5 calibration – Pulsafeeder PulsaPro 900 EN User Manual
Page 24
20
6.2.5 Calibration
All metering pumps must be calibrated to accurately specify stroke length settings to achieve
required flow rates.
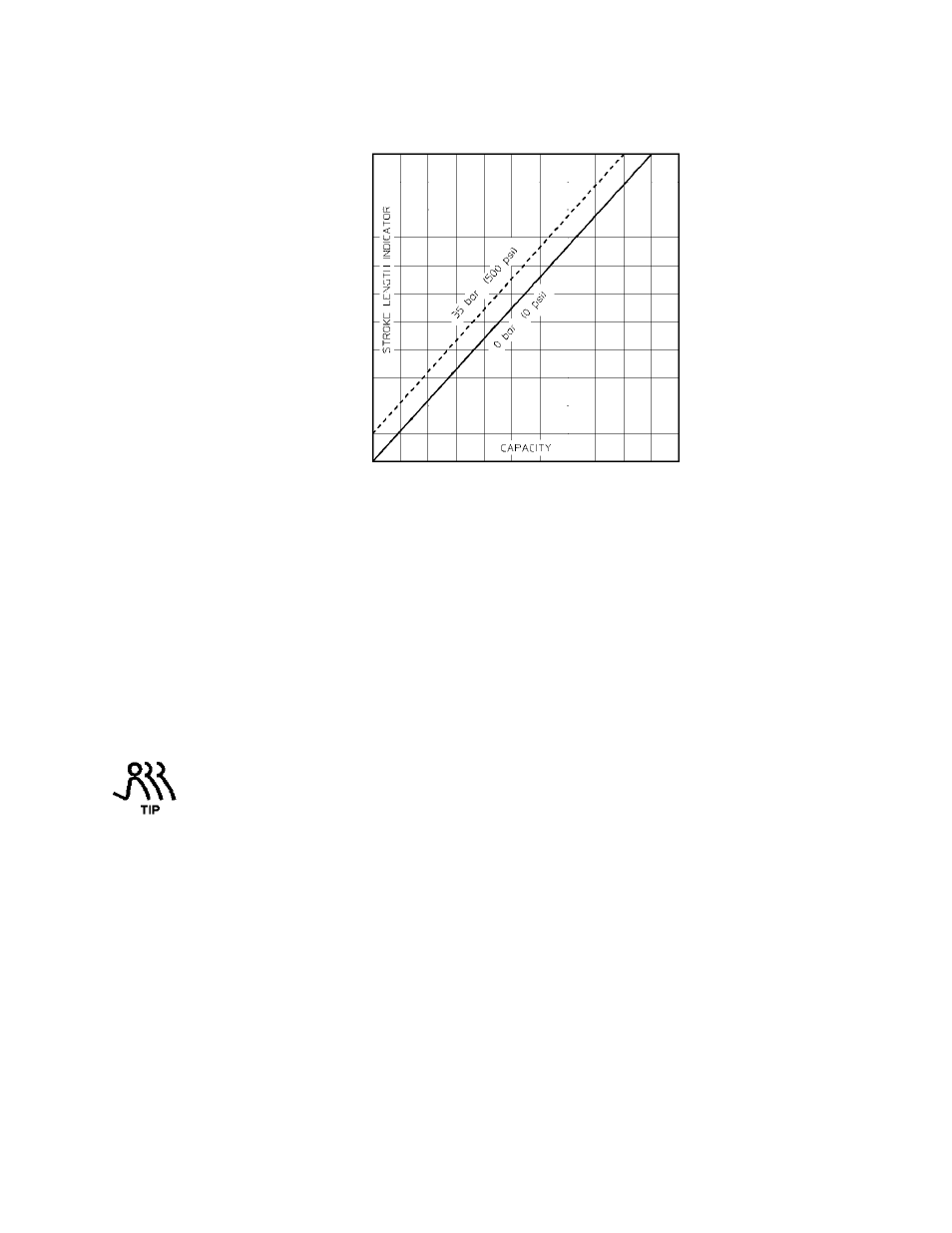
Figure 11
A typical calibration chart is shown in Figure 11. Although output is linear with respect to
stroke length setting, an increase in discharge pressure decreases output uniformly, describing a
series of parallel lines, one for each pressure (only two are shown in the figure).
The theoretical output flow rate at atmospheric pressure is based on the displacement of the
hydraulic piston (the product of the piston cross-sectional area and stroke length) and the
stroking rate of the pump.
Whenever possible, calibration should be performed under actual process conditions (i.e., the
same or a similar process liquid at system operating pressure).
To assure a sound hydraulic system, run the pump for 15-20 minutes prior to calibration. This
will allow the PTP (automatic bleed) valve to purge any air from the system.
Allowing the pump to run for several hours prior to performing a calibration will
provide better results.
Procedure for constructing a calibration chart,
1. Measure the flow rate several times at three or more stroke settings (e.g., 25, 50, 75, and
100%).
2. Plot these values on linear graph paper.
3. Draw a best-fit line through the points.
For stable conditions, this line should predict stroke settings to attain required outputs.
