Dissipation method, Electrical description of the quartz crystal, Dissipation – INFICON RQCM - Quartz Crystal Microbalance Research System User Manual
Page 61: Method -9, Electrical, Description, Quartz, Crystal -9, Igure, Rystal
RQCM – RESEARCH QUARTZ CRYSTAL MICROBALANCE
THEORY OF OPERATION
5-9
S
ω
= Angular frequency at series resonance (
f
π
2
)
For example, the decay length for a 5 Mhz crystal in water at 20°C is 2.5×10
-7
m = 0.25 microns.
5.5 DISSIPATION
METHOD
The Dissipation Method is an alternate way of measuring the crystal to determine the properties
of the film and/or the liquid. In this method, the crystal is driven at its resonant frequency by an
oscillator then the crystal shorted and both the resonant frequency and the oscillation decay time
are measured. The crystal dissipation is related to Q and R as follows:
Equation 10
L
R
Q
D
S
⋅
=
=
ω
1
Where:
D = Dissipation
Q = Quality Factor
R = resistance in Ω
L = inductance in H
D can be determined from R if L is known. It has been shown that L will remain constant unless
there is an acoustic resonance in the film on the crystal. Independent studies
have shown that as
long as the effect of the parasitic capacitance (C
S
) is properly cancelled, the results provided by
the RQCM System are in good agreement with those obtained by the Dissipation Method.
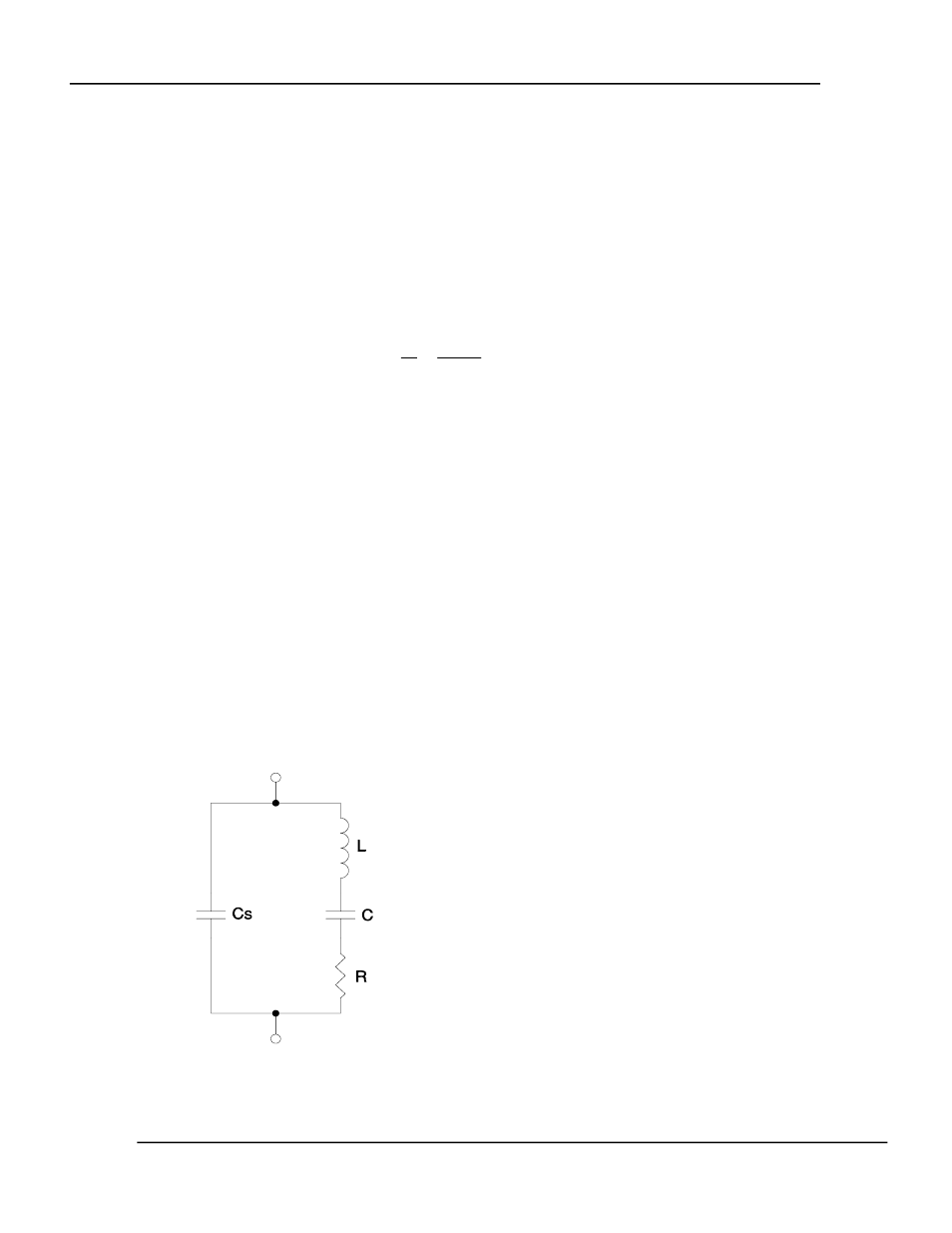
5.6 ELECTRICAL DESCRIPTION OF THE QUARTZ CRYSTAL
Figure 16 shows the equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal. The circuit has two branches. The
motional branch, which contains the L, R & C, is the branch that is modified by mass and viscous
loading of the crystal. The shunt branch, which contains the lone Cs element, represents the
shunt capacitance of the crystal electrodes and any cable and fixture capacitance.
Figure 16 Crystal Equivalent Circuit
