Loopbacks, Able 7-1 – Paradyne 7612 SNMP DSU User Manual
Page 58
Testing
7-7
7612-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
Loopbacks
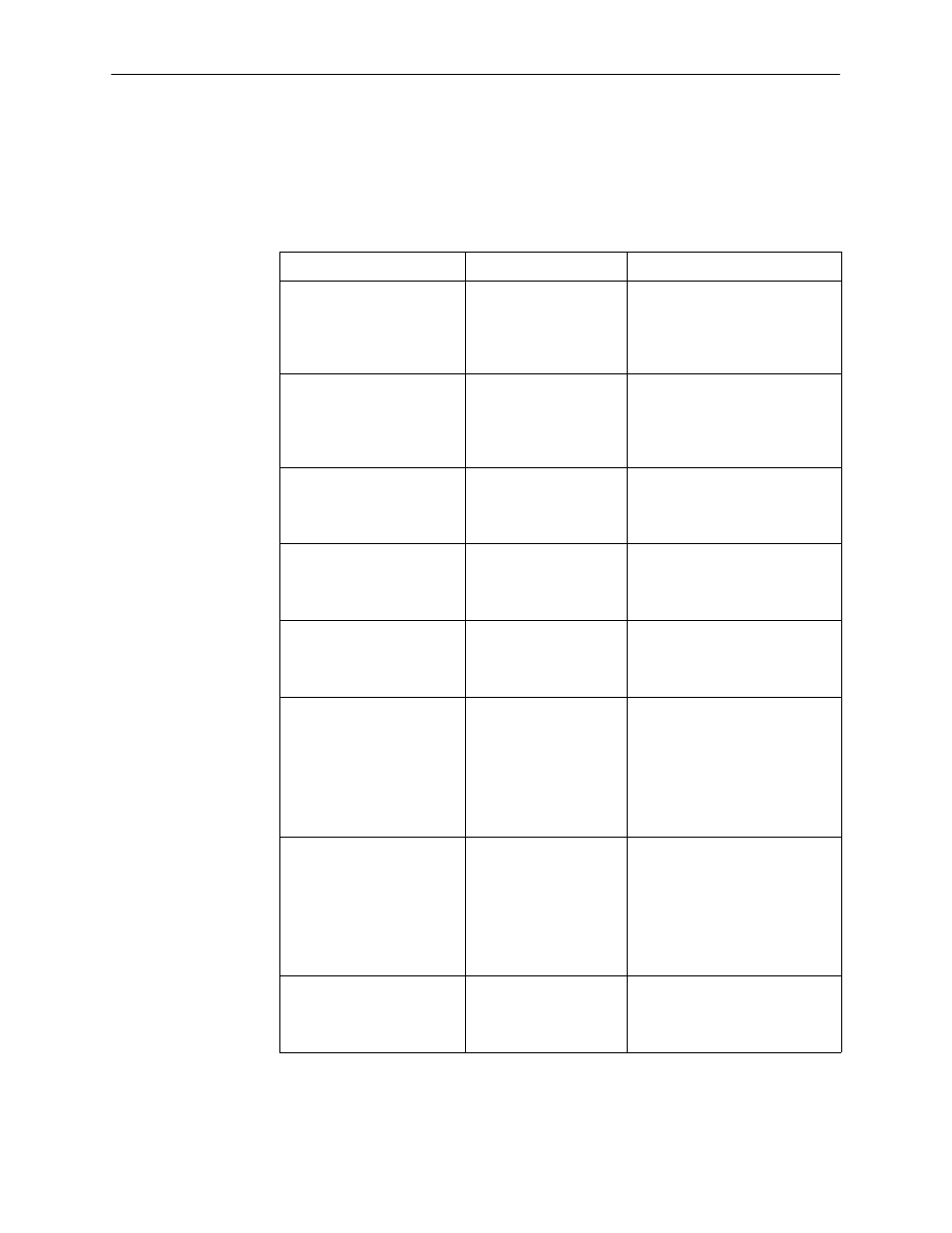
Loopbacks can be started from a variety of points in the network. Refer to
Table 7-1 for further information.
Table 7-1.
Loopbacks
Loopback Type
Initiated By
Notes
Bilateral Loopback
H
ATI
H
NMS
H
Remote unit sending
V.54 sequence
When enabled, running a DSU
loopback also automatically
starts a local loopback. Refer to
Table A-3,
enable.
56 kbps CSU Loopback
(Non-latching loopback)
64 kbps CC CSU Loopback
(Latching loopback)
H
ATI (Network tests)
H
NMS
H
DDS Network, by
loop current reversal
When initiated by the network,
CSU Loopback cannot be
disabled by the user. When IMC
is enabled, the aggregate data
is looped back to the network.
DSU Loopback (Digital)
H
ATI
H
NMS
When IMC is enabled, only user
data is looped back to the
network. Refer to Table A-3,
Local Loopback
H
ATI
H
DTE via CT141
H
NMS
Control via CT141 can be
disabled. Refer to Table A-3,
Network-initiated
56 kbps DSU Loopback
(Non-latching loopback)
H
DDS Network
When IMC is enabled, the
aggregate data stream is looped
back to the network. Cannot be
disabled by user.
Network-initiated
64 kbps CC DSU Loopback
(Latching loopback)
H
DDS Network
Includes optional data
scrambling and uses 25-second
timer to detect the network
sequence. When IMC is
enabled, the aggregate data
stream is looped back to the
network. Can be disabled by
user.
Remote Digital Loopback
H
Remote unit sending
V.54 sequence
Same as a DSU Loopback but
initiated by a remote unit via
V.54 sequence. When IMC is
enabled, only user data is
looped back to the network. Can
be disabled locally. Refer to
Table A-2,
V.54 Sequences to remote
unit
H
ATI
H
NMS
H
DTE via CT140
Control via CT140 can be
disabled. Refer to Table A-3,
