Apple Soundtrack User Manual
Page 17
Chapter 1
Audio and Music Basics
17
Digital recording technology offers several advantages over analog technology for
recording sound, including lower noise, wider frequency response, and less distortion
(if the sound is recorded at the proper level). In addition, digital recordings can be
reproduced any number of times without any loss of audio quality. These advantages,
combined with the popularity of personal computers, have led to the rapid
development of digital audio as a leading technology for music production.
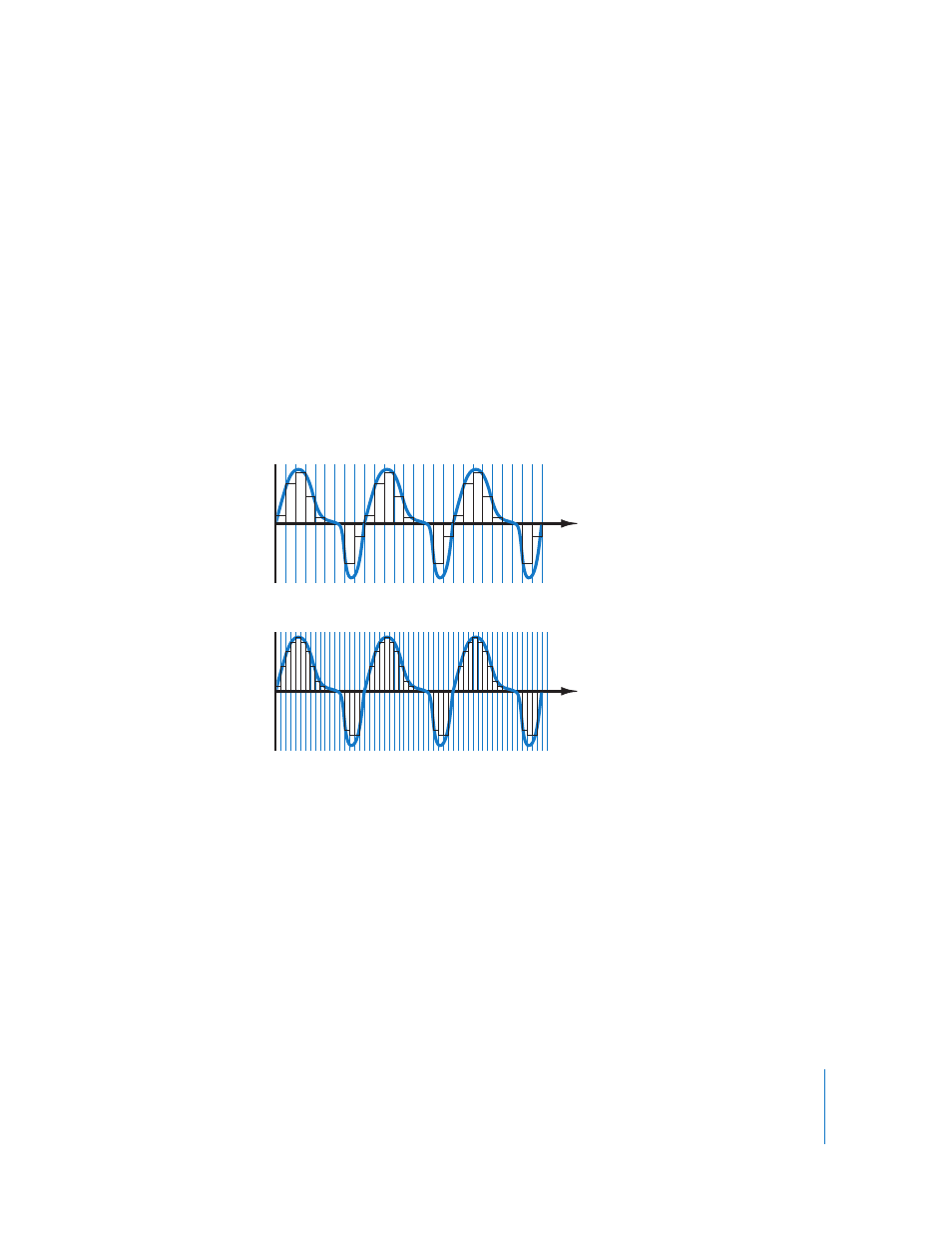
Sample Rate and Bit Depth
The audio quality of any digital recording depends on two factors: the sample rate and
the bit depth used to record the signal. The sample rate is the number of samples
recorded per second. The bit depth is the number of digital bits each sample contains.
Together, these two factors determine the amount of information contained in a digital
audio recording. The higher the sample rate and bit depth of a recording, the more
accurately the recording reproduces the original sound.
Recording music digitally requires a very high sample rate and bit depth to reproduce
the nuances in the music satisfactorily. The Nyquist theorem states that sounds must be
recorded at no less than double the rate of the highest frequency being sampled to
accurately reproduce the original sound. Audio CDs are recorded at a sample rate of
44.1 kHz and a bit depth of 16 bits (some CDs use a higher 20- or 24-bit depth). Audio
for DVDs is often recorded using a slightly higher sample rate of 48 kHz. Soundtrack
lets you record and play back digital audio files at sample rates of up to 96 kHz, and at
bit depths of up to 24 bits.
Low sample rate
High sample rate
Time
Time
