Pegasus user’s guide – Orbital Pegasus User Manual
Page 57
Release 7.0
Apr 2010
46
Pegasus User’s Guide
meeting the intent of individual requirements. This
is especially critical for newly designed hazardous
systems, or new applications of existing hardware.
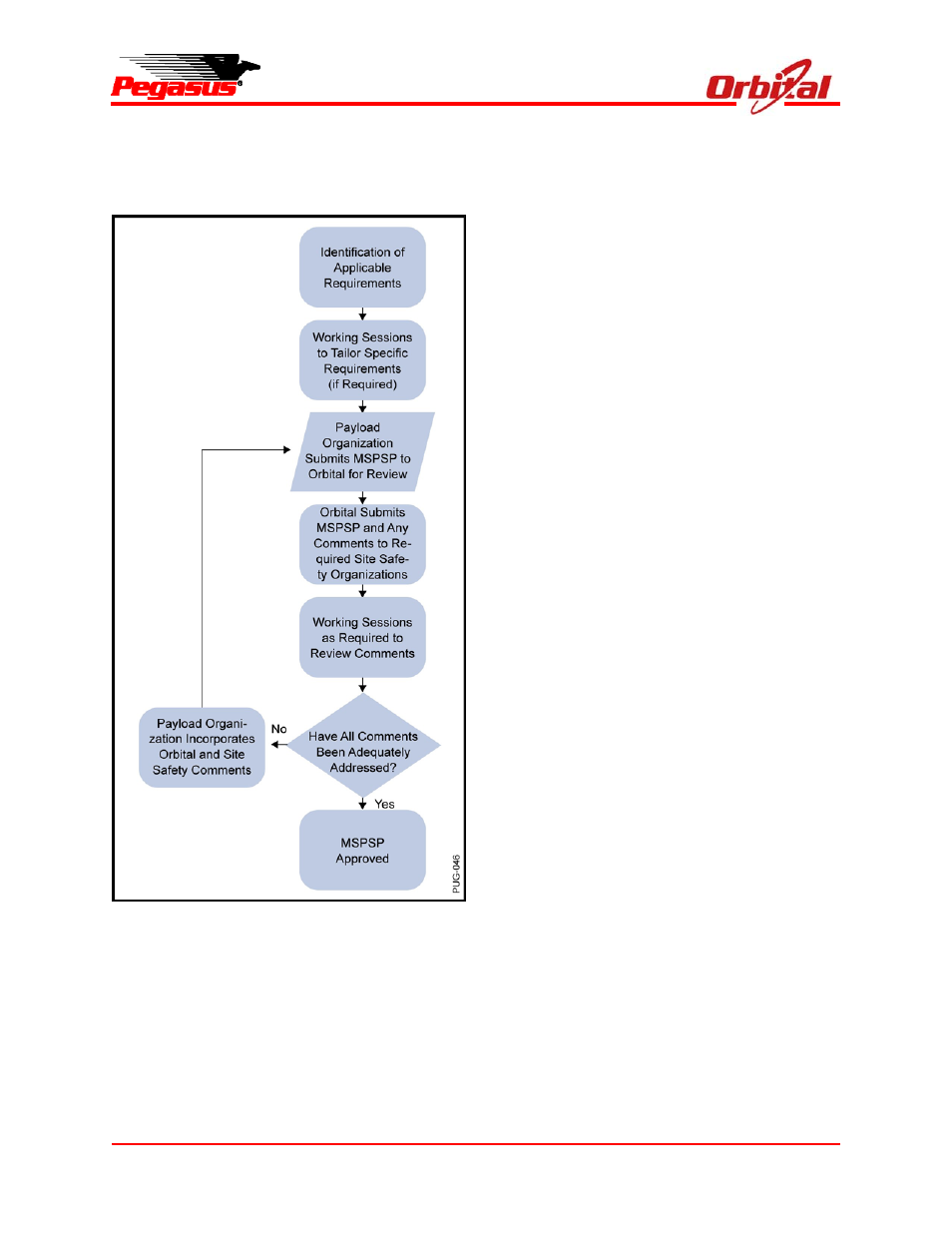
Figure 6-5. Safety Approval Process
It is encouraged that safety data be submitted as
early as practical in the spacecraft development
schedule. The review and approval process
usually consists of several iterations of the SSPP,
MSPSP, GOP, and hazardous procedures to
ensure that all requirements are met and all
hazards are adequately controlled. Working
sessions are held periodically to clarify the intent
of requirements and discuss approaches to hazard
control. These working sessions are normally
scheduled to coincide with existing MIWGs and
GOWGs.
When certain requirements cannot be satisfied as
specifically stated in the regulation, the approving
safety organization at the processing and launch
sites may waive the requirement when provided
with sufficient justification. This request for
variance must contain an identification of the
requirement, assessment of the risk associated
with not meeting the letter of the requirement, and
the design and procedural controls that are in
place to mitigate this risk. As stated previously,
the use of variances is discouraged and approval
cannot be guaranteed.
7. PEGASUS/PAYLOAD INTEGRATION
OVERVIEW
The Pegasus system is designed to minimize both
vehicle and payload handling complexity as well
as launch base operations time. Horizontal
integration of the Pegasus vehicle and payload
simplifies integration procedures, increases safety,
and provides excellent access for the integration
team. In addition, simple mechanical and
electrical interfaces and checkout procedures
reduce vehicle and payload integration times, and
increase system reliability. Pegasus’ well-defined
payload integration process at the Vehicle
Assembly Building at VAFB is readily adaptable to
other potential integration sites.
7.1. Ground and Launch Operations
Figure 7-1 shows a typical ground and launch
processing flow that is conducted in three major
phases:
Launch Vehicle Integration: Assembly and
test of the Pegasus vehicle;
