Early ref. 1, Early ref. 2, Early ref. 3 – Yamaha GEP50 User Manual
Page 17: Early ref. 4, Gate reverb, Reverse gate, Gate reverb 44. reverse gate
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
r
25. Rev 1 Hall
26. Rev 2 Hall
27. Rev 3
Room
28. Rev 4 Vocal
29. Rev 5 Vocal
30. Rev 6 Plate
31. Early Ref. 1
Reverberation is the warm musicai "ambience” you experience
when listening to music in a hall or other properly-designed
acoustic environment. The GEP50 offers six different reverb
effects, simuiating types of reverberation you wouid experience
in different haiis (25
—
26), in a smaller room (27), reverb
effects ideally suited to vocals (28
—
29), and the type of
reverberation produced artificially by a plate reverberator (30).
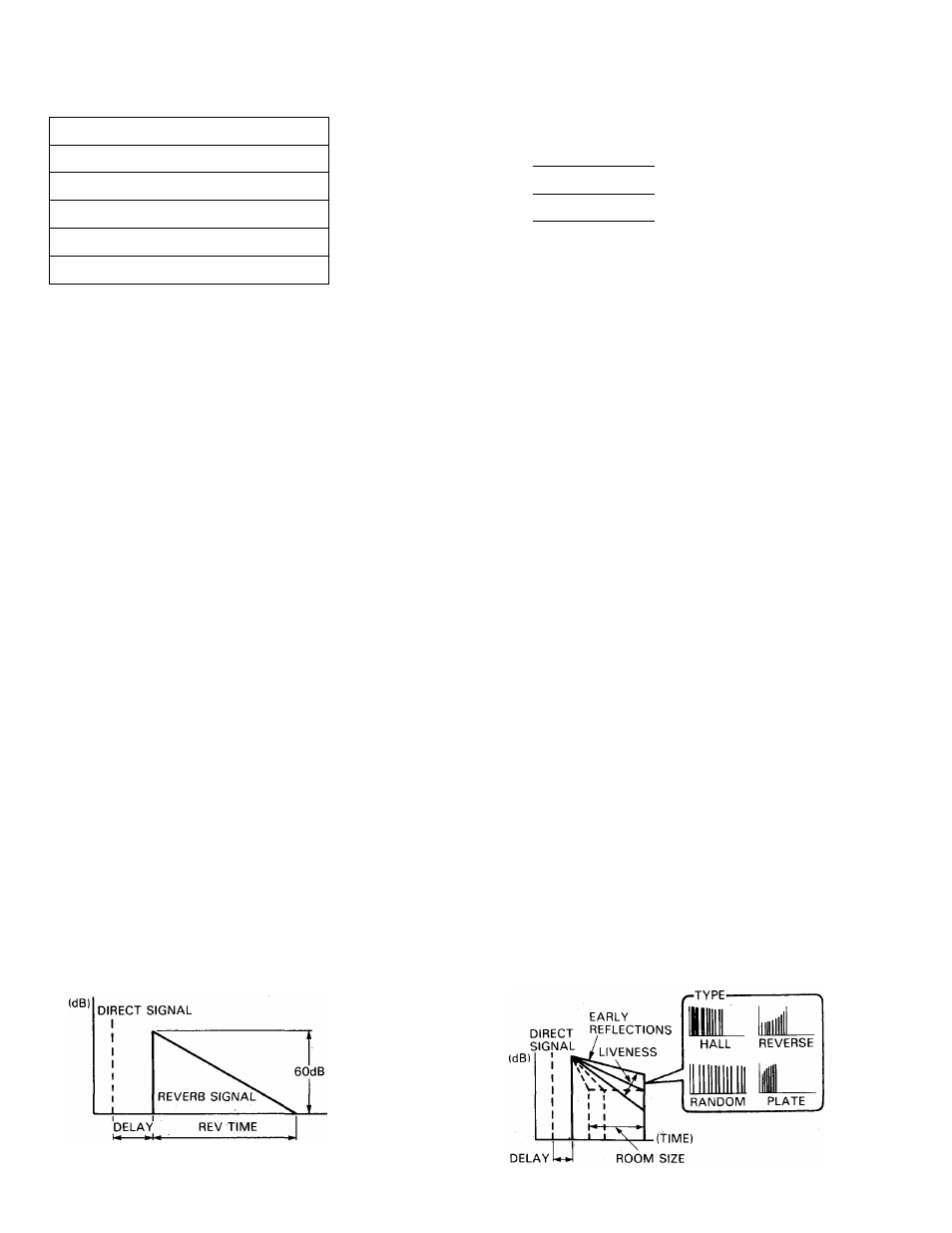
Reverb Time (REV TIME): 0.3 — 99 seconds
The length of time it takes for the level of reverberation at 1
kHz to decrease by 60 dB — virtually to silence. In a live
setting, this depends on several factors; room size, room
shape, type of reflective surfaces, and others.
High Frequency Reverb Time Ratio (HIGH): xO.1 —
x1.0
Natural reverberation varies according to the frequency of
the sound. The higher the frequency, the more sound tends
to be absorbed by walls, furnishings and even air. This
parameter allows alteration of the high-frequency reverb time
in relation to the overall reverb time.
32. Early Ref. 2
33. Early Ref. 3
34. Early Ref. 4
43. Gate Reverb
44. Reverse Gate
These effects are created using different groupings of “early
reflection^”
—
the first cluster of reflections that occurs after the
direct sound but before the dense reflections that are known as
reverberation begin.
Early Reflection Pattern (TYPE): HALL/RANDOM/
REVERSE/PLATE
The TYPE parameter selects one of four different patterns of
early reflections. HALL produces a typical grouping of early
reflections that would occur in a performing environment
such as a hall. RANDOM produces an irregular series of
reflections that could not occur naturally. PLATE produces a
typical grouping of reflections that would occur in a plate
reverb unit. REVERSE generates a series of reflections that
increase in level — like the effect produced by playing a
recorded reverberation sound backwards.
Room Size (ROOM SIZE): 0.1 — 20
This parameter sets the time intervals between the early re
flections — a feature of natural early reflections which is
directly proportional to the size of the room.
Initial Delay (DELAY): 0 . 1 — 5 0 milliseconds
This parameter represents the delay between the direct
sound of an instrument and the first of the many reflections
that together form reverberation.
High-pass Filter (HPF): THRU, 32 Hz — 1000 Hz
Permits rolling off the low-frequency content of the reverb
signal below the set frequency. The HPF is OFF when set to
THRU.
Low-pass Filter (LPF): 1 k H z — 1 1 kHz, THRU
Permits rolling off the high-frequency content of the reverb
signal above the set frequency. The LPF is OFF when set to
THRU.
(TIME)
Liveness (LIVENESS): 0— 10
Tiveness” refers to the rate at which the reflected sounds
fade. An acoustically “dead” room is simulated by setting this
parameter to zero. Increasing the value of this parameter
creates an increasingly “live” sound, simulating an increas
ing area of reflective surfaces in the room.
Delay (DELAY): 0.1
—
400 milliseconds
The time delay between the direct sound of the instrument
and the first of the early reflections.
Low-pass Filter (LPF): 1 k H z — 1 1 kHz, THRU
Permits rolling off the high-frequency content of the early
reflection signal above the set frequency. The LPF is OFF
when set to THRU.
18
