Table 2-6, Table 2-7, Figure 2-16 – SMC Networks ARM PL241 User Manual
Page 50: Asynchronous write -30
Functional Overview
2-30
Copyright © 2006 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
ARM DDI 0389B
Note
In multiplexed-mode, both address and data are output by the SMC on the
smc_data_out_0[31:0] output bus. Read data is accepted on the smc_data_in_0[31:0]
bus.
Asynchronous write
Table 2-6 and Table 2-7 list the smc_opmode0_<0-3> and SRAM Register settings.
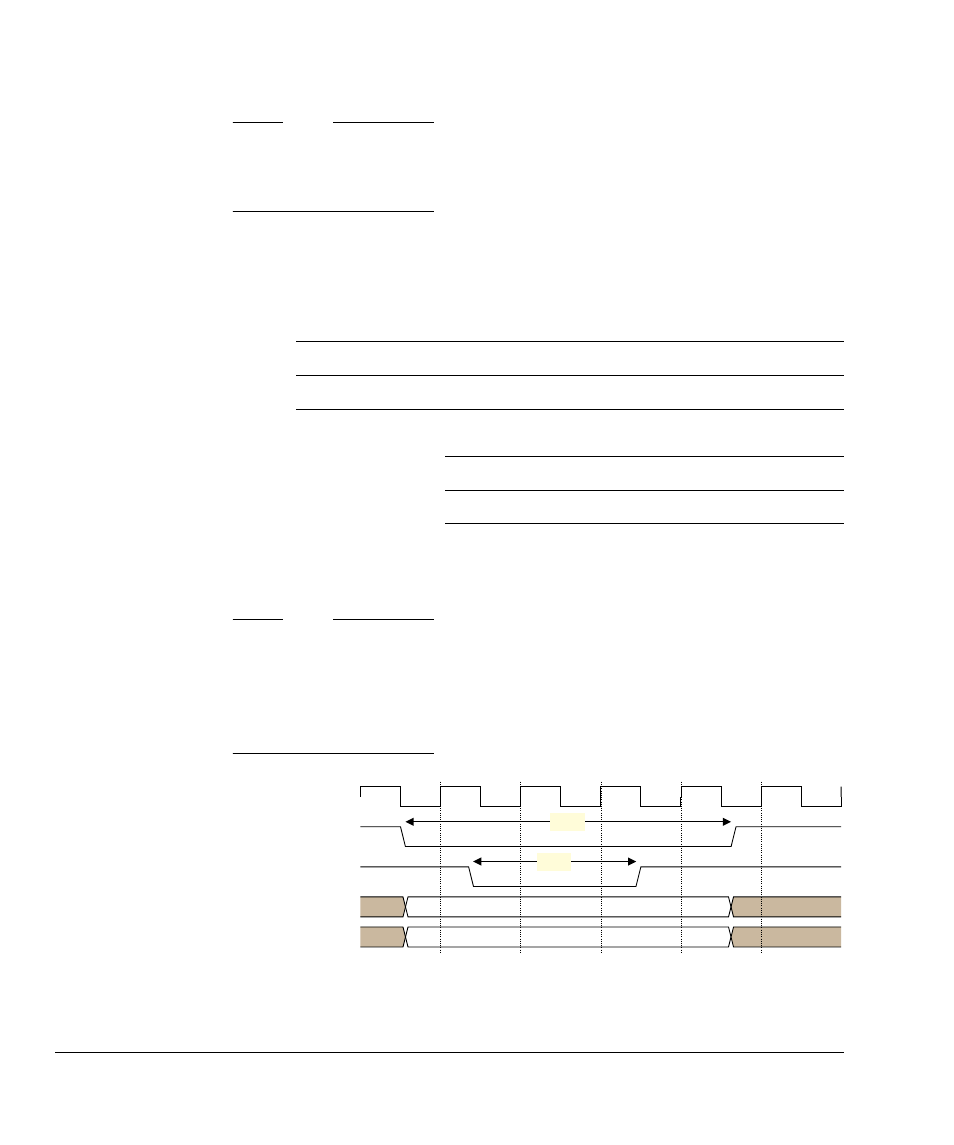
Figure 2-16 shows an asynchronous write with a write cycle time t
WC
of four cycles and
a smc_we_n_0 assertion duration, t
WP
, of two cycles.
Note
The timing parameter t
WC
is controlling the deassertion of smc_we_n_0. You can use
it to vary the hold time of smc_cs_n_0[3:0], smc_add_0[31:0] and
smc_data_out_0[31:0]. This differs from the read case where the timing parameter
t
CEOE
controls the delay in the assertion of smc_oe_n_0. Additionally, smc_we_n_0 is
always asserted one cycle after smc_cs_n_0[3:0] to ensure the address bus is valid.
Figure 2-16 Asynchronous write
Table 2-6 Asynchronous write opmode chip register settings
Field
mw
rd_sync
rd_bl
wr_sync
wr_bl
baa
adv
bls
ba
Value
-
-
-
b0
b000
-
-
-
-
Table 2-7 Asynchronous write SRAM cycles register settings
Field
t_rc
t_wc
t_ceoe
t_wp
t_pc
t_tr
Value
-
b0100
-
b010
-
-
VPFBFVBQB>@
VPFBZHBQB
VPFBDGGB>@
VPFBGDWDBRXWB>@
VPFBPFON
W
:&
W
:3
$
'
