Interface and service domain ip address commands – Paradyne 6342 User Manual
Page 80
A. Command Line Interface
A-6
November
2003
6300-A2-GB20-10
Interface and Service Domain IP Address Commands
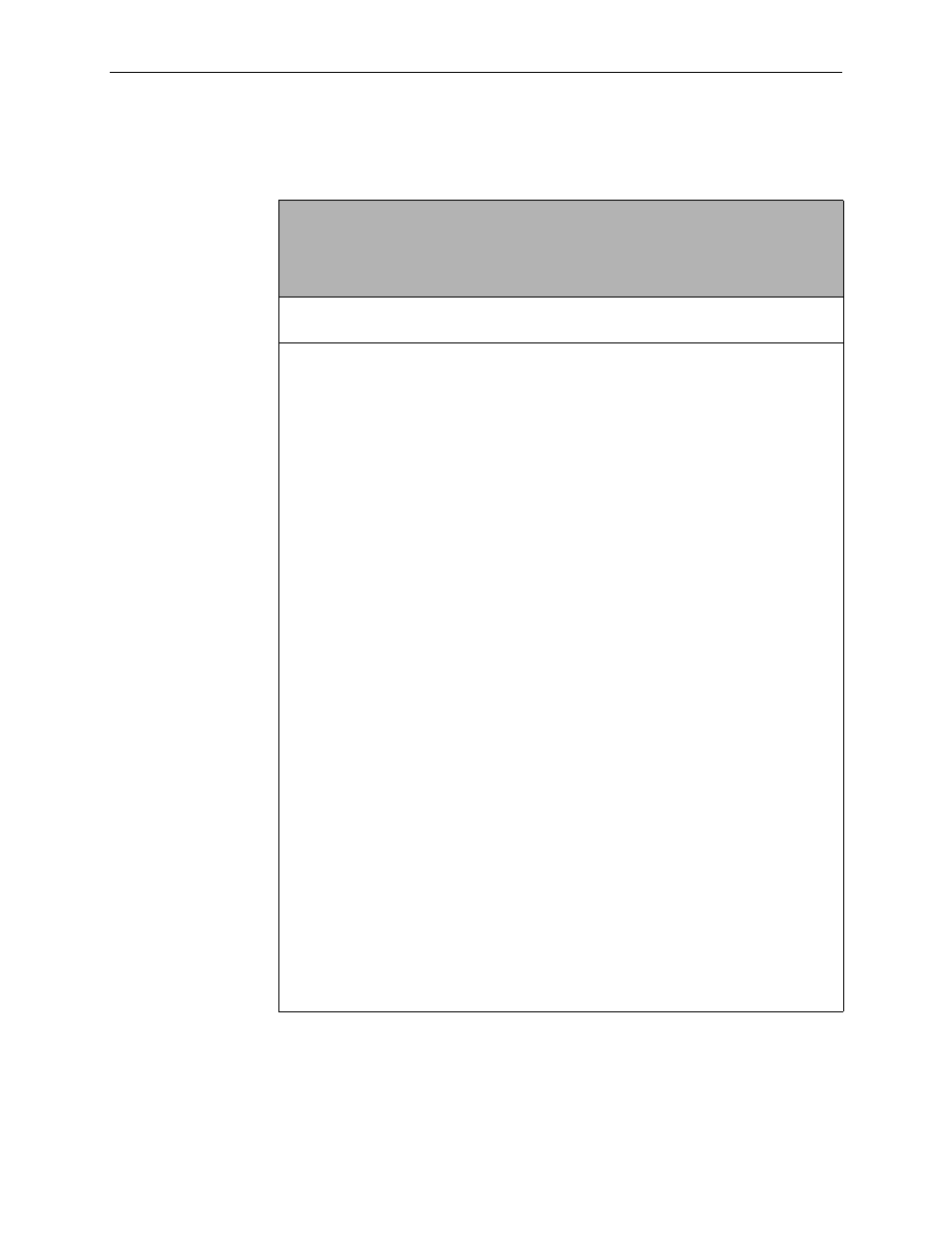
Table A-4.
Interface and Service Domain IP Address Commands
ifn address
{eth1[:ifn ] | dsl1[:ifn] } ip-address mask [primary]
ifn {dsl1[
:ifn ] | eth1[:ifn] } primary
ifn address dsl1 unnumbered
delete {dsl1[
:ifn ] | eth1[:ifn ] }
Minimum Access Level: Administrator
Command Mode: Config
Specifies the IP address associated with either the Ethernet or DSL interface.
Examples: ifn address dsl1 135.300.41.8 255.255.255.0
ifn dsl1 primary
Up to four (4) IP addresses can be assigned on each interface. An interface address and
mask cannot be changed while there is a static route (upstream or downstream) that uses
it. Interface IP address ranges must not overlap.
eth1, eth1:1, eth1:2, eth1:3, eth1:4 – Ethernet interface (eth1 is the same as eth1:1).
dsl1, dsl1:1, dsl1:2, dsl1:3, dsl1:4 – DSL interface (dsl1 is the same as dsl1:1).
ip-address – The IP address associated with the specified interface.
mask – The subnet mask associated with the specified IP address.
primary – The Primary designation of a numbered interface marks that interface as the
one whose IP address will be used as the Router ID. (The Router ID is important when the
DSL interface is unnumbered.) If no interface is defined as Primary, the last numbered
interface created will become the Primary IP Address.
unnumbered – Specifies that the DSL interface is to be unnumbered.
NOTES:
– For each defined Ethernet interface, a corresponding upstream next hop router IP
address must be configured for routing of packets received on that interface, unless
FUNI/MPOA link encapsulation is being used or PPPoE is enabled. See
create upstream eth1[:ifn] next-hop-ip
on page A-8 for more details.
– When the eth1 is assigned an IP address, this section also defines the logical
network (subnet) containing the locally attached hosts. An IP route table entry will
automatically be created to correspond to the subnet defined by the mask.
– When the DSL interface is numbered, multiple logical Ethernet interfaces can be
assigned to the same DSL logical interface by configuring the same upstream next
hop router. This is not necessary if FUNI/MPOA link encapsulation is being used or
PPPoE is enabled.
– The configured DSL logical interfaces must be either all numbered or a single
unnumbered interface.
– When NAT is being used, the DSL interface must be numbered.
– When NAT, DHCP Server, or DHCP Relay is enabled, there can be only one service
domain configured. Only one logical interface must be defined for each physical
interface, i.e., one IP address to each interface.
