Dns configuration task list, Configuring the ipv4 dns client, Configuring static domain name resolution – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 116: Configuring basic ipv6 settings, Overview, Ipv6 features
103
15B
Configuring basic IPv6 settings
The device operates in IRF or standalone (the default) mode. For information about IRF mode, see IRF
Configuration Guide.
115B
Overview
IPv6, also called IP next generation (IPng), was designed by the IETF as the successor to IPv4. One
significant difference between IPv6 and IPv4 is that IPv6 increases the IP address size from 32 bits to 128
bits.
251B
IPv6 features
370B
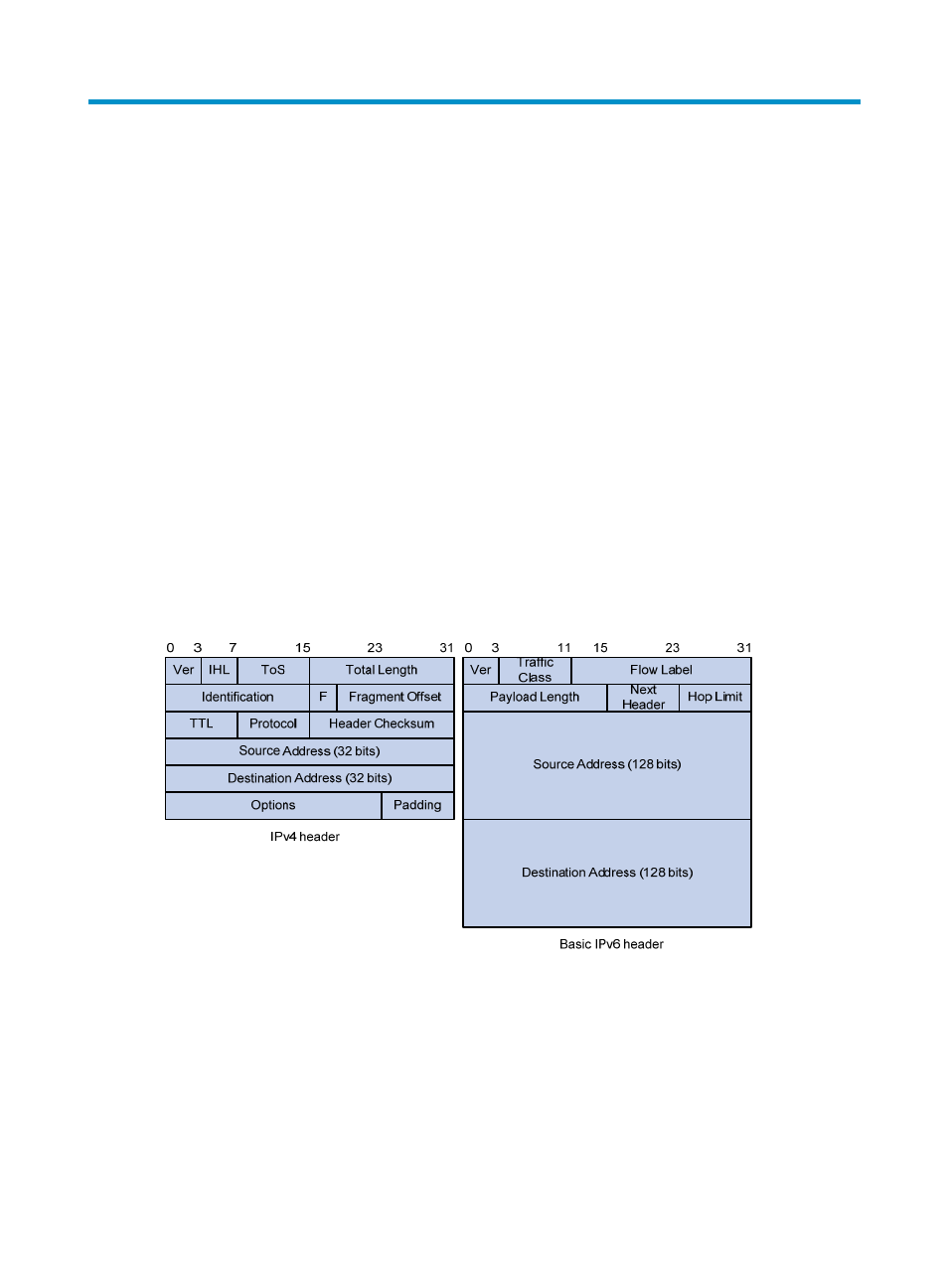
Simplified header format
IPv6 removes several IPv4 header fields or moves them to the IPv6 extension headers to reduce the length
of the basic IPv6 packet header. The basic IPv6 packet header has a fixed length of 40 bytes to simplify
IPv6 packet handling and improve forwarding efficiency. Although the IPv6 address size is four times the
IPv4 address size, the basic IPv6 packet header size is only twice the size of the option-less IPv4 packet
header.
Figure 41 IPv4 packet header format and basic IPv6 packet header format
371B
Larger address space
IPv6 can provide 3.4 x 10
38
addresses to meet the requirements of hierarchical address assignment for
both public and private networks.
372B
Hierarchical address structure
IPv6 uses a hierarchical address structure to speed up route lookup and reduce the IPv6 routing table size
through route aggregation.
- H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C S6800 Series Switches H3C S3100V2 Series Switches H3C S12500-X Series Switches H3C S9800 Series Switches
