Subcooling – Fieldpiece HG2 - HVAC Guide System Analyzer User Manual
Page 12
22
WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.COM WWW.FIELDPIECE.CO
3.1
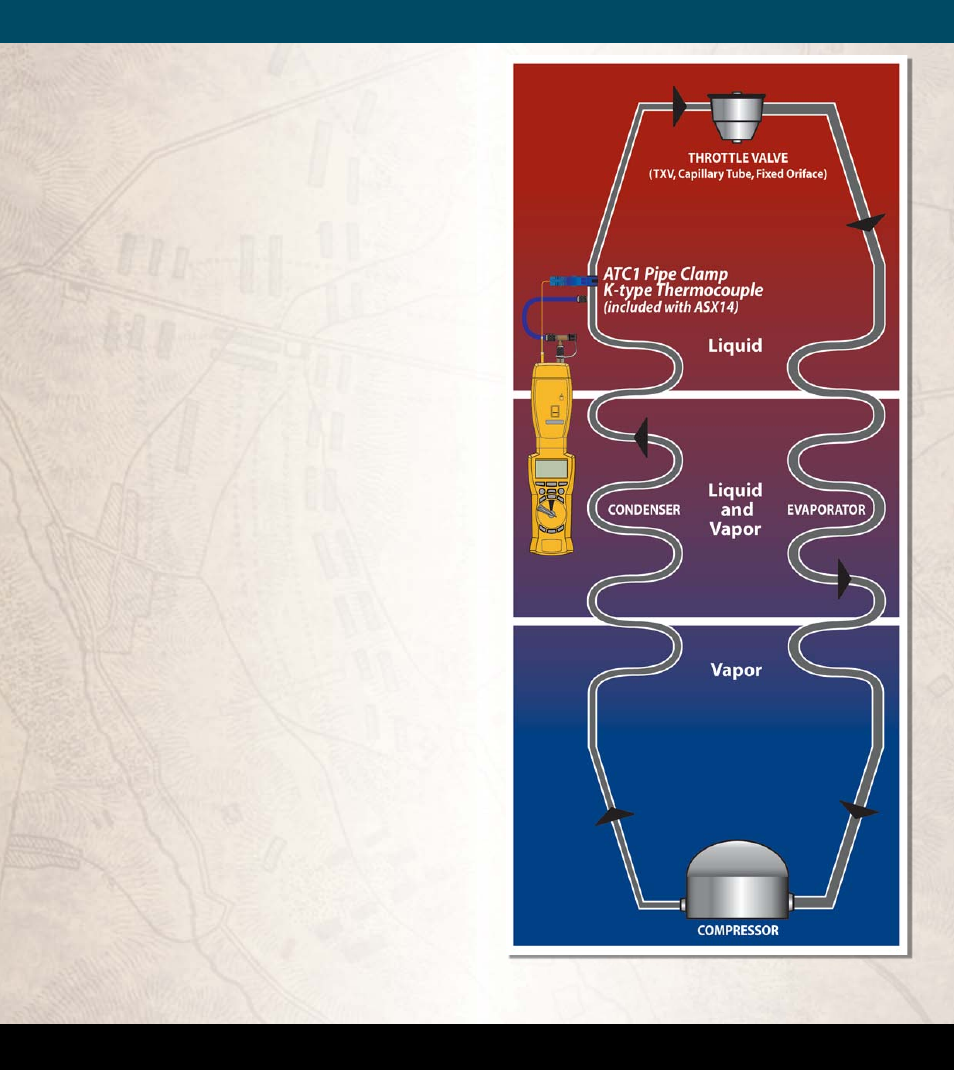
Subcooling
Subcooling is the temperature decrease below the
boiling point (same as the condensing point) in the con-
denser. Too high, and refrigerant condenses too early in
the condenser and ‘wastes’ most of the capacity of the
condenser. Too low, and a mixture of gas and liquid can
be delivered to the expansion valve, reducing effi
ciency.
Subcooling is the best way to obtain proper refriger-
ant charge for a TXV/EXV system.
If the air conditioner is in good working order and
the airfl ow is adjusted properly, comparing the actual
and target subcooling will tell you if refrigerant needs
to be added or recovered (ensure the pressure never ex-
ceeds the manufacturer's maximum overload pressure
guidelines).
In a properly working TXV/EXV system, the super-
heat is held constant. Ensure the TXV/EXV bulb is in-
stalled properly, there is proper refrigerant to obtain tar-
get subcooling, and there are no liquid line restrictions.
Adjust refrigerant charge so that the actual subcooling is
within ±3°F of target subcooling.
Figure 11. Using the ASX14 Superheat/Subcooling Head to gather liquid line
temperature and pressure for the HVAC Guide
TM
tester Subcooling Test.
