Introduction, Principles of operation, 1 general description – Pulsafeeder PulsaPro 900 EN User Manual
Page 5: 1 overall operation
1
1. Introduction
1.1 General
Description
Diaphragm Metering pumps are positive displacement reciprocating pumps that combine the
high efficiency of the plunger pump with a sealed diaphragm that prevents product leakage.
Each pump consists of a power end and a process end separated by a hydraulically operated
diaphragm. Individual pumps will vary in appearance due to various liquid ends, accessories,
and multiplexing - however, the basic principles of operation remain the same.
2. Principles
of
Operation
2.1 Overall
Operation
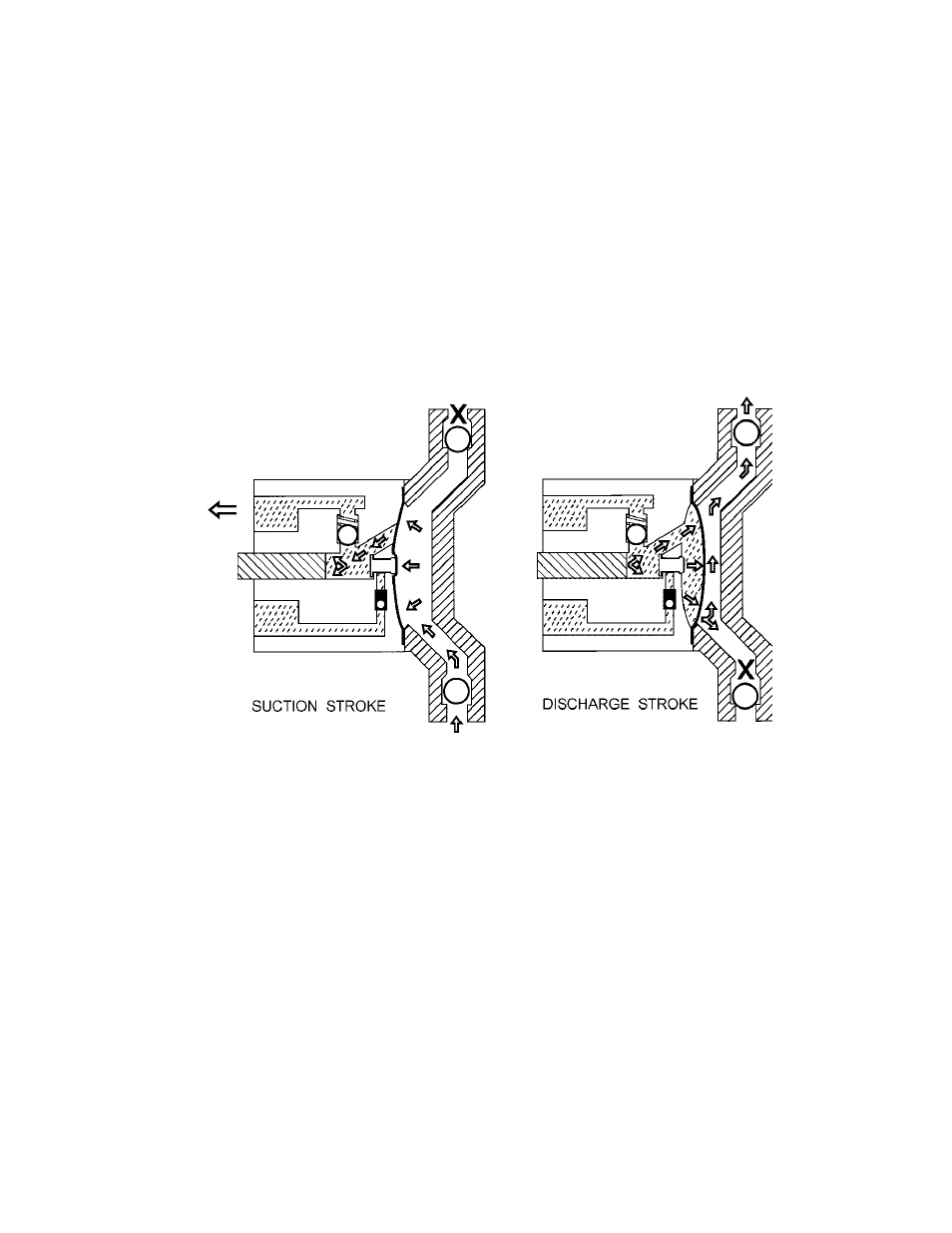
Figure 1
A piston reciprocates within an accurately sized cylinder at a preset stroke length, displacing
an exact volume of hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic fluid acts against a sealed diaphragm,
which pumps the chemicals.
The piston and associated mechanisms are enclosed by a chamber called the Pump Head or
intermediate housing. This also acts as a hydraulic oil reservoir.
The diaphragm separates the hydraulic oil from the product pumped. The diaphragm moves
in exact response to the piston displacement. The diaphragm does no work, and acts only as a
separator.
The displacement of the oil is translated into an equal displacement of the chemical being
pumped. Therefore, piston retraction causes the product to enter through the suction check
valve. Piston advance causes the discharge of an equal amount of the product through the
discharge check valve.
