Interrupt pragma, Interrupt pragma –4, Interrupt pragma” on – Altera Nios II C2H Compiler User Manual
Page 122
6–4
9.1
Altera Corporation
Nios II C2H Compiler User Guide
November 2009
Interrupt Pragma
Interrupt
Pragma
To use a hardware accelerator in interrupt mode, add the following line
to your function source code:
#pragma altera_accelerate \
enable_interrupt_for_function
At the next software compilation, the C2H Compiler creates a new header
file containing all the macros needed to use the accelerator and service the
interrupts it generates.
This pragma causes the function (which is assumed to be a top-level
accelerated function, not an accelerated subfunction) to be an interrupt-
mode accelerator. Specifically, the following things change:
■
The accelerator's control slave has an IRQ signal, which is asserted
every time the function has completed execution.
■
The polling loop in the generated driver file is removed. When the
function is called, the CPU immediately returns after launching the
accelerator.
■
A header file is generated, providing macros and definitions
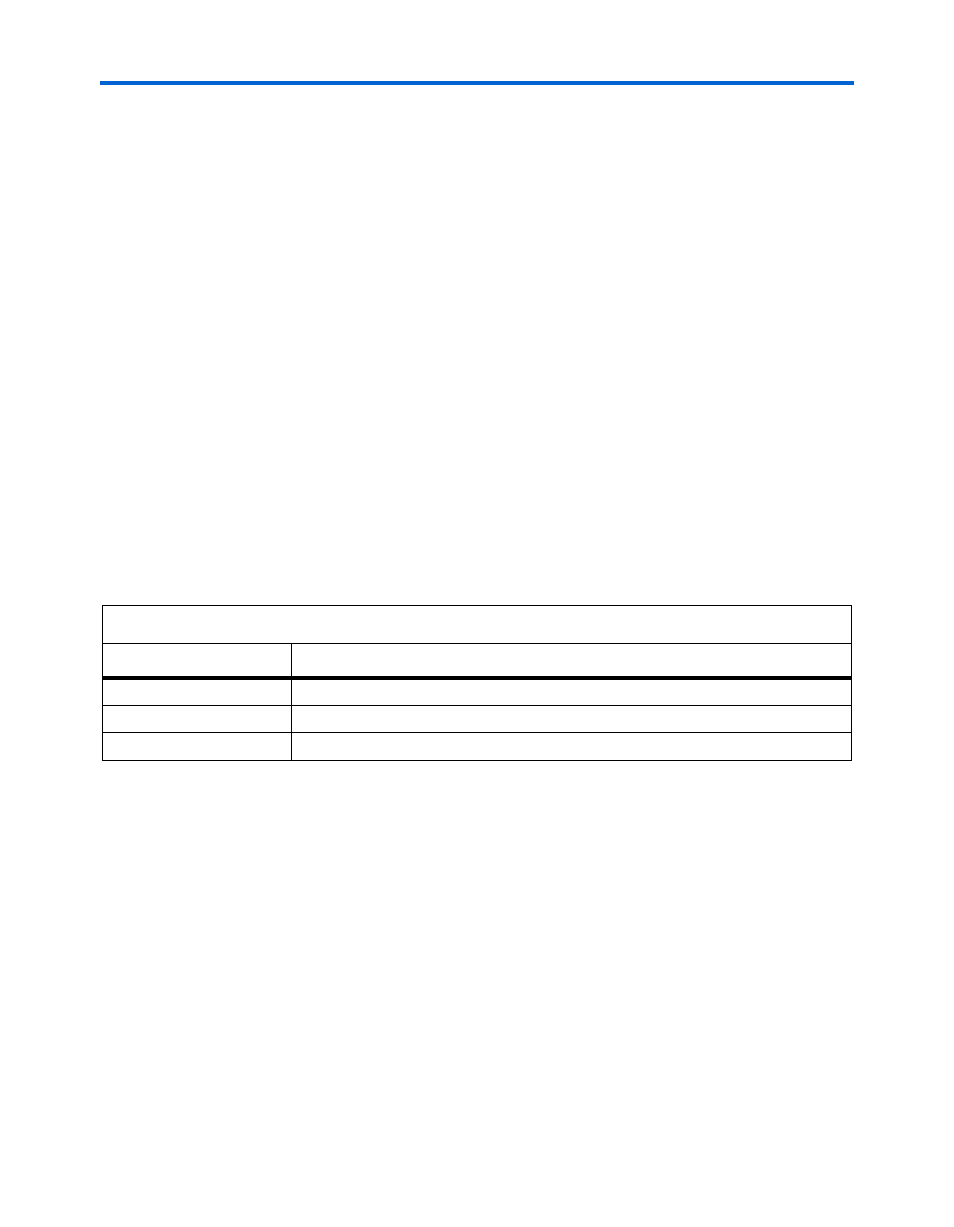
required for you to write an ISR. The macros are summarized in
.
An example of this header file is shown in
for an
accelerated function called
coprocess()
in a Nios II IDE project
called my_project. The file is generated in
directory, and
(Release or Debug). The file name is ACCELERATOR_
of the project (usually the same as
Table 6–1. C2H Accelerator Interrupt Macros
Purpose
Macro Name
Return value
ACCELERATOR
_
_
_
GET_RETURN_VALUE()
Interrupt clear
ACCELERATOR
_
_
_
CLEAR_IRQ()
Check status
ACCELERATOR
_
_
_
BUSY()
