Qos and vpn interaction, Qos and vpn interaction -22, Route – Enterasys Networks Security Router X-PeditionTM User Manual
Page 304
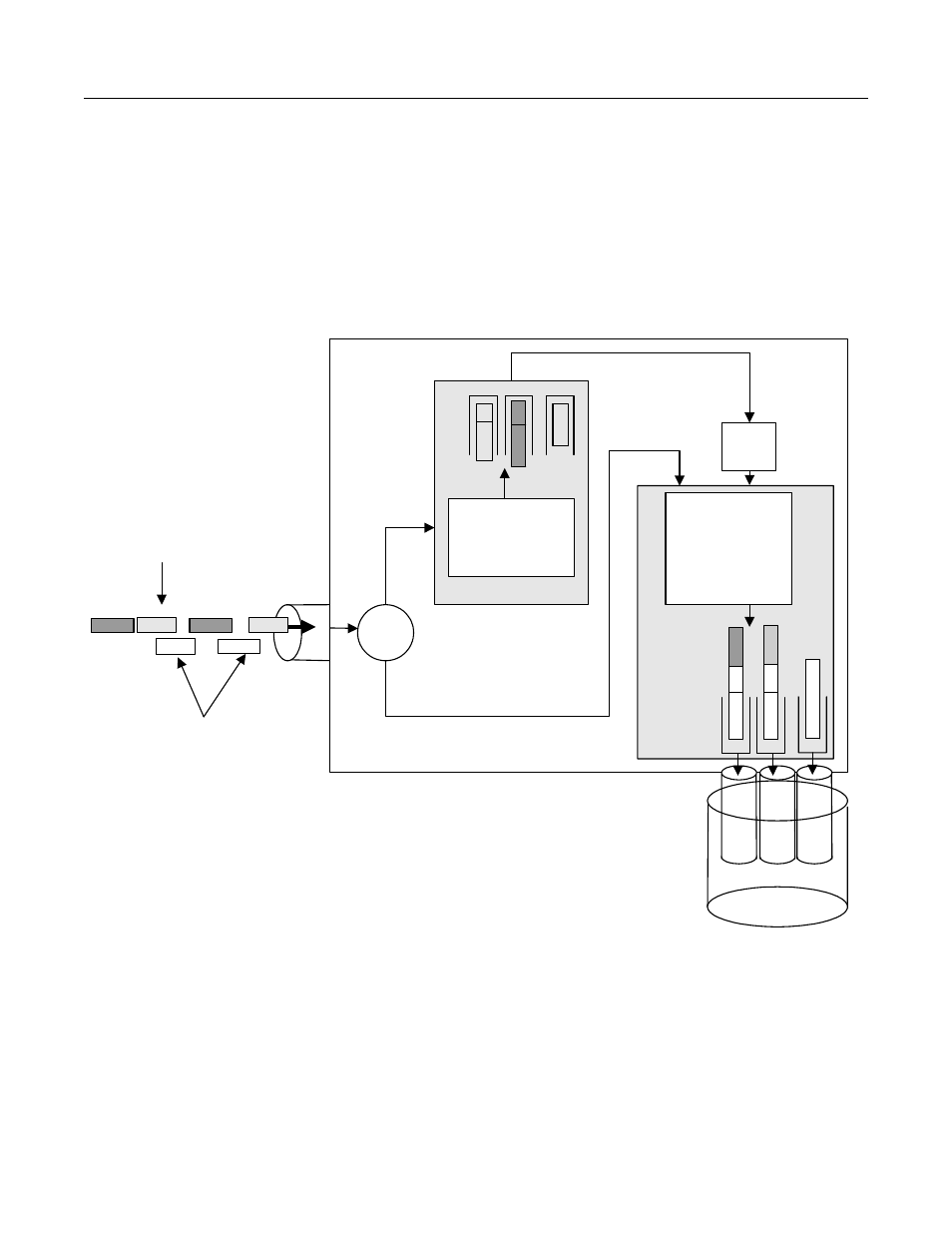
QoS on VPN
12-22 Configuring Quality of Service
XSR(config)#interface vpn 1
XSR(config-int-vpn)#ip address 20.20.20.1/24
XSR(config-int-vpn)#copy-tos
XSR(config-int-vpn)#service-policy output vpn
XSR(config-tms-tunnel)#tunnel t1
XSR(config-tms-tunnel)#set protocol gre
XSR(config-tms-tunnel)#set peer 10.10.10.2
XSR(config-tms-tunnel)#set active
XSR(config-tms-tunnel)#no shutdown
Figure 12-7 Bandwidth Allocation of VPN/Non-VPN Traffic on Virtual Interface
QoS and VPN Interaction
The mechanism underlying the VPN interface requires that packets be routed twice in the packet
processor. In their first pass, packet s are routed from the input interface to the VPN interface and
in the second pass, they are routed from the VPN interface to the output physical port. The output
physical port is determined purely by routing information and can change over time as the
reachability of the tunnel peer changes. As a result, the VPN interface and consequently QoS has
no prior knowledge about the output physical port.
`
`
RTP
FTP
FTP
RTP
IPsec
A
RTP
IPsec
B
FT
P
policy Ser
class RTP-A
priority high 100
class FTP-B
bandwidth perc 20
Crypto
Serial QoS
Rest
100K
20% rest
IP
/Ip
Sec
IP
IP
Non
VPN
traffic
VPN
traffic
FT
P
A
RT
P
B
policy VPN
class RTP
set ip dscp A
class FTP
set ip dscp B
Virtual interface QoS
IP
route
