3 operation, 1 electrochemical detection, 1 classes of substances which can be determined – Metrohm 791 VA Detector User Manual
Page 21
3.1 Electrochemical detection
791 VA Detector
15
3 Operation
3.1 Electrochemical
detection
3.1.1
Classes of substances which can be determined
A precondition for the use of electrochemical detection is that the sub-
stances to be determined are electrochemically active on the particular
working electrode used, i.e. they can easily be oxidized or reduced. The
electrical current produced by this reaction is proportional to the con-
centration of the substance throughout a wide range. It is measured,
amplified and recorded as a function of time by the 791 VA Detector in
the form of a chromatogram.
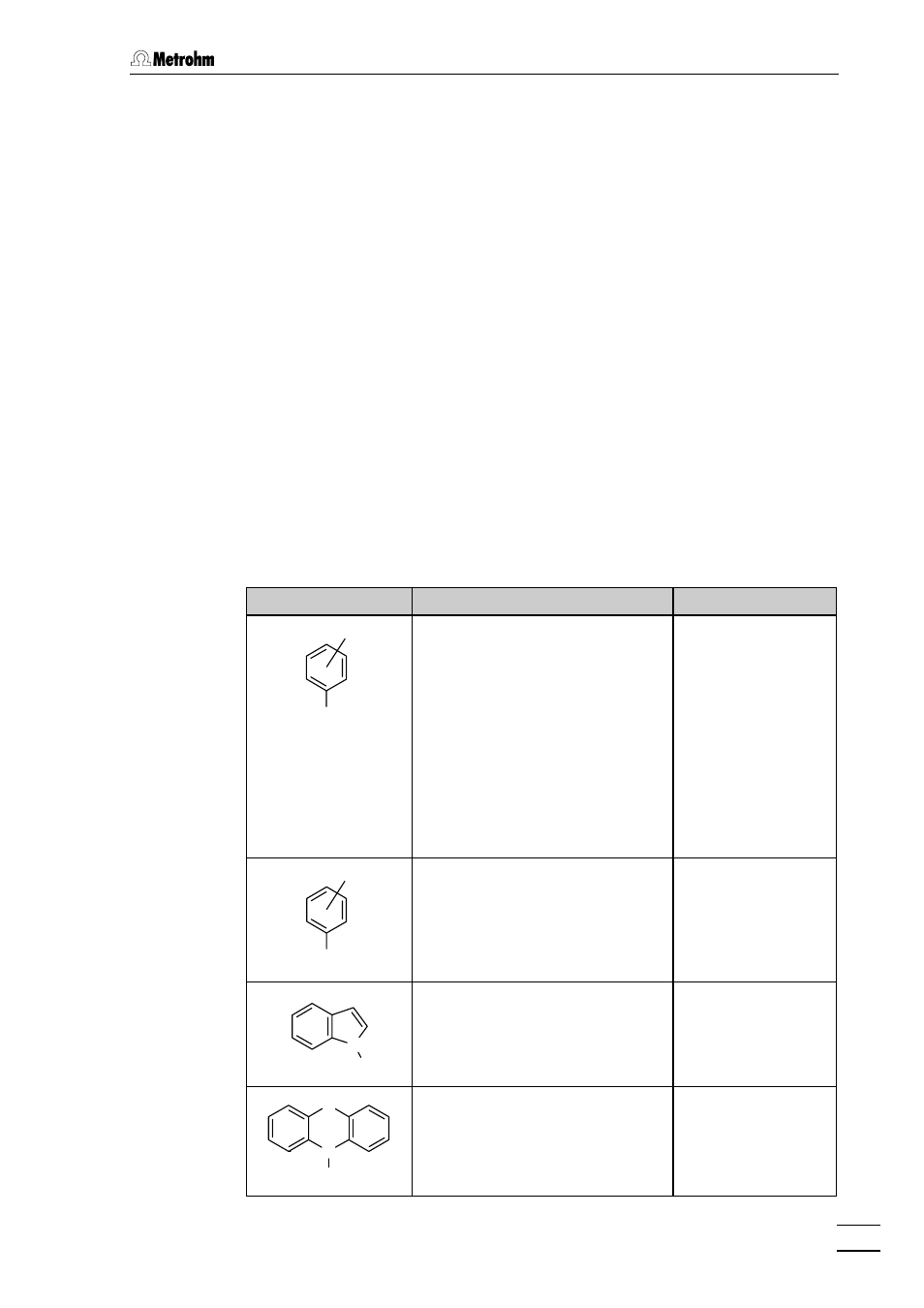
The following table provides an overview of the classes of substances
and ions which can be detected by oxidation or reduction. The ap-
proximate polarization voltage obtained when an Ag/AgCl/c(KCl) =
3 mol/L reference electrode is used is given; this depends to a large ex-
tent on the working electrode and eluents used (see section 3.2). The
limits of detection which can be achieved are in the lower ppb range.
Structural formula
Classes/substances
Polarization voltage
OH
R
Aromatic hydroxy compounds
Antioxidants
Catecholes
Flavones
Halogenated phenols
Hydroxybiphenyls
Hydroxycumarines
Methoxyphenols
Oestrogens
Phenols
Tocopherols
+800
…
+1200 mV
+ 800
mV
+
1000
mV
+
1200
mV
+ 800
mV
+
1000
mV
+ 800
mV
+
1000
mV
+
1200
mV
+ 800
mV
NH
2
R
Aromatic amines
Anilines
Benzidines
Sulfonamides
+
1000
mV
+ 600
mV
+
1200
mV
N
H
3
5
Indols
Indolyl-3-compounds
5-Hydroxy-indols
+
1000
mV
+ 800
mV
N
S
H
Phenothiazines
+
1000
mV
