Select the test switch positions – Fieldpiece HG2 - HVAC Guide System Analyzer User Manual
Page 4
6
WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.CO
Select the Test
Switch Positions
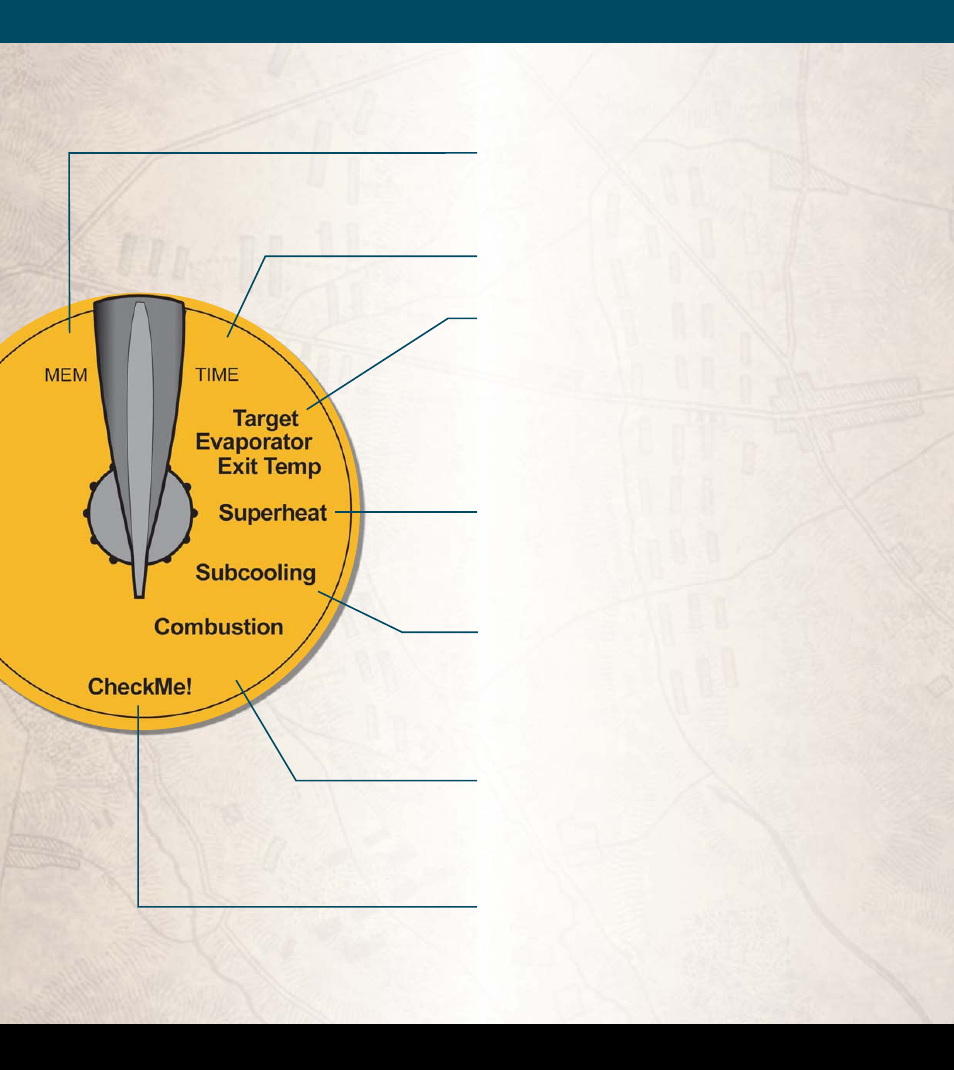
MEM:
Erase a single test, an entire customer’s set of
tests, or all data. MEM also allows you to check
memory status, fi rmware version, and communi-
cate with a PC for data transfer.
TIME:
Set current time and date for internal clock. All
tests are time stamped and cannot be changed later.
Target Evaporator Exit Temperature:
By mea-
suring the return wet bulb and dry bulb, the HVAC
Guide
TM
tester calculates a target evaporator exit
temperature. To ensure that the A/C system has the
proper airfl ow per tonnage, the actual evaporator
exit temperature must be within ±3°F of the target
evaporator exit temperature as outlined in CA title
24.
Superheat:
For a fi xed restrictor air conditioning sys-
tem, the HVAC Guide
TM
tester uses the indoor wet
bulb and outside dry bulb to calculate a target su-
perheat and uses the suction line temperature and
pressure to calculate actual superheat.
Subcooling:
For a TXV/EXV air conditioning system,
the HVAC Guide
TM
tester uses liquid line tempera-
ture and pressure to calculate actual subcooling. If
the manufacture’s target subcooling is not available,
the HVAC Guide
TM
tester provides a conservative
estimate.
Combustion:
For combustion equipment, the HVAC
Guide
TM
tester uses %O
2
, fl ue temperature, primary
temperature and CO ppm to calculate %CO
2
, % Ex-
cess Air, CO (air free), Net Temperature, Standard
Effi
ciency and Siegert Effi
ciency.
CheckMe!® (model HG2):
Th
is is a more advanced
test for determining the overall state of an air con-
ditioning system. Th
e CheckMe!® test will give you a
diagnosis of the system in plain English and a list of
potential problems in the system.
