Sfc_stop structure – Rockwell Automation Logix5000 Controllers Sequential Function Charts Programming Manual User Manual
Page 47
Design a sequential function chart Chapter 1
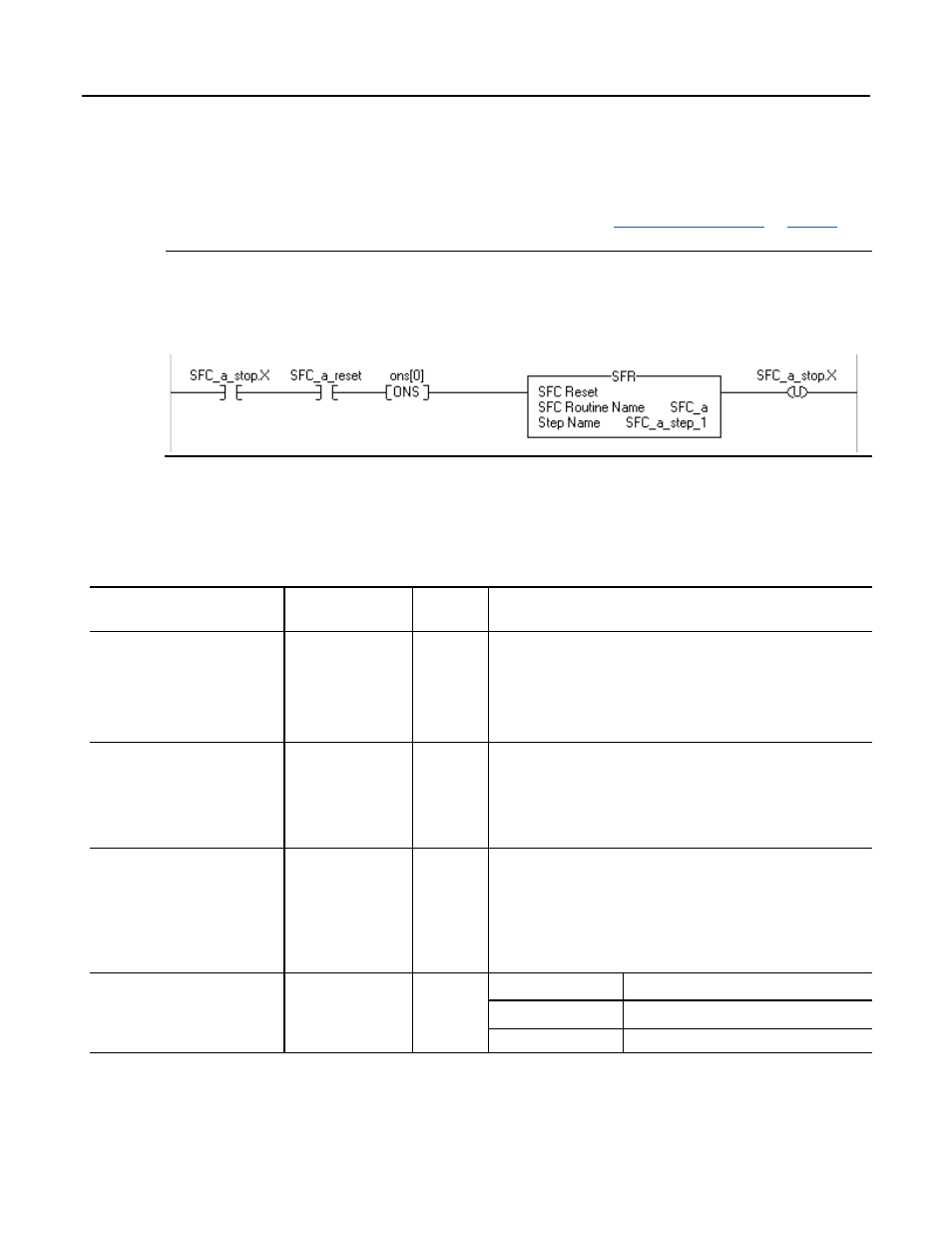
Example
This example shows the use of the SFC Reset (SFR) instruction to restart the SFC
and clear the X bit of the stop element (see
on
If SFC_a_stop.X = on (SFC_a is at the stop) and SFC_a_reset = on (time to reset the SFC) then for one scan (ons[ 0 ] = on):
Reset SFC_a to SFC_a_Step_1
SFC_a_stop.X = 0
SFC_STOP structure
Each stop uses a tag to provide information about the stop element.
If you want to
Then check or set this
member
Data type
Details
Determine when the SFC is at the stop
X
BOOL
• When the SFC reaches the stop, the X bit turns on.
• The X bit clears if you configure the SFCs to restart at the initial step and the
controller changes from program to run mode.
• In a nested SFC, the X bit also clears if you configure the SFCs for automatic reset
and the SFC leaves the step that calls the nested SFC.
Determine the target of an SFC Reset (SFR)
instruction
Reset
BOOL
An SFC Reset (SFR) instruction resets the SFC to a step or stop that the instruction
specifies.
• The Reset bit indicates to which step or stop the SFC will go to begin executing
again.
• Once the SFC executes, the Reset bit clears.
Determine how many times a stop has
become active
Count
DINT
This is not a count of scans of the stop.
• The count increments each time the stop becomes active.
• It increments again only after the stop goes inactive and then active again.
• The count resets only if you configure the SFC to restart at the initial step. With that
configuration, it resets when the controller changes from program mode to run
mode.
Use one tag for the various status bits of
this stop
Status
DINT
For this member
Use this bit
Reset
22
X
31
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM006F-EN-P - October 2014
47
