Specifying the source interface for dns packets – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 119
106
•
An unspecified address—0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 (or ::). It cannot be assigned to any node. Before
acquiring a valid IPv6 address, a node fills this address in the source address field of IPv6 packets.
The unspecified address cannot be used as a destination IPv6 address.
381B
Multicast addresses
IPv6 multicast addresses listed in
751H
Table 7
are reserved for special purposes.
Table 7 Reserved IPv6 multicast addresses
Address Application
FF01::1
Node-local scope all-nodes multicast address.
FF02::1
Link-local scope all-nodes multicast address.
FF01::2
Node-local scope all-routers multicast address.
FF02::2
Link-local scope all-routers multicast address.
Multicast addresses also include solicited-node addresses. A node uses a solicited-node multicast
address to acquire the link-layer address of a neighboring node on the same link and to detect duplicate
addresses. Each IPv6 unicast or anycast address has a corresponding solicited-node address. The format
of a solicited-node multicast address is FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FFXX:XXXX. FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF is fixed and
consists of 104 bits, and XX:XXXX is the last 24 bits of an IPv6 unicast address or anycast address.
382B
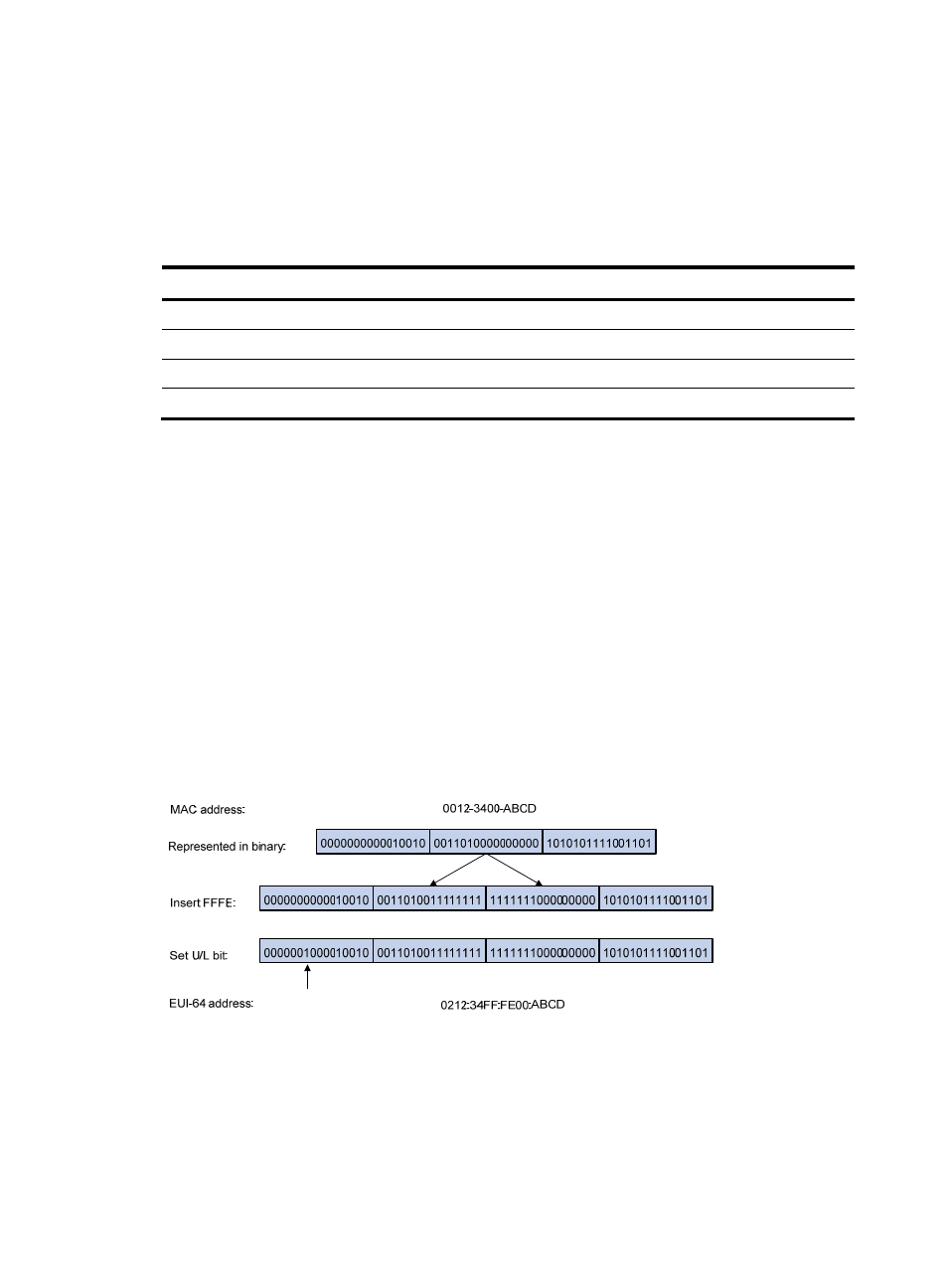
EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers
An interface identifier is 64-bit long and uniquely identifies an interface on a link. Interfaces generate
EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers differently.
•
On an IEEE 802 interface (such as an Ethernet interface and a VLAN interface)—The interface
identifier is derived from the link-layer address (typically a MAC address) of the interface. The MAC
address is 48-bit long. To obtain an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier, insert the
hexadecimal number FFFE (16 bits of 1111111111111110) into the MAC address (behind the 24th
high-order bit), and set the universal/local (U/L) bit (which is the seventh high-order bit) to 1,
ensuring that the obtained interface identifier is globally unique.
Figure 42 Converting a MAC address into an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier
•
On a tunnel interface—The lower 32 bits of the EUI-64 address-based interface identifier are the
source IPv4 address of the tunnel interface. The higher 32 bits of the EUI-64 address-based
interface identifier of an ISATAP tunnel interface are 0000:5EFE, whereas those of other tunnel
interfaces are all zeros. For more information about tunnels, see "Configuring tunneling."
•
On an interface of another type (such as a serial interface)—The EUI-64 address-based interface
identifier is generated randomly by the device.
- H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C S6800 Series Switches H3C S3100V2 Series Switches H3C S12500-X Series Switches H3C S9800 Series Switches
