Apple Soundtrack User Manual
Page 24
24
Chapter 2
Setting Up Your System
FireWire (IEEE 1394)
FireWire is a professional and consumer standard for both audio and video equipment.
The combination of fast data-transfer rates, high storage capacities, and plug-and-play
connection makes FireWire an attractive choice for working with digital audio files.
FireWire is included on all current Macintosh computers, and a number of FireWire
audio interfaces are available.
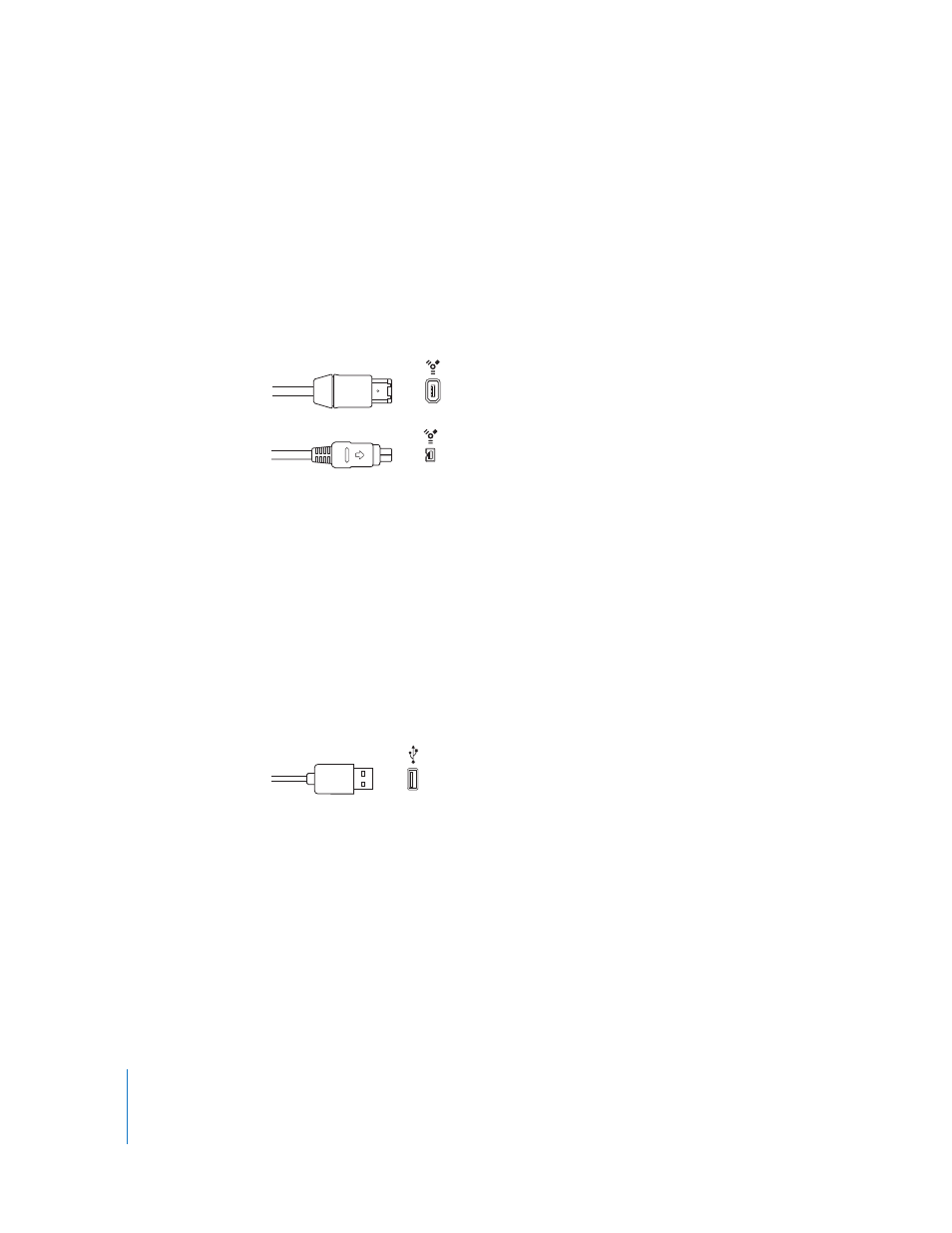
There are two kinds of FireWire connectors: a 4-pin connector (typically found on
video equipment) and a 6-pin connector (used for computer and audio equipment).
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
USB is a consumer standard used on computer peripherals and other devices. USB
offers a lower data-transfer rate than FireWire, but supports plug-and-play operation
and the ability to connect several devices in sequence (daisy-chaining). Some USB
devices draw their power over the USB cable, while others require a separate power
connection. USB is included on all current Macintosh computers.
There are two kinds of USB connectors: an A connector, typically used to connect a
device to a USB hub, and a B connector, typically used to connect devices together, and
also to connect a device to a computer. USB audio interfaces should always be directly
connected to your computer, not connected via a hub or to the computer’s display,
keyboard, or another peripheral.
PCI (Peripheral Connect Interface)
PCI interfaces, unlike FireWire and USB interfaces, require that you install a dedicated
sound card in your computer. PCI provides high bandwidth and fast data-transfer rates,
allowing you to record and play back large numbers of files at the highest possible
sample rates and bit depths.
FireWire 400 (6-pin)
(Sometimes labeled iLINK)
FireWire 400 (4-pin)
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
