How a filter works – Waldorf Edition User Manual
Page 71
Waldorf Edition
User Manual
71
Waldorf
How a filter works
What is a filter? In general a filter is used to dampen certain parts of the frequency ran-
ge of an audio signal. If you send recorded audio through a filter, certain parts of the
original signal are removed. Depending on the filter type used, it might be the high or
the low frequencies, both, or the medium frequencies that are removed from the origi-
nal signal. As a result, the processed signal will sound more muffled or thinner, more
hollow or have its emphasis on the mid frequencies.
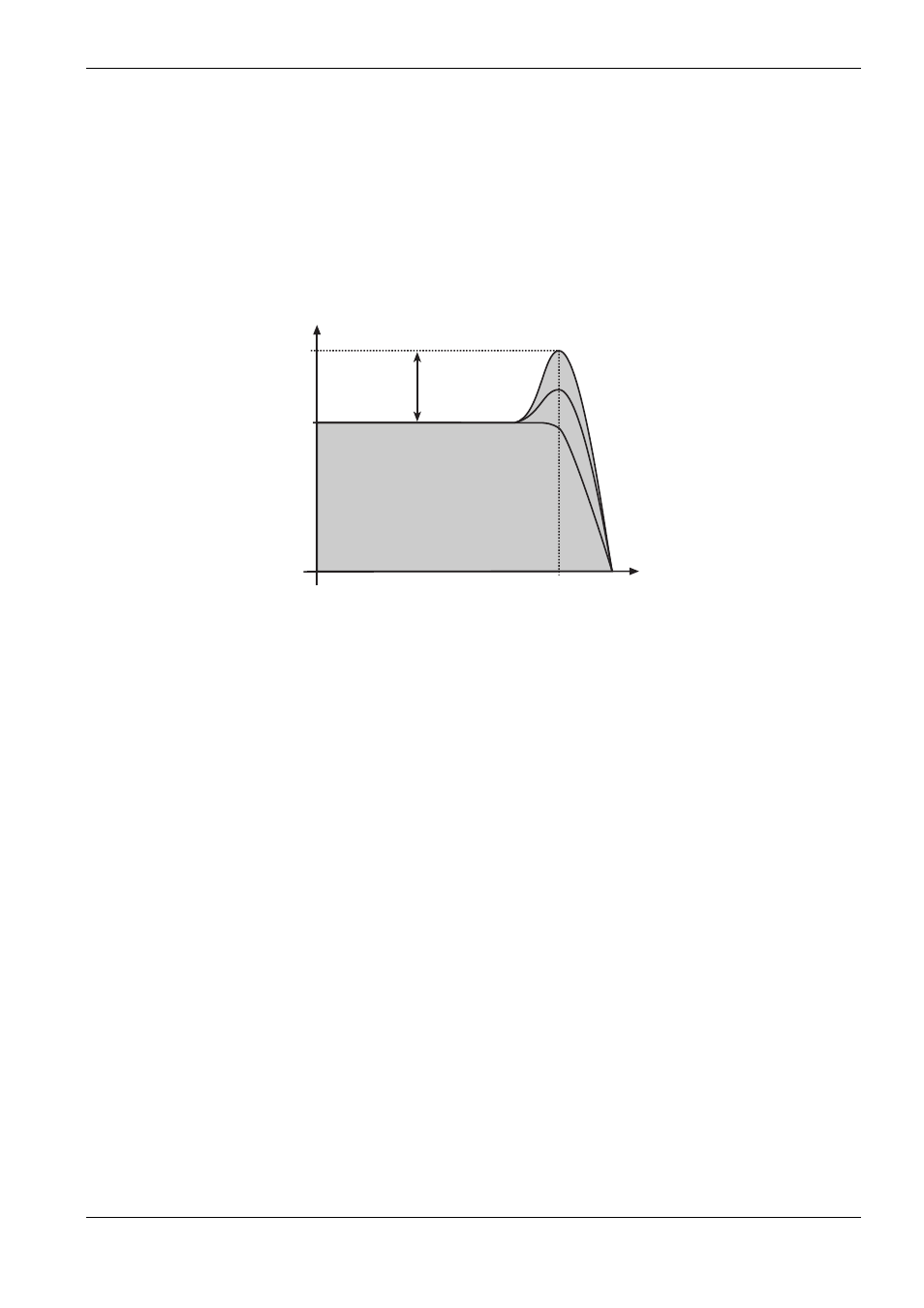
The illustration below shows you how a Low Pass filter works.
Stop band and Pass band
The frequency range that is dampened by the filter is called Stop band, as it is stopped
by the filter. The frequency range that passes the filter without being changed or hin-
dered is called Pass Band. A filter can have one or several Stop and Pass Bands, and
this is where the various filter types differ from each other.
Center, Corner and Cutoff frequency
The frequency at which the filter starts to set in is called Cutoff or Corner frequency.
This marks the borderline between the unfiltered and the filtered parts of the complete
signal range. But in certain filter types this frequency can lie somewhere inside or
outside the Pass Band. In these cases it is called Center frequency.
Slope
The intensity with which the Stop band frequencies are dampened is called Slope. This
is generally shown as dB per octave and indicates the number of dB by which the input
signal is dampened one octave away from the Cutoff frequency. For a standard Low
Pass filter 24 dB per octave is a common setting. This means that one octave above the
Cutoff frequency the input signal will be dampened by 24 dB. Two octaves above
Cutoff frequency the signal is dampened by 48 dB, three octaves above Cutoff fre-
quency it’s dampened by 72 dB, etc. Another common Slope setting is 12 dB per octa-
ve. A filter with this Slope setting has a more subtle effect, and is therefore better suited
to process pad sounds.
Frequency
Level
Cutoff
Resonance
