4 modulator stability — mflag, 5 modulator clock input — mclk, 6 modulator synchronization — msync – Cirrus Logic CS5374 User Manual
Page 20: Modulator stability — mflag, Modulator clock input — mclk, Modulator synchronization — msync, Table 1. 24-bit output coding, Cs5374
CS5374
CS5374
20
offset and the modulator internal offset are re-
moved from the final conversion result.
4.4 Modulator Stability — MFLAG
The CS5374
ΔΣ modulators have a fourth-order ar-
chitecture which is conditionally stable and may go
into an oscillatory condition if the analog inputs are
over-ranged more than 5% past either positive or
negative full scale.
If an unstable condition is detected, the modulator
collapses to a first-order system to regain stability
and transitions the MFLAG output low-to-high to
signal an error condition to the CS5376A digital
filter. The MFLAG output connects to a dedicated
input on the digital filter, causing an error flag to be
set in the status byte of the next output data word.
The analog input signal must be reduced to within
the full-scale range for at least 32 MCLK cycles for
the modulator to recover from an oscillatory condi-
tion. If the analog input remains over-ranged for an
extended period, the modulator will cycle between
fourth-order and first- order operation and the
MFLAG output will be seen to pulse.
4.5 Modulator Clock Input — MCLK
The CS5376A digital filter generates the master
clock for the CS5374, typically 2.048 MHz, from a
synchronous clock input from the external system.
If MCLK is disabled during operation, the CS5374
will enter a power down state after approximately
40
µ
S. By default, MCLK is disabled at reset and
is enabled by writing the digital filter CONFIG reg-
ister.
MCLK must have low jitter to guarantee full ana-
log performance, requiring a crystal- or VCXO-
based system clock input to the digital filter. Clock
jitter on the digital filter CLK input directly trans-
lates to jitter on MCLK.
4.6 Modulator Synchronization —
MSYNC
The CS5374 modulators are designed to operate
synchronously with other modulators in a distribut-
ed measurement network, so a rising edge on the
MSYNC input resets the internal conversion state
machine to synchronize analog sample timing.
MSYNC is automatically generated by the
CS5376A digital filter after receiving a synchroni-
zation signal from the external system, and is chip-
to-chip accurate within ± 1 MCLK period. The in-
put SYNC signal to the CS5376A digital filter sets
a common reference time t
0
for measurement
events, thereby synchronizing analog sampling
across a measurement network. By default,
MSYNC generation is disabled at reset and is en-
abled by writing the digital filter CONFIG register.
The CS5374 MSYNC input is rising-edge trig-
gered and resets the internal MCLK counter/divid-
er to guarantee synchronous operation with other
system devices. While the MSYNC signal syn-
chronizes the internal operation of the modulators,
by default, it does not synchronize the phase of the
sine wave from the CS4373A test DAC unless en-
abled in the digital filter TBSCFG register.
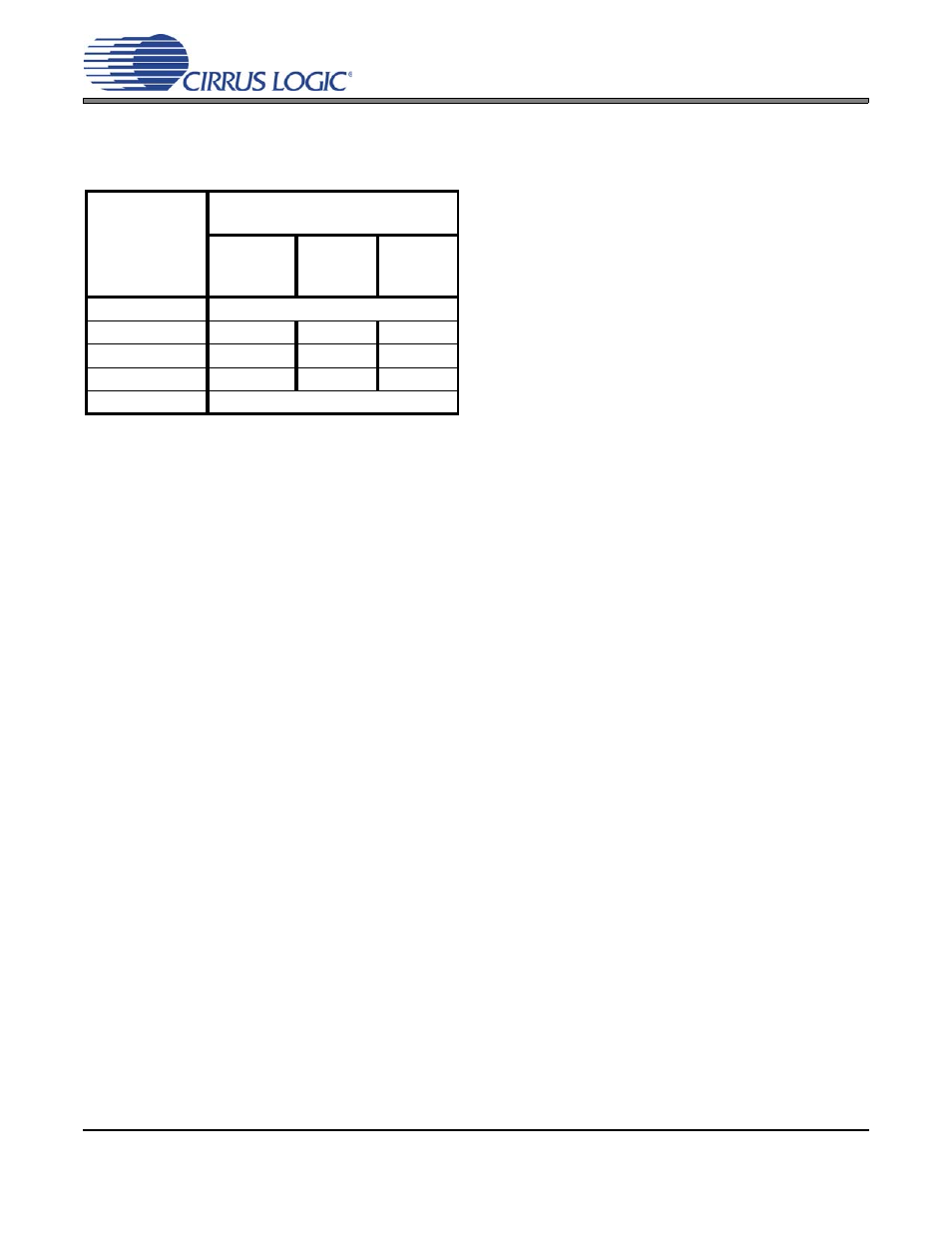
Table 1. 24-bit Output Coding
Modulator
Differential
Analog Input
Signal
CS5376A Digital Filter
24-Bit Output Code
Offset
Corrected
CH1
–60 mV
Offset
CH2
–35 mV
Offset
> + (VREF+5%)
Error Flag Possible
+ VREF
5D18CA
5ADCCE
5BCB22
0 V
000000
FDC404
FEB258
– VREF
A2E736
A0AB3A
A1998E
> – (VREF+5%)
Error Flag Possible
for the CS5374 Modulator and
CS5376A Digital Filter Combination
