8 power and energy results, Figure 5. low-rate calculations, Figure 6. two-channel power summation – Cirrus Logic CS5467 User Manual
Page 16: See figures, Figure 5, Cs5467
CS5467
16
DS714F3
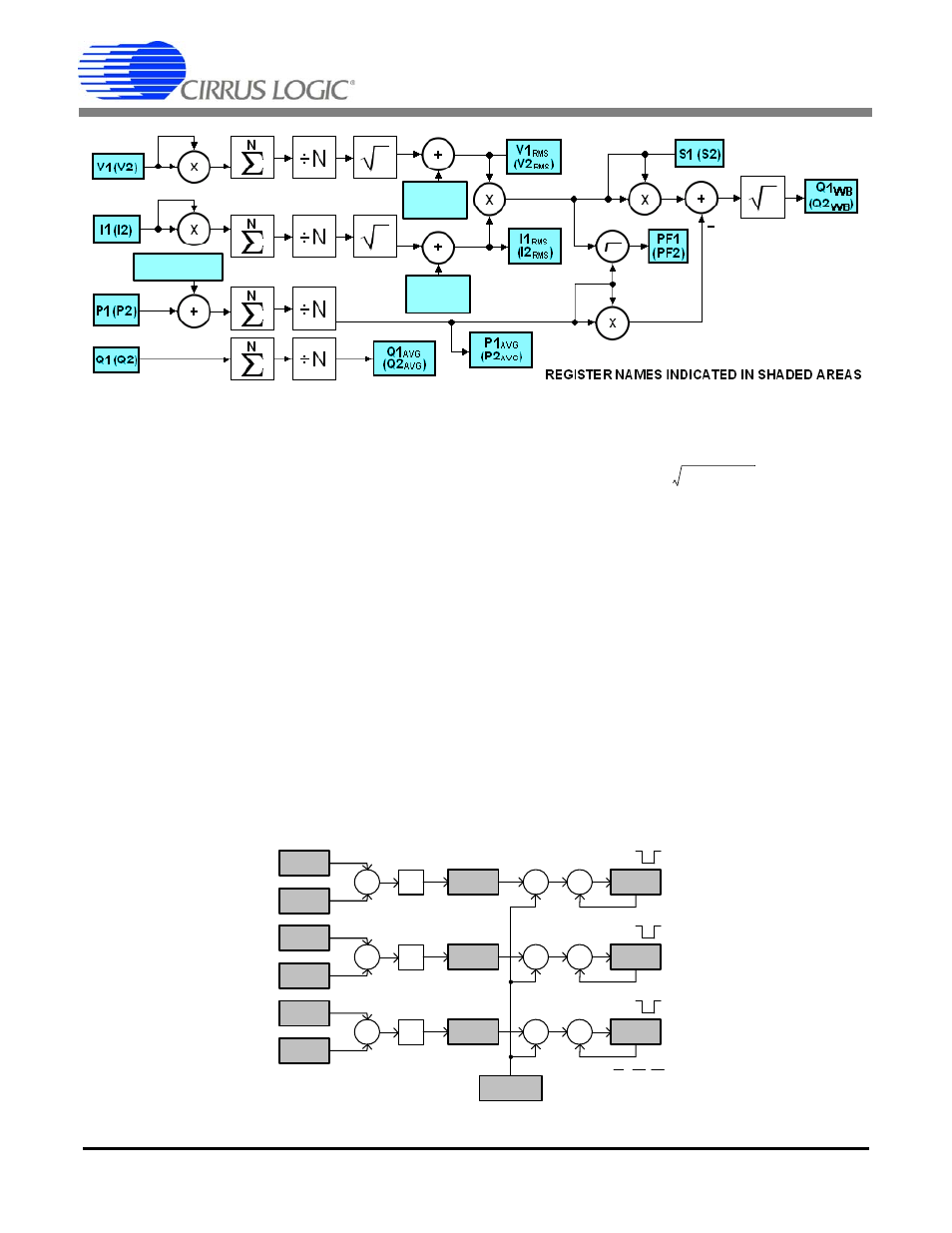
4.8 Power and Energy Results
The instantaneous voltage and current samples are
multiplied to obtain the instantaneous power (P1, P2)
(see
and
). The product is then averaged over
N
conversions to compute active power (P1
AVG
,
P2
AVG
).
Apparent power (S1, S2) is the product of RMS voltage
and current as shown:
Power factor (PF1, PF2) is active power divided by ap-
parent power as shown below. The sign of the power
factor is determined by the active power.
Wideband reactive power (Q1
WB
, Q2
WB
) is calculated
by doing a vector subtraction of active power from ap-
parent power.
Quadrature power (Q1, Q2) are sample rate results ob-
tained by multiplying instantaneous current (I1, I2) by in-
stantaneous quadrature voltage (V1Q, V2Q) which are
created by phase shifting instantaneous voltage (V1,
V2
) 90 degrees using first-order integrators. (See
and
). The gain of these integrators is inversely
related to line frequency, so their gain is corrected by
the Epsilon register, which is based on line frequency.
Reactive power (Q1
Avg
, Q2
AvG
) is generated by inte-
grating the instantaneous quadrature power over N
samples.
Active power (P1
AVG
, P2
AVG
), apparent power (S1, S2),
and reactive power (Q1
AVG
, Q2
AVG
) of the two channels
are summed up and then divided by 2. The calculation
results are placed in E
PULSE
, S
PULSE
, and Q
PULSE
reg-
isters which can be configured to drive energy pulse
outputs. (See
V1
ACOFF
(V2
ACOFF
)
I1
ACOFF
(I2
ACOFF
)
P1
OFF
(P2
OFF
)
Figure 5. Low-rate Calculations
S
V
RMS
I
RMS
=
PF
P
Active
S
------------------
=
Q
WB
S
2
P
Active
2
–
=
P1
AVG
÷2
P2
AVG
E
PULSE
E
ACCM
+
×
+
OVF=
S1
÷2
S2
S
PULSE
S
ACCM
+
×
+
OVF=
Q1
AVG
÷2
Q2
AVG
Q
PULSE
Q
ACCM
+
×
+
OVF=
PulseRate
( E1, E2, E3 )
Figure 6. Two-channel Power Summation
