2 construction of the cob identifier, 3 definition of the used data types, Cob-id – BECKHOFF AX2000 CANopen communication profile User Manual
Page 16: Data types, Construction of the cob identifier, Definition of the used data types, Beckhoff
3.2
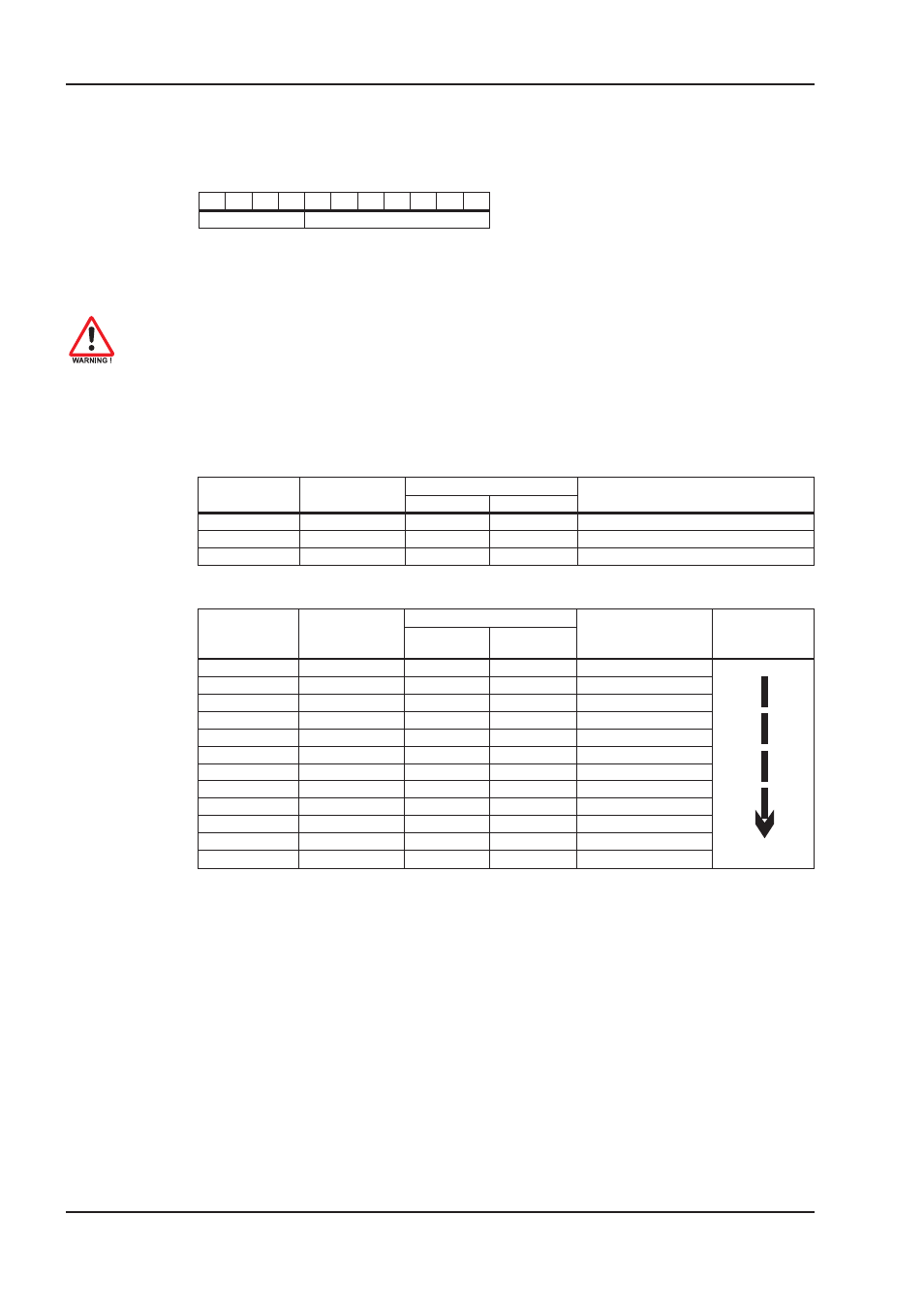
Construction of the COB Identifier
The following diagram shows the layout of the COB Identifier (COB-ID). The Function Code defines
the interpretation and priority of the particular Object.
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Code
Module-ID
Bit 0 .. 6
Module ID (station number, range 1 ... 63; is set up in the operator software
or the servo amplifier,
Þ 2.1.1)
Bit 7... 10
Function Code (number of the Communication Object that is defined in the server)
Attention:
If an invalid station number (=0 or >63) is set, then the module will be set internally to 1. The
ASCII Object MDRV can be used to expand the address range from 63 through to127.
The following tables show the default values for the COB Identifier after switching on the servo
amplifier. The objects, which are provided with an index (Communication Parameters at Index), can
have a new ID assigned after the initialization phase. The indices in brackets are optional.
Predefined broadcast Objects (send to all nodes):
Object
Function code
(binary)
Resulting COB-IDs
Communication parameters
at index
Dec.
Hex.
NMT
0000
0
0
h
—
SYNC
0001
128
80
h
(1005
h
)
TIME
0010
256
100
h
—
Predefined Peer-to-Peer Objects (node sends to node):
Object
Function code
(binary)
Resulting COB-IDs
Communication para-
meters
at index
Piority
Dec.
Hex.
EMERGENCY
0001
129...255
81
h
...FF
h
—
high
TPDO 1
0011
385...511
181
h
...1FF
h
1800
h
RPDO 1
0100
513...639
201
h
...27F
h
1400
h
TPDO 2
0101
641...767
281
h
...2FF
h
1801
h
RPDO 2
0110
769...895
301
h
...37F
h
1401
h
TPDO 3
0110
897...1023
381
h
...3FF
h
1802
h
RPDO 3
1000
1025...1151
401
h
...47F
h
1402
h
TPDO 4
1001
1153...1279
481
h
...4FF
h
1803
h
RPDO 4
1010
1281...1407
501
h
...57F
h
1403
h
SDO (tx*)
1011
1409...1535
581
h
...5FF
h
SDO (rx*)
1100
1537...1663
601
h
...67F
h
Nodeguard
1110
1793...1919
701
h
...77F
h
(100E
h
)
low
*
tx = direction of transmission: AX2xxx
Þ Master
rx = direction of transmission: Master
Þ AX2xxx
3.3
Definition of the used data types
This chapter defines the data types that are used. Each data type can be described by bit- sequen-
ces. These bit-sequences are grouped into “Octets” (bytes). The so-called “Little – Endian” for-
mat (a.k.a. Intel format) is used for numerical data types (see also: DS301 Application Layer “Gene-
ral Description of Data Types and Encoding Rules”).
16
CANopen for AX2000/2500
CANopen communication profile
07/2007
BECKHOFF
