Video reference connections, Introduction – Grass Valley NV5128 v.2.5 User Manual
Page 29
NV5128 Multi-Format Router • User’s Guide
19
2. Introduction
Module Slots and Rear Connectors
Using Video and Audio References
on page 6.) For optimum audio output, signals must
be clock-locked to the same reference. Input impedance is selected by setting jumpers on the con-
trol card. (See
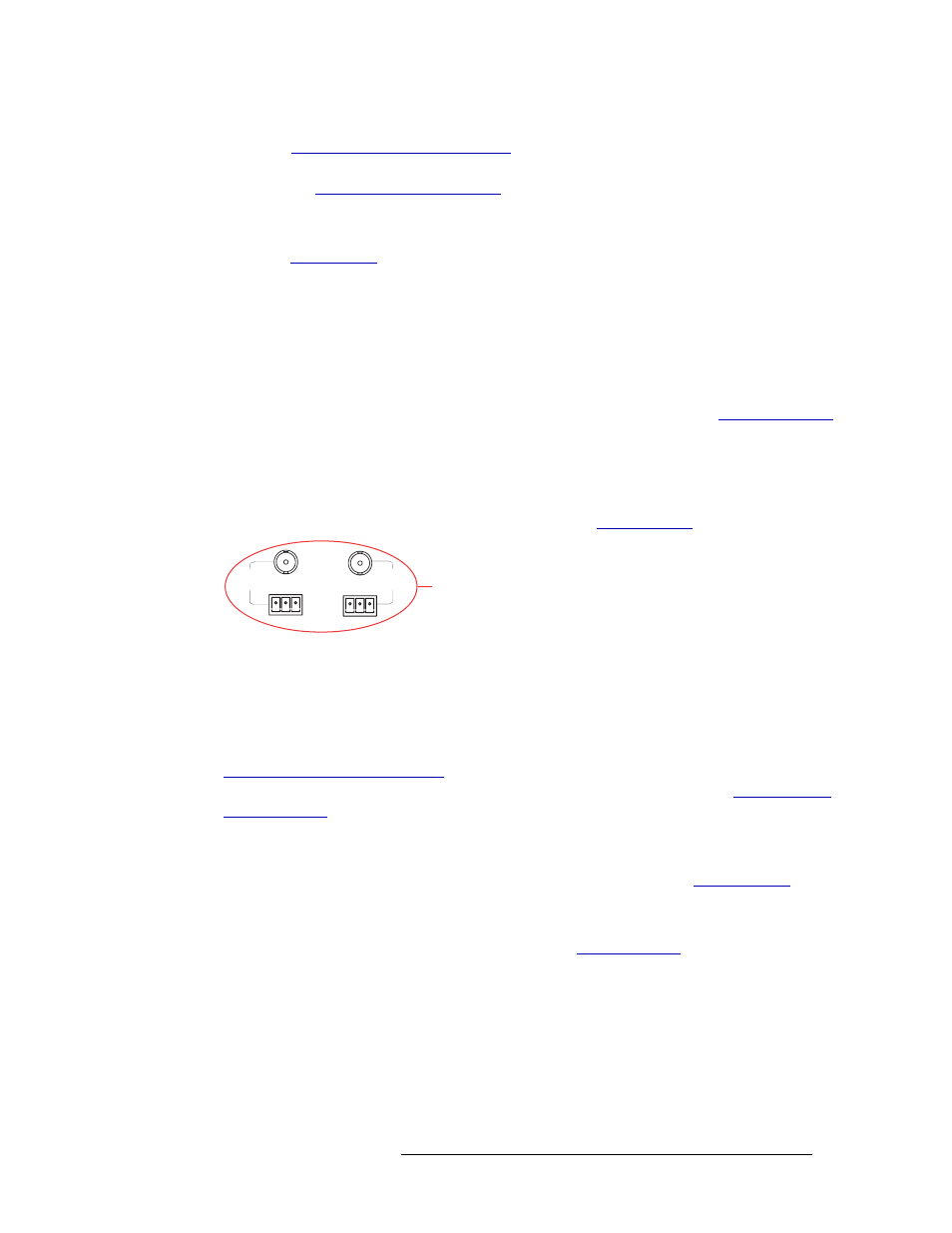
The NV5128 has two AES reference connections labeled ‘AES REF1’ and ‘AES REF2’, as shown
in Figure 2-13. Both connections are shared by the primary control card and the secondary control
card. (See
on page 21.) The AES reference connections are “redundant” and use the
same reference type. When both reference connections are connected, if one reference fails, the
control card automatically fails-over to the redundant reference.
Synchronous AES input cards can work with inputs that are not locked to a common AES refer-
ence. These inputs are treated as non-synchronous AES signals. Although possible, this is not rec-
ommended for high-quality program audio feeds because the audible effects may be unpredictable,
depending on the program content and the degree of offset in the incoming data rate.
An AES reference is required when using synchronous AES output cards. (See
on page 23.) While it is possible to let the clock generator on the control card free-run, the synchro-
nous AES outputs may contain ticks and pops, the severity of which depends on the difference in
clock rate.
The AES reference connection requires a stable signal source of AES with a sample rate of 48kHz.
For instructions on making AES reference connections, see
Figure 2-13. Connections to AES References (Rear View)
Video Reference Connections
The NV5128 provides timing reference connections for video signals, labeled ‘VIDEO REF 1’ and
‘VIDEO REF 2’, as shown in Figure 2-14 on page 20. These connections provide a reference input
for determining the router’s video frame switch point and are required for certain signals. (See
Using Video and Audio References
on page 6.) The same reference can be used for both connec-
tions or a different reference used for each connection. For more information, see
If a video reference is present, signals switch at the defined frame and line switch points. If a video
reference is not present, the router still switches the signal, but to an internal reference. When the
video reference is not connected the control card red LEDs remain lit. (See
page 76.)
The video reference connections require a stable source of PAL, NTSC or Tri-level sync. For
instructions on making video reference connections, see
Redundant and Dual References
There are two video reference connections. The same reference can be used for both connections or
a different reference for each connection. When using the same, or “redundant,” references for both
connections, if one reference fails, the control card automatically fails-over to the redundant refer-
ence. When using different references, or “dual” references, routing switch takes can be configured
AES
REF1
AES
Reference
AES
REF 2
