Learn more about feeds, Indexing database content – Google Search Appliance Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance User Manual
Page 27
Google Search Appliance: Getting the Most from Your Google Search Appliance
Crawling and Indexing
27
2.
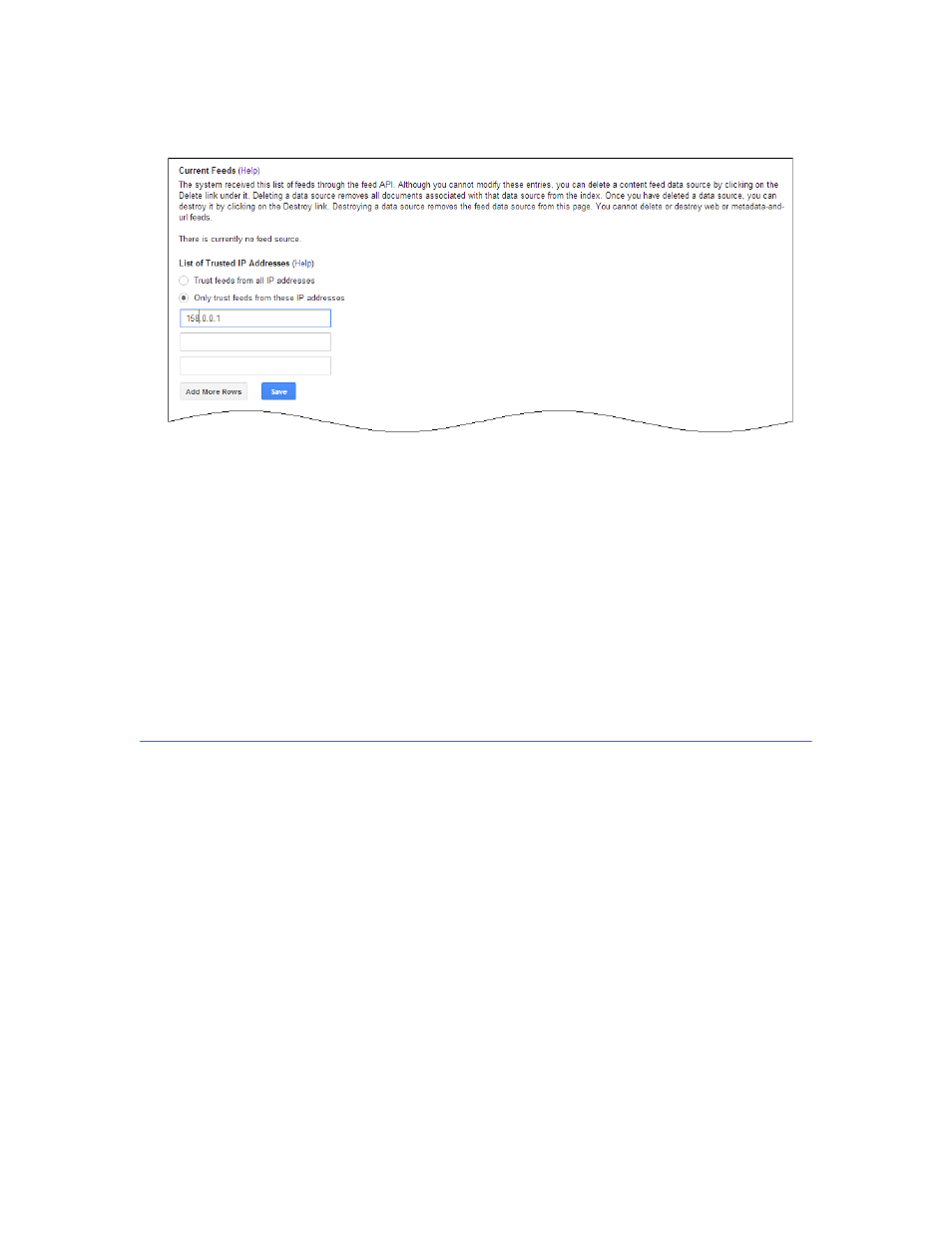
Configuring the search appliance to accept the feed by using the Content Sources > Feeds page,
shown in the following figure. To prevent unauthorized additions to your index, feeds are only
accepted from machines that are specified on this page.
3.
Running the feed client script.
4.
Monitoring the feed by using the Admin Console.
5.
Checking for search results from the feed within 30 minutes of running the feed client script.
Learn More about Feeds
For complete documentation on feeds, refer to the Feeds Protocol Developer’s Guide.
Indexing Database Content
The Google Search Appliance can also index records in a relational database. The Google Search
Appliance supports indexing of the following relational database management systems:
•
IBM DB2 type4
•
MySQL
•
Oracle
•
Microsoft SQL Server
•
Sybase
The search appliance provides access to data stored in relational databases by crawling the content
directly from the database and serving the content. The process of crawling a database is called
“synchronizing a database.” To access content in a database, the Google Search Appliance sends SQL
(Structured Query Language) queries using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) adapters provided by
database companies. It crawls the contents of the database and then pushes records from a database
into the search appliance’s index using feeds.
