Weidmuller WI-I/O 9-L: Wireless I/O Transmitter / Receiver v1.3 User Manual
Page 77
WI-I/O 9-L Configuration Manual
WI-I/O 9-L Wireless I/O
page 77 of 108
"
!
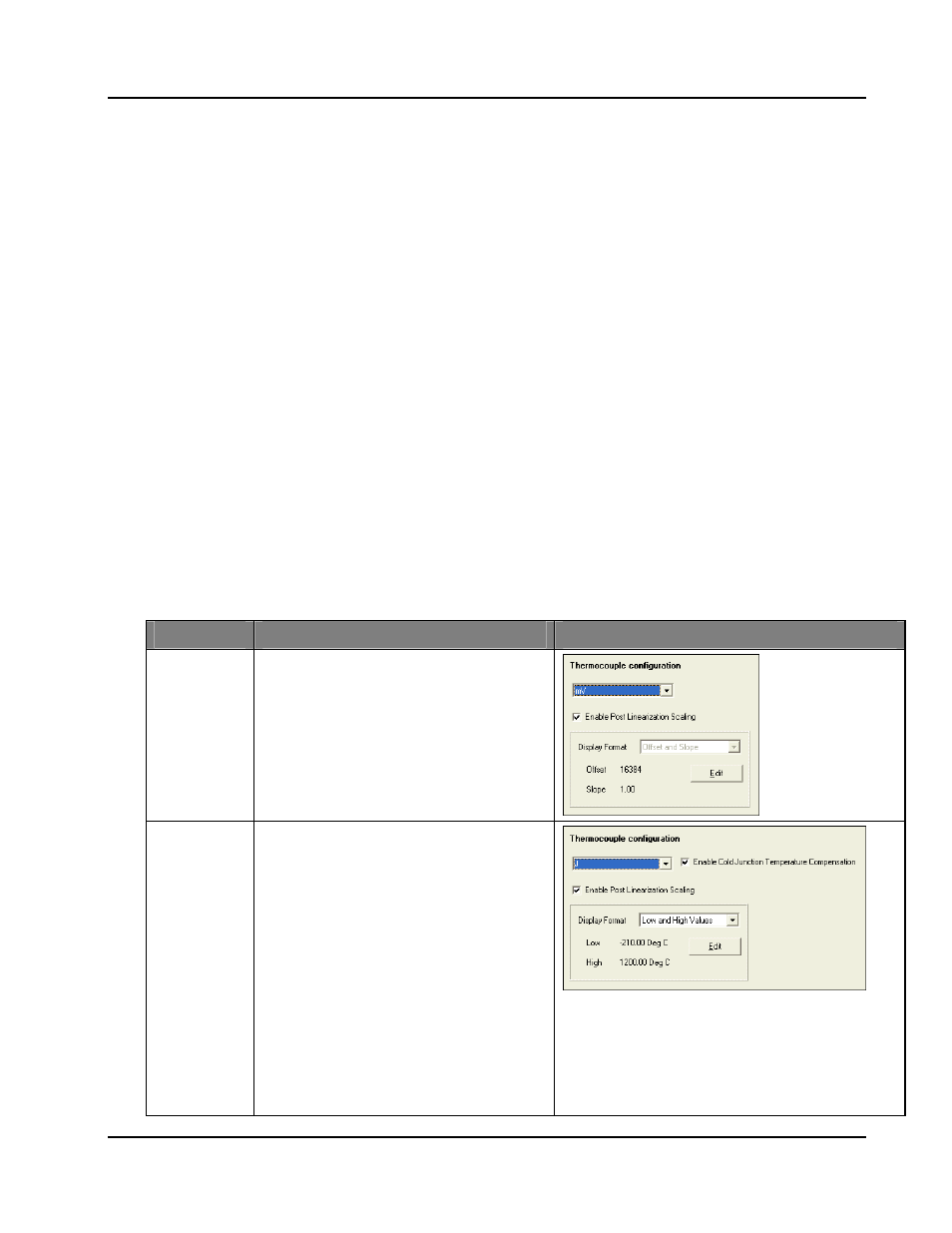
WI Series lets you set the thermocouple that you want to use with your module
The thermocouple measurement system works in conjunction with the on-board cold-junction
temperature measurement to provide cold-junction compensation using the following options:
Enable Cold Junction Compensation
- this option is normally selected unless you
are using an external cold junction compensation circuit.
Enable Post Linearization Scaling
- lets you to change the range of temperature
reported by the thermocouple system. This is a scale factor applied after linearizing the
thermocouple voltage to a temperature range.
If you are using one of the default thermocouple types, you can set the display format
to “Low and High value”, then enter the temperature you want to correspond to 4mA
(Low) and the temperature that you want to correspond to 20 mA (High).
WI Series automatically configures the Cold Junction and Linearization tables for supported
thermocouple types.
To set thermocouple tables:
1. Open the project.
2. Select the unit you want to change.
3. Select
Tables
.
4. Select the table required:
Table type
Description
Example
Millivolt input
Automatically disables cold junction
compensation and bypasses the
thermocouple linearization table.
Post linearization scaling is set to
(16384,1.00) to scale the range 0-100 mV to
correspond to an output value of 4-20 mA.
E, J, K, or T
tables
The WI-I/O 9LT has built-in linearization
tables and cold-junction compensation tables
for E, J, K and T type thermocouples.
Select the desired thermocouple type.
You should normally select
Enable
temperature compensation
. You should de-
select this option if using an external
compensation circuit.
By default, the linearized data is scaled to
correspond to the normal range of the
thermocouple.
To select a different output range, select
Enable Post Linearization Scaling
and
enter a different
Low
and
High
value.
Low is the temperature that corresponds to a
