Setting local ip addresses – D-Link DI-1162 User Manual
Page 90
DI-1162 Remote Access Router
80
Configuration and Management
made. Since there are only 5 global IP addresses in the example above,
there can only be 5 mappings at any one time. In other words, much
like static NAT, only 5 local machines can access the Internet at any
one time. However, contrary to static NAT, the router will discard the
mapping between the global and local IP addresses after a certain
length of time (which is quite long so rarely happens), or after the
session is finished (an example of a session is when requesting a web
page, the entire page has completed downloading). The most common
implementation of NAT is to define a range of dynamic addresses to be
used by hosts, but assign static addresses to your servers if you wish for
them to be accessible from outside your network.
Setting Local IP Addresses
When implementing NAT and thus creating a private network that is
isolated from the Internet, you can assign any IP addresses to host
computers without problems. However, the Internet Assigned Numbers
Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP
Addresses specifically for private networks:
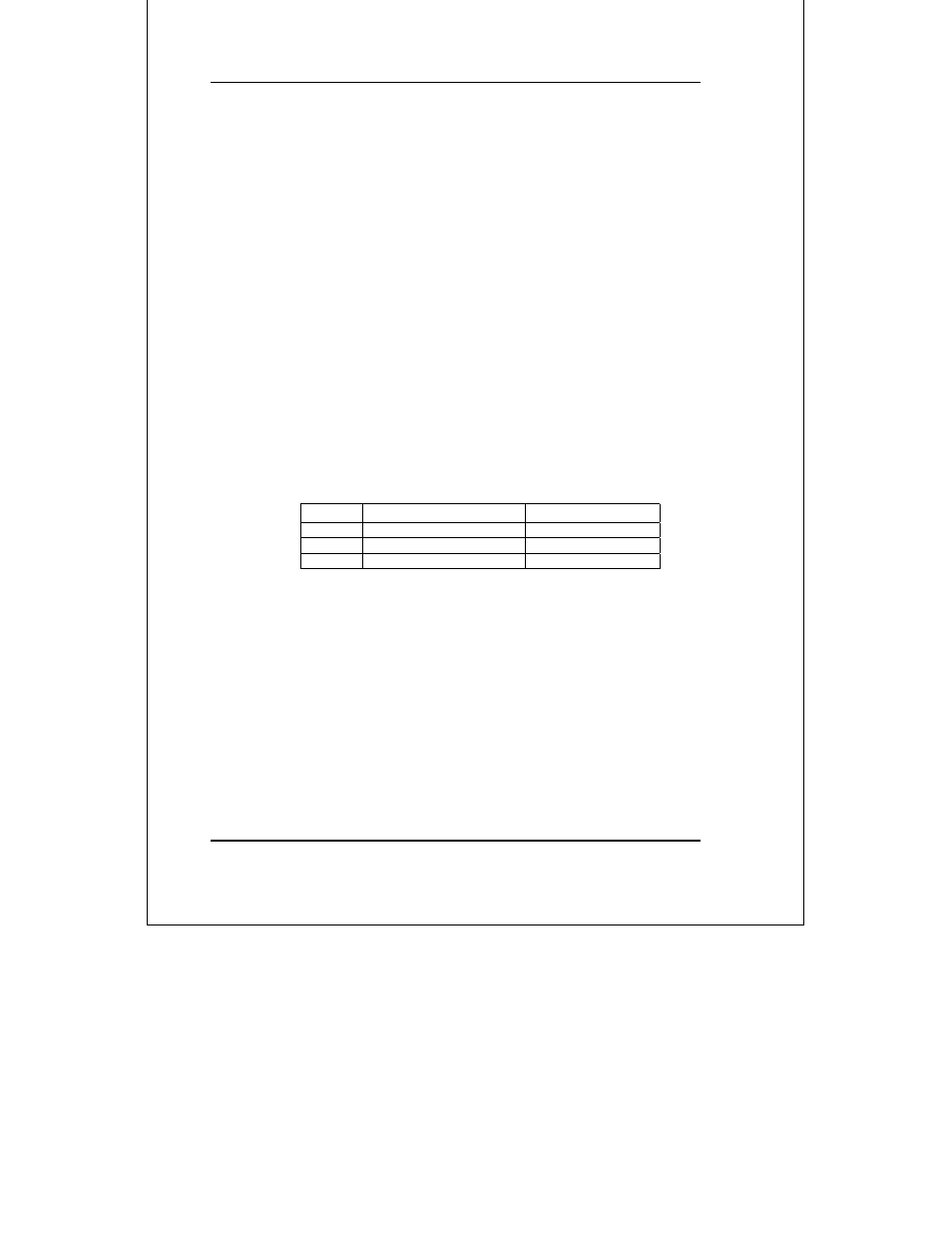
Class
Beginning Address
Ending Address
A
10.0.0.0
10.255.255.255
B
172.16.0.0
172.31.255.255
C
192.168.0.0
192.168.255.255
It is recommended that you choose local IP addresses for use with NAT
from the private network IP addresses in the above list. For more
information on address assignment, refer to RFC 1597, Address
Allocation for Private Internets and RFC 1466, Guidelines for
Management of IP Address Space.
