
190-00647-02 Rev. A
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Mooney M20M/M20R/M20TN
315
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EIS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL
FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
TSO-C151b. However, the displayed information should never be understood as being all-inclusive and data
may be inaccurate.
TAWS uses information provided from the GPS receiver to provide a horizontal position and altitude. GPS
altitude is derived from satellite measurements. GPS altitude is converted to a mean sea level (MSL)-based altitude
(GPS-MSL altitude) and is used to determine TAWS alerts. GPS-MSL altitude accuracy is affected by factors such
as satellite geometry, but it is not subject to variations in pressure and temperature that normally affect pressure
altitude devices. GPS-MSL altitude does not require local altimeter settings to determine MSL altitude. Therefore,
GPS altitude provides a highly accurate and reliable MSL altitude source to calculate terrain and obstacle alerts.
The terrain and obstacle databases used by TAWS are referenced to mean sea level (MSL). Using the GPS
position and GPS-MSL altitude, TAWS displays a 2-D picture of the surrounding terrain and obstacles relative to
the position and altitude of the aircraft. Furthermore, the GPS position and GPS-MSL altitude are used to calculate
and “predict” the aircraft’s flight path in relation to the surrounding terrain and obstacles. In this manner, TAWS
can provide advanced alerts of predicted dangerous terrain conditions.
Baro-corrected altitude (or indicated altitude) is derived by adjusting the altimeter setting for local atmospheric
conditions. The most accurate baro-corrected altitude can be achieved by frequently updating the altimeter setting
to the nearest reporting station along the flight path. However, because actual atmosphere conditions seldom
match the standard conditions defined by the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) model (where pressure,
temperature, and lapse rates have fixed values), it is common for the baro-corrected altitude (as read from the
altimeter) to differ from the GPS-MSL altitude. This variation results in the aircraft’s true altitude differing from
the baro-corrected altitude.
DISPLAYING TAWS DATA
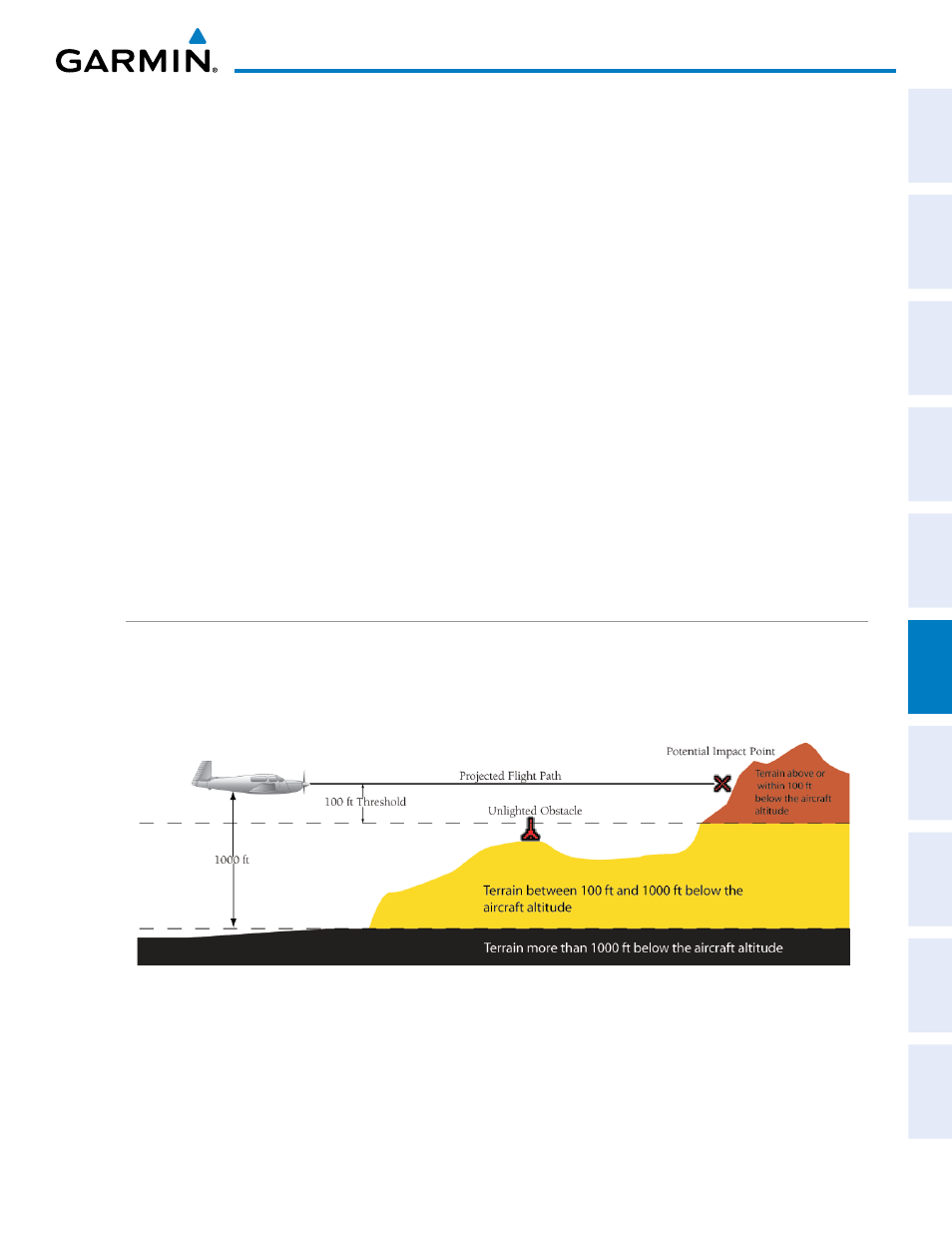
TAWS uses yellow (caution) and red (warning) to depict terrain and obstacles (with heights greater than 200
feet above ground level, AGL) alerts relative to aircraft altitude. Colors are adjusted automatically as the aircraft
altitude changes. The colors and symbols in Figure 6-60 and Table 6-10 are used to represent terrain, obstacles,
and potential impact points.
Figure 6-60 Terrain Altitude/Color Correlation for TAWS
