Switching configurations, Introduction – Grass Valley NV5128 v.2.5 User Manual
Page 18
8
Rev 2.5 • 24 Sep 09
2. Introduction
Switching Configurations
and routed to outputs is determined by the router control system. For more information on mono
signal switching, see
Setting Jumpers and Switches on Cards and Card Sets
Switching Configurations
Switching is performed by the output card. Each output card receives signals from the input card
via the motherboard and routing commands from the control card. The inputs are then sent to a
crosspoint array on the output card that performs the switching.
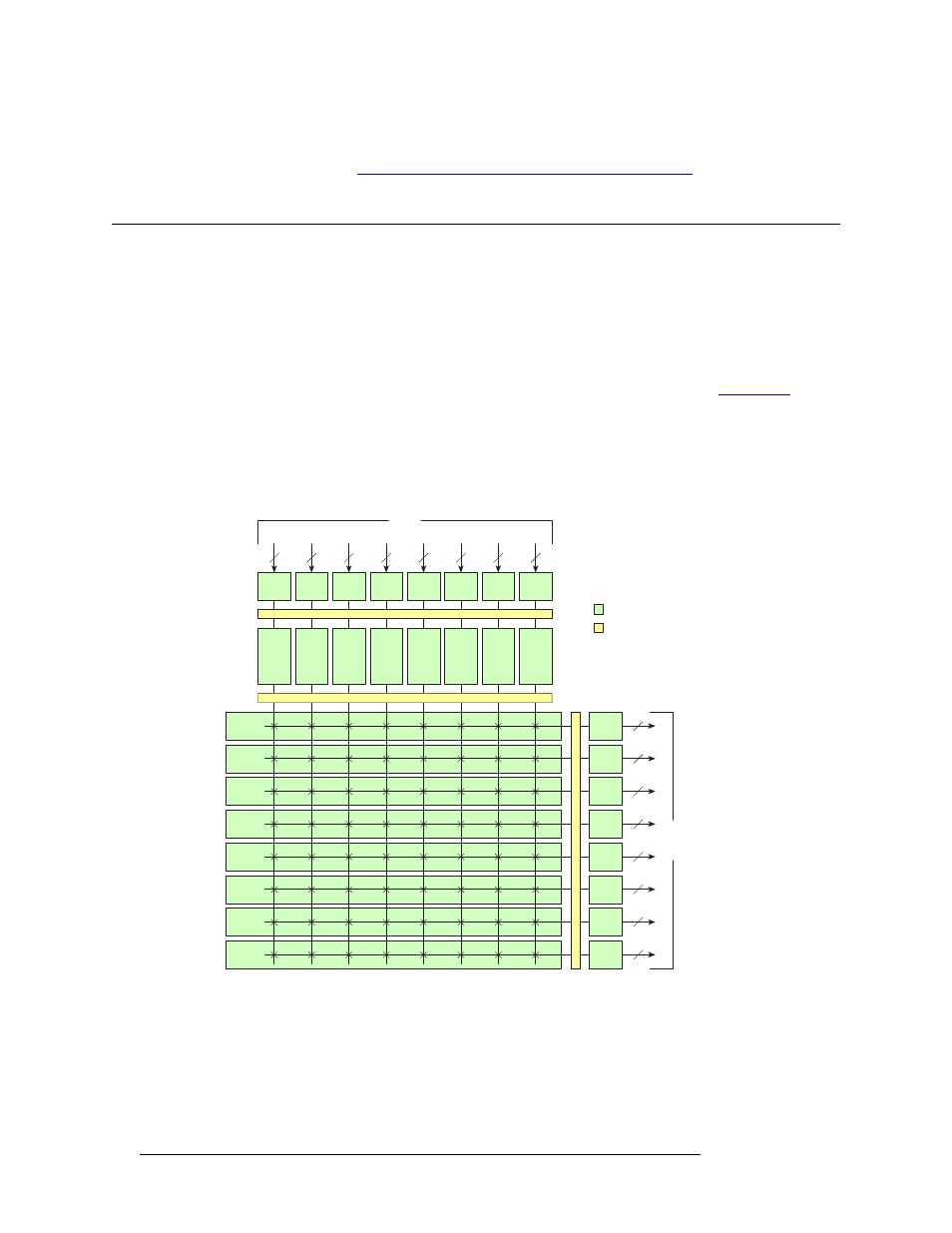
Figure 2-2 shows the basic architecture of the NV5128 switching configuration and the relationship
between the backplanes and the input cards and output cards. Backplanes house connections that
receive and distribute signals to and from the router. For more information, see
Each “X” (crosspoint symbol) represents a 16 input x 16 output crosspoint array. Taken together,
eight crosspoints create a 128 input x 16 output crosspoint array. This unique architecture creates a
fully non-blocking matrix such that an input can be switched to any output, and one input to one
output, or one input to many outputs.
Figure 2-2. NV5128 Crosspoint Architecture
In general, input cards and output cards follow the 16 inputs x 16 outputs architecture, with one
router card slot per card. There are three exceptions: Classic SWB card sets, Standard SWB cards
and machine control card sets. Each card set switching configuration is discussed in the proceeding
sections.
Slot 2
Slot 3
Slot 4
Slot 13
Slot 14
Slot 15
Slot 16
Slot 1
Slot 1
Slot 2
Slot 3
Slot 4
Slot 13
Slot 14
Slot 15
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Inputs
Slot 5
Slot 12
Slot 6
Slot 7
Slot 8
Slot 9 Slot 10 Slot 11
Slot 5
Slot 12
Slot 6
Slot 7
Slot 8
Slot 9 Slot 10 Slot 11
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
116
1732
3348 4964 6580
8196 97112 113128
Modules
Motherboard
Input Backplanes
Input Matrix Modules
Output
s
Output Backplanes
Output Matrix Modules
Slot 16
