Refrigeration details – Scotsman EH330 C with ECC Condensing Unit ECC1200 User Manual
Page 36
EH330, EH430 and ECC Condensing Unit
Remote Low Side Cuber Service Manual
July 2013
Page 35
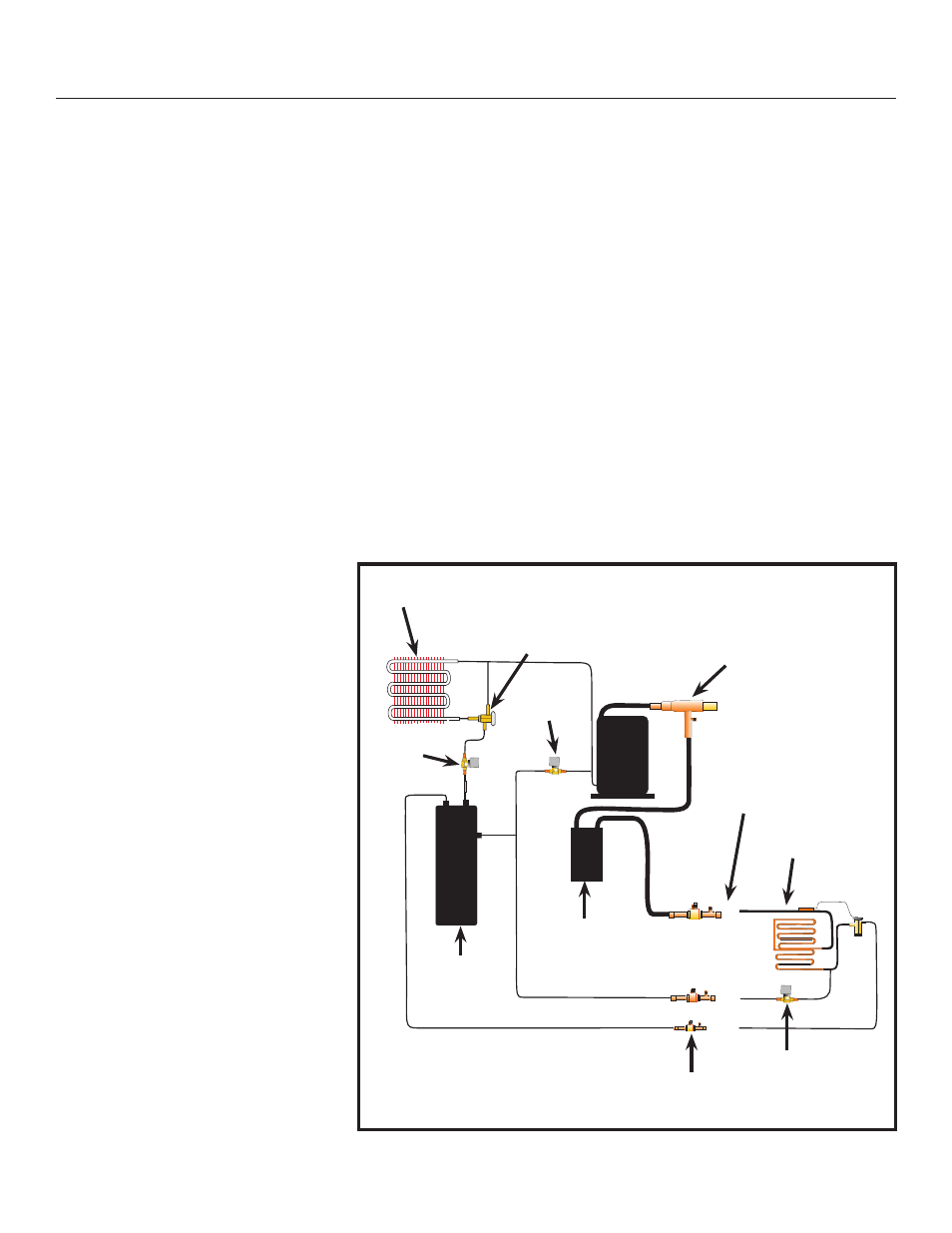
Refrigeration Details:
The compressor provides the force that circulates
refrigerant in the refrigeration system. During freeze,
when the vapor inlet and condenser by pass valves
are closed, discharge gas flows from the compressor
into the condenser, where its heat is discharged into
the air stream. Liquid refrigerant flows out of the
condenser and through the normally open liquid line
outlet valve on its way to the receiver inlet. Under low
ambient/low pressure conditions, the headmaster
valve closes the liquid outlet of the condenser and
opens a bypass route to direct refrigerant gas to the
receiver inlet until discharge pressure builds back up
to the headmaster’s set point.
From the receiver liquid outlet, liquid refrigerant
flows into the liquid line and into the ice making
section. At the ice making section, the refrigerant
flows into the expansion valves where a pressure
change takes place. The liquid refrigerant moves
from the expansion valves into a low-pressure area
(the evaporators) where it can rapidly evaporate
and absorb heat. Heat is absorbed from the copper
evaporator tubing, attached copper and
the water flowing over the evaporator.
The low-pressure refrigerant gas
then flows into the suction line, which
carries it back to the condensing unit,
where it enters the accumulator. In the
accumulator most of any liquid carried
with the suction gas is separated and
only vapor flows out of the accumulator
through the CPR valve and to the
compressor where the cycle continues.
During harvest discharge gas flows
through the open condenser by pass
valve into the vapor line. Power is also
applied to the coil of the liquid inlet
valve, closing it. At the same time, in
the ice making section, the vapor inlet
valves open.
Discharge gas, combined with some
vapor from the receiver’s outlet,
then flows through the vapor line
to the evaporator inlet. The gas-
vapor combination, when entering
the relatively cold evaporator,
condenses, transferring latent heat
to the evaporator, which warms it.
Ice releases and falls into the bin.
The low-pressure refrigerant then flows out of the
evaporator and into the suction line. The suction line
brings the refrigerant, now consisting of a vapor-
liquid combination, to the accumulator. From the
accumulator the vapor-liquid combination (now
more vapor than liquid) goes to the Crankcase
Pressure Regulator valve which limits the amount of
dome pressure in the compressor, where the cycle
continues.
Vapor Valve
Ice Making Head
Condenser
Head Pressure
Valve
CPR Valve
Bypass
Valve
Accumulator
Receiver
Ball Valves
Interconnecting
Tubing
Liquid
Inlet
(NO)
