Read operations with latency, Figure 3–17 – Altera Nios II C2H Compiler User Manual
Page 77
Altera Corporation
9.1
3–37
November 2009
Nios II C2H Compiler User Guide
C-to-Hardware Mapping Reference
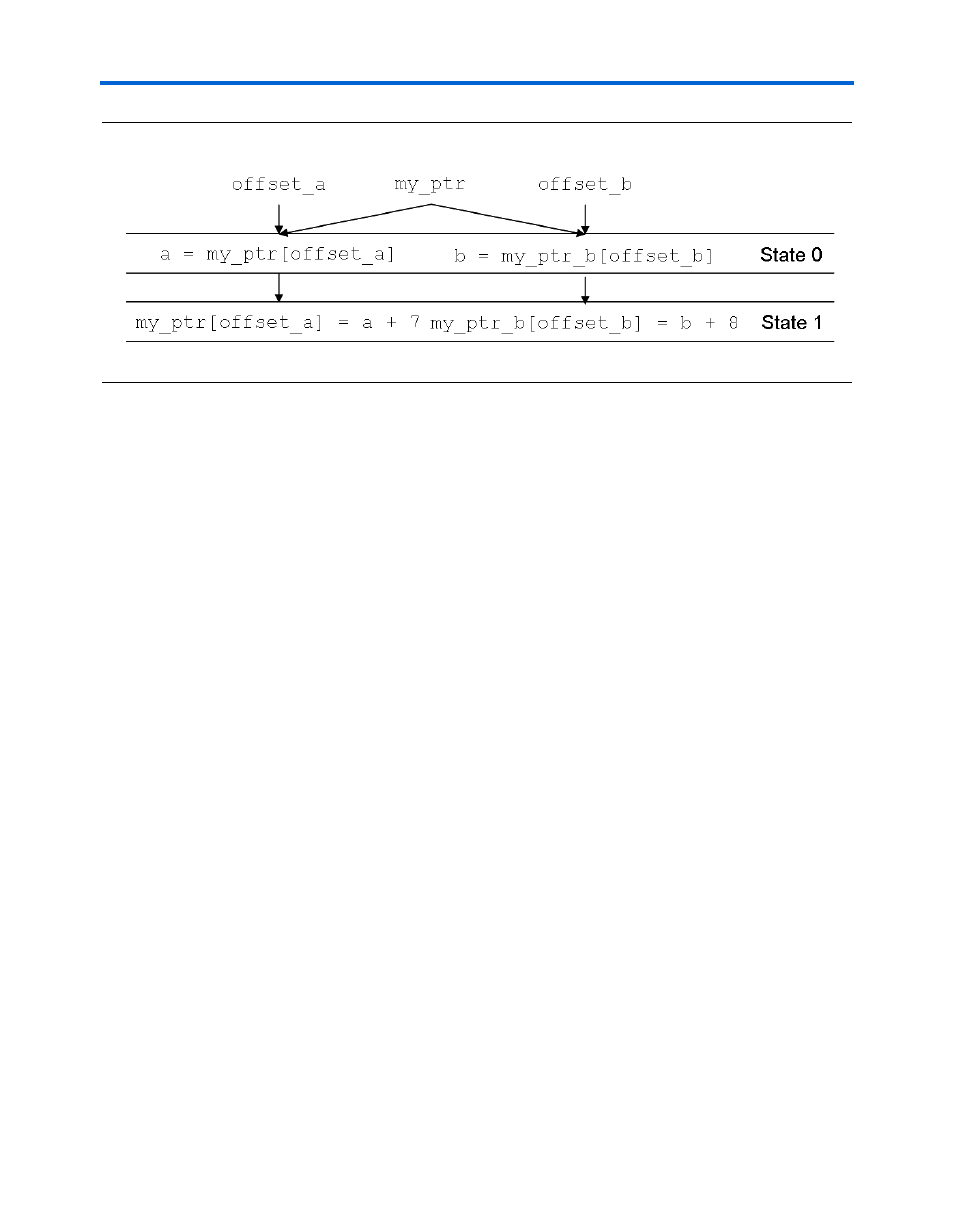
Figure 3–17. Using Another Pointer to Avoid Self-Dependence
1
If a data structure is referenced by two pointers and one or more
of them is restrict-qualified, the ISO C 99 standard specifies that
the behavior is undefined. Therefore, make sure that you fully
understand the range of values that a pointer can take on during
the execution of your application before applying the
_ _ restrict_ _
qualifier. Improper application can result in
undesirable functional changes to the code than cannot be
debugged in software, due to the limitations of restrict-based
optimizations in conventional compilers.
1
The ISO C 99 standard specifies that the
volatile
type
qualifier overrides the
_ _ restrict_ _
pointer type. This
means that
_ _ restrict_ _
has no effect on
volatile
pointers. To break pointer dependencies between
volatile
pointers, use separate interrupt-enabled accelerators instead of
multiple loops in the same accelerator. For details about
interrupt-enabled accelerators, see
Using Physically Separate Slave Ports to Break Dependencies
If the master ports associated with two pointers do not access any shared
slave ports in the SOPC Builder system, then the C2H Compiler assumes
that the pointers do not alias. Section
describes how to limit the master-slave connections, which can
be an effective method to prevent aliasing.
Read Operations with Latency
Memory latency and other access delays affect how the C2H Compiler
schedules operations. Inherently, an operation cannot proceed until the
data for the operation arrives, which depends on memory latency. The
C2H Compiler generates logic within hardware accelerators to manage
