Lull 944E-42 Service Manual User Manual
Page 46
Boom
3-16
944E-42
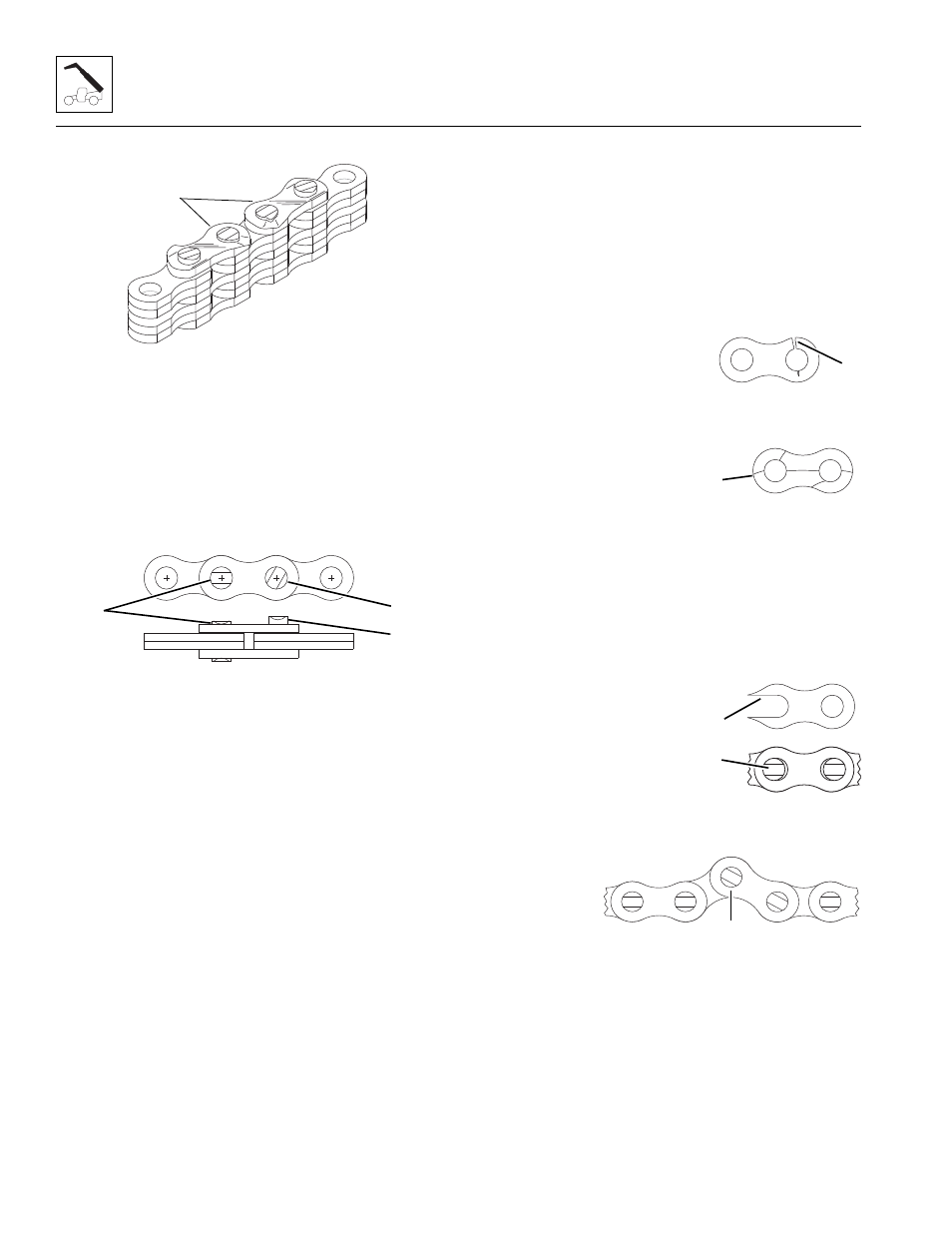
Distorted or Battered Link Plates
Distorted or battered link plates (5) on a leaf chain can
cause tight joints and prevent flexing.
Turning or Protruding Pins
Highly loaded chain, operating with inadequate
lubrication can generate abnormal frictional forces
between pin and link plates. When chain is allowed
to operate in this condition, a pin or series of pins,
can begin to twist out of a chain, resulting in failure.
Examine the pin head rivets to determine if the
“VEE” flats are still in correct alignment (6). Chain
with rotated/displaced heads (7) or abnormal pin
protrusion (8) should be replaced immediately.
DO NOT attempt to repair the chain by welding or
driving the pin(s) back into the chain. Once the press
fit integrity between outside plates and pins has
been altered, it cannot be restored.
Any wear pattern on the pin heads or the sides of the
link plates indicates misalignment in the system.
This condition damages the chain as well as
increases frictional loading and should be corrected.
Cracked Plates
Inspect the chains very carefully, front and back as
well as side to side, for any evidence of cracked
plates. If any one crack is discovered, the chain
should be replaced in its entirety.
It is important, however to determine the cause of
the crack before installing a new chain so the
condition does not repeat itself.
The types of cracks are:
• Fatigue Cracking -
Fatigue cracks (9) are a
result of repeated
cyclic loading beyond
the chain’s endurance
limit.
• Stress Corrosion
Cracking - The
outside link plates
are particularly
susceptible to stress
corrosion cracking (10).
• Corrosion Fatigue Cracking - Corrosion
fatigue cracks are very similar to fatigue
cracks in appearance. Corrosion fatigue is the
combined action of an aggressive
environment and cyclic stress.
Other Modes of Failure
• Ultimate Strength Failure -
These types of failures are
caused by overloads far in
excess of the design load.
Either fractured plates (1) or
enlarged holes (2) can
occur. If either of these
failures occurs, the chain
should be replaced immediately.
• Tight Joints
- All joints in
the chain
should flex
freely. Tight
joints (3)
resist flexing.
If the problem is caused by dirt or foreign substance
packed in the joints, clean and lubricate thoroughly
before re-installing the chain.
If the problem is caused by corrosion and rust or
bent pins, replace the chain.
8
MZ1466
5
MZ1465
6
7
8
MZ1467
9
MZ1468
10
MZ1469
MZ1470
1
2
MZ1471
3
