Programming – Rockwell Automation 1746-QS,D17466.19 SYNCHRONIZED AXES MODULE User Manual
Page 7
1–3
Publication 1746-6.19 March 1998
The
MODE, ACCELERATION, DECELERATION, SPEED,
and
COMMAND VALUE
(requested position) are used to generate the
profile. You send these command words to the module through the
processor’s output image table. You may change them “on-the-fly“
while the axis is moving.
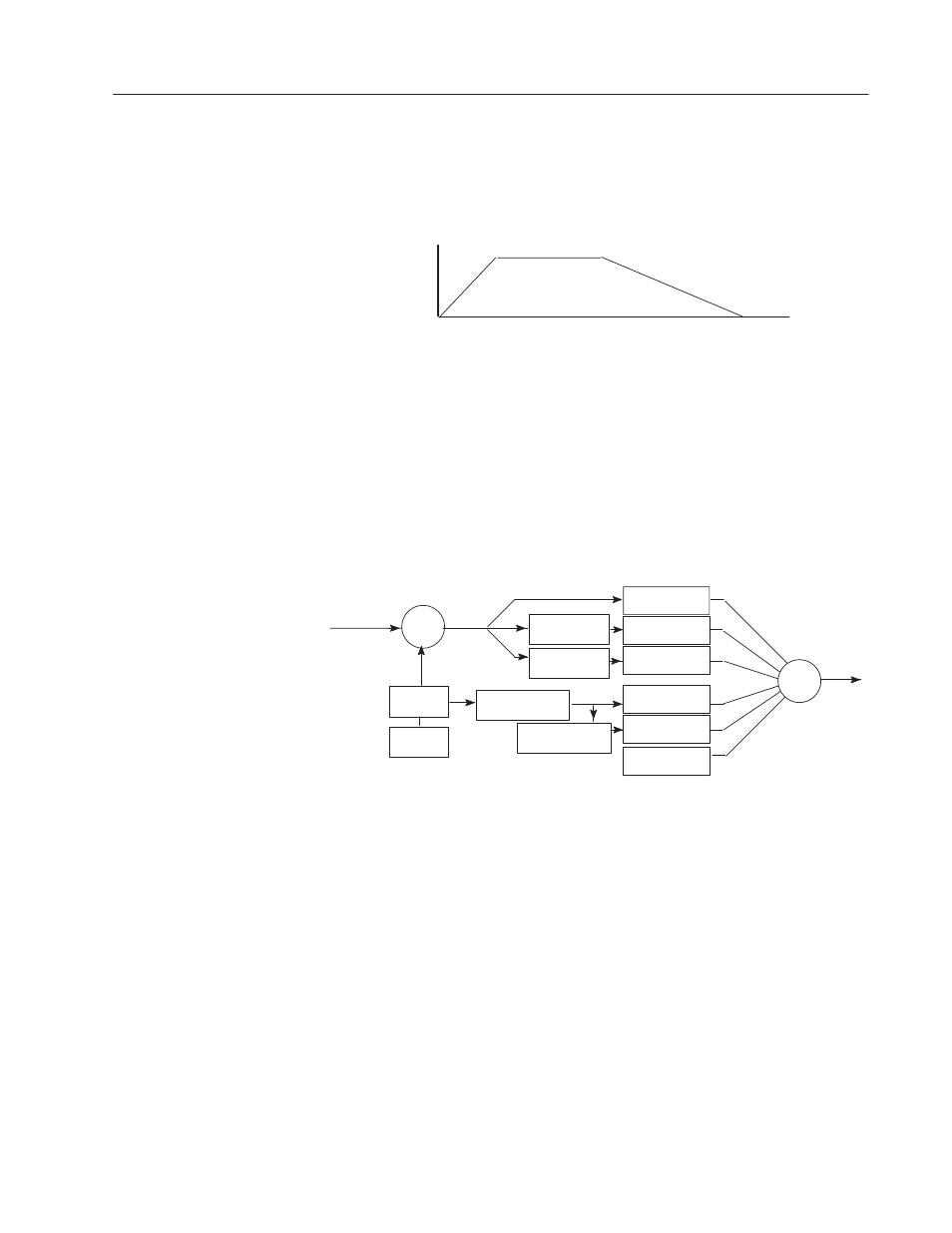
Motion Profile
Speed
Time
Accel
Ramp
Decel
Ramp
Max Speed
Command Value
(Final Position)
The module compares
ACTUAL POSITION
with
TARGET POSITION
to
determine position error. Every update, it uses the position error to adjust
drive output. PID gains are adjustable and can be applied selectively.
The module also provides two different feedforward algorithms;
EXTEND
/
RETRACT FEEDFORWARD
, and
EXTEND
/
RETRACT
ACCELERATION FEEDFORWARD
. These feedforward terms provide
additional drive output to help the axis follow the target, freeing the
PID loop to correct for system nonlinearity and changes in load.
Diagram of the Control Loop
Proportional Gain
Integral Gain
Differential Gain
Feedforward
Accel
Feedforward
Deadband
Eliminator
Accumulator
(Integrator)
Change in Error
(Differentiator)
Change in Position
(Velocity)
Change in Velocity
(Acceleration)
Target
Generator
SLC
Processor
Position
Error
Actual
Position
Target
Position
Drive
Output
+
–
ȍ
ȍ
Programming
A sample ladder program for the module is available from
Allen-Bradley’s website on the Internet. You can download it as an
executable file to your PC’s disk drive and transfer it to your SLC
processor. But, you must modify it for your application.
