Measurement Computing LGR-5320 Series User Manual
Page 18
LGR-5320 Series User's Guide
Functional Details
18
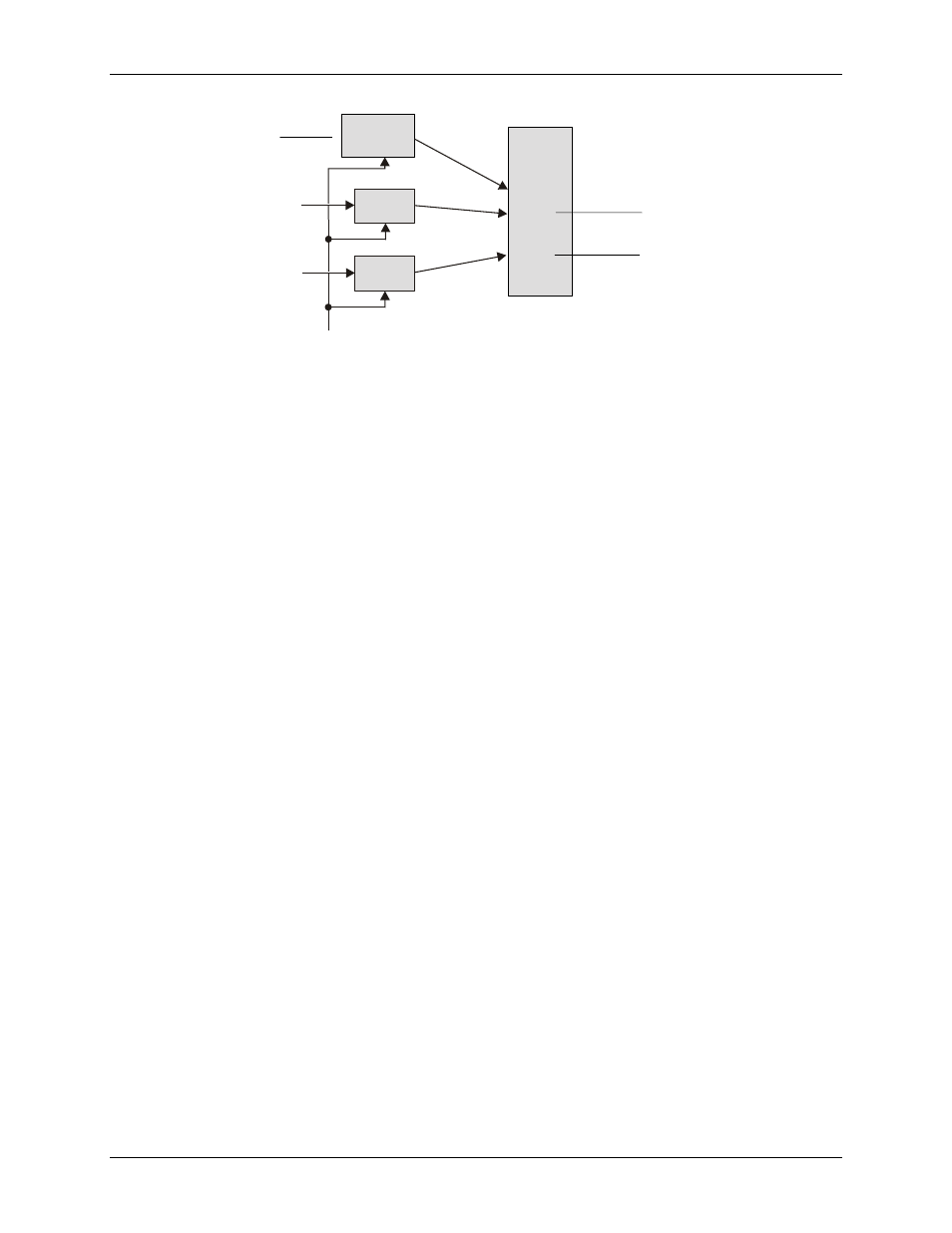
Figure 11. Multichannel trigger detection
The logical relationship among three elements—polarity, duration, and initialization—determine if a trigger is
valid in a multichannel environment.
Analog trigger types (LGR-5325) and multichannel trigger types (LGR-5327/5329)
Each trigger type is a combination of three elements: slope, duration, and initialization.
Slope (above/rising or below/falling)—Sets whether the trigger is valid when the signal is above the threshold
(rising) or below the threshold (falling).
Duration (instantaneous or latched)—Specifies the action to take if the signal level becomes invalid after it has
been valid:
Instantaneous triggers are valid in scans where that channel trigger condition is met. They can become
invalid in subsequent scans when the trigger condition is not met.
With the LGR-5327 and LGR-5329, instantaneous triggers are used to trigger when all channels triggers
are valid (multichannel "AND" mode) or when any of the channel trigger conditions are valid
(multichannel "OR" mode).
Latched triggers remain valid until the acquisition is complete. These trigger types are used to trigger scans
when two or more signals have already become valid.
With the LGR-5327 and LGR-5329, you can use a combination of instantaneous and latched triggers in
multichannel triggering.
The trigger duration only makes a difference in multichannel AND triggering.
In multichannel "OR" triggering, the acquisition is triggered as soon as any channel becomes valid—what
happens when a channel becomes invalid does not matter.
In contrast, "AND" triggering waits for all triggers to be valid, making latching important for rapidly
changing signals.
Initialization (level or edge)—Specifies the sequence necessary for a signal to be a valid trigger:
Level triggers become valid when they reach or exceed the threshold, even if they are already past the
threshold when the acquisition starts.
Edge triggers first wait until the signal level is invalid. Then they wait for the signal to reach the threshold
before becoming valid. Thus, level triggers look for a signal level, whenever it occurs, and edge triggers
look for a rising or falling transition that reaches the threshold.
Trigger
logic
AND
(all)
OR
(any)
Trigger
detector
Trigger
detector
Trigger
detector
Analog
input
signals
Invalid trigger
Valid trigger
Valid trigger
Re-arm command
from control circuits
No trigger
Trigger
