General concepts, 2 general concepts – ProSoft Technology MVI56-PDPS User Manual
Page 58
MVI56-PDPS ♦ ControlLogix Platform
Reference
Profibus DP Slave Communication Module
Page 58 of 88
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
April 22, 2008
PROFIBUS supports a variety of network types. The network type supported by
the MVI56-PDPS module is PROFIBUS DP (Device Bus) version 0, which is
designed for remote I/O systems, motor control centers, and variable speed
drives.
5.2.2 General
Concepts
The following discussion explains several concepts that are important for
understanding the operation of the MVI56-PDPS module.
Module Power Up
On power up the module begins performing the following logical functions:
1
Initialize hardware components
o
Initialize ControlLogix backplane driver
o
Test and Clear all RAM
o
Initialize the PROFIBUS Slave port
2
Reads configuration from Compact Flash Disk
3
Initialize Module Register space
4
Enable Slave Driver on PROFIBUS port
After the module has received the Module Configuration, the module is waiting to
communicate with other nodes on the network, depending on the configuration.
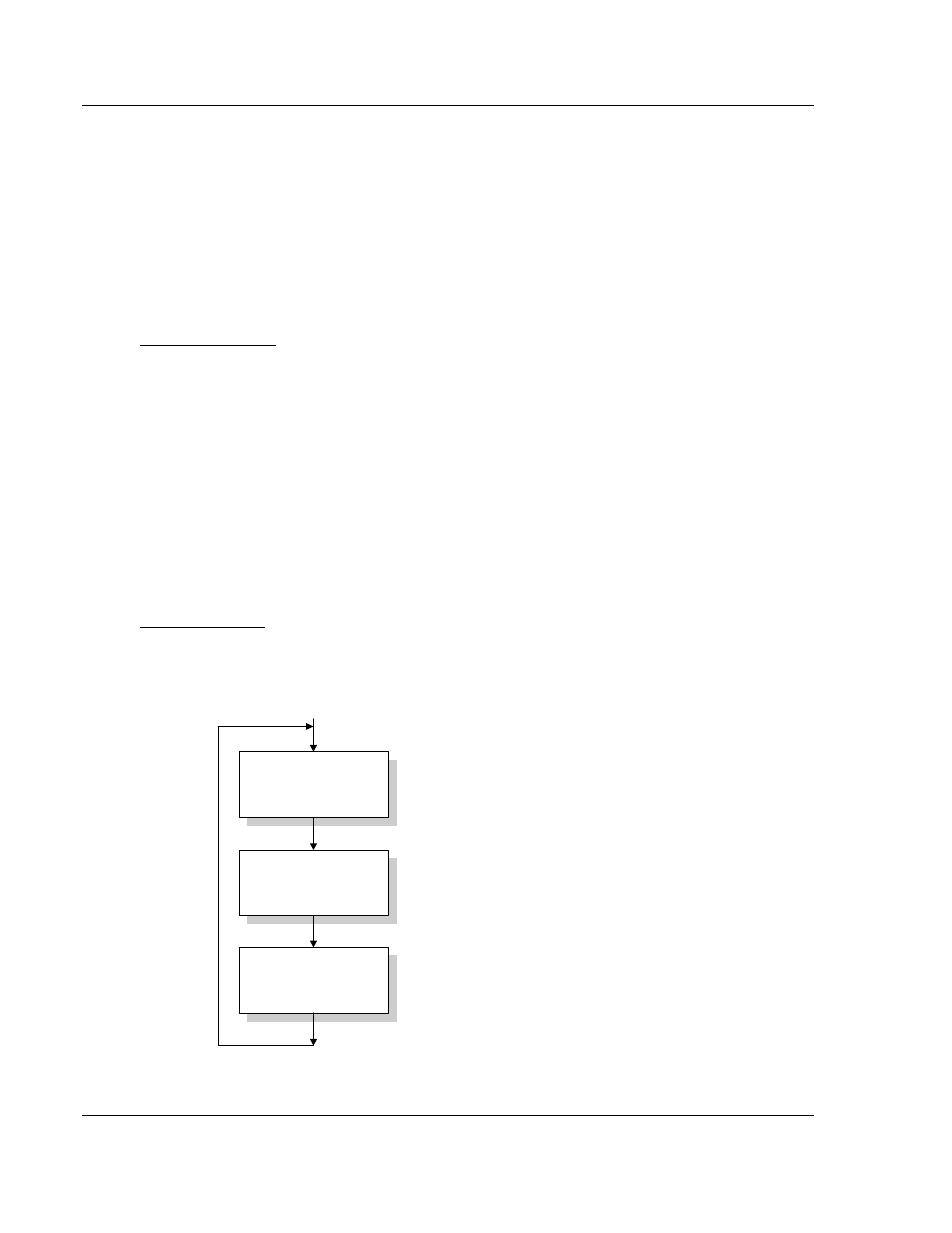
Main Logic Loop
Upon completing the power up configuration process, the module enters an
infinite loop that performs the functions shown in the following diagram.
Call I/O Handler
Call CFG/DEBUG Port
Driver
Call Network
Slave Drivers
Call I/O Handler
Transfers data between the module and processor
(user, status, etc.)
Call Serial Port Driver
Rx and Tx buffer routines are interrupt driven. Call to
serial port routines check to see if there is any data
in the buffer, and depending on the value, will either
service the buffer or wait for more characters.
Call Network Slave Drivers
Respond to messages received.
From Power Up Logic
