Spanning tree protocol, Star, Switch – Cirrus Logic CobraNet User Manual
Page 145: Switching hub, Trunking, Unicast addressing
CobraNet Programmer’s Reference
Glossary of Terms
DS651PM25
©
Copyright 2006 Cirrus Logic, Inc.
145
Proprietary single mode fiber systems each have their own run length limits; all exceed
the 2 kilometer multimode limit. Some systems offer lengths in excess of 100 kilometers.
Spanning Tree Protocol
An IEEE standard protocol (802.1D) allowing detection and elimination of loops in
Ethernet networks. Spanning tree protocol is implemented on most managed switches.
More information on spanning tree protocol is available at
http://www.peakaudio.com/
Index.htm
.
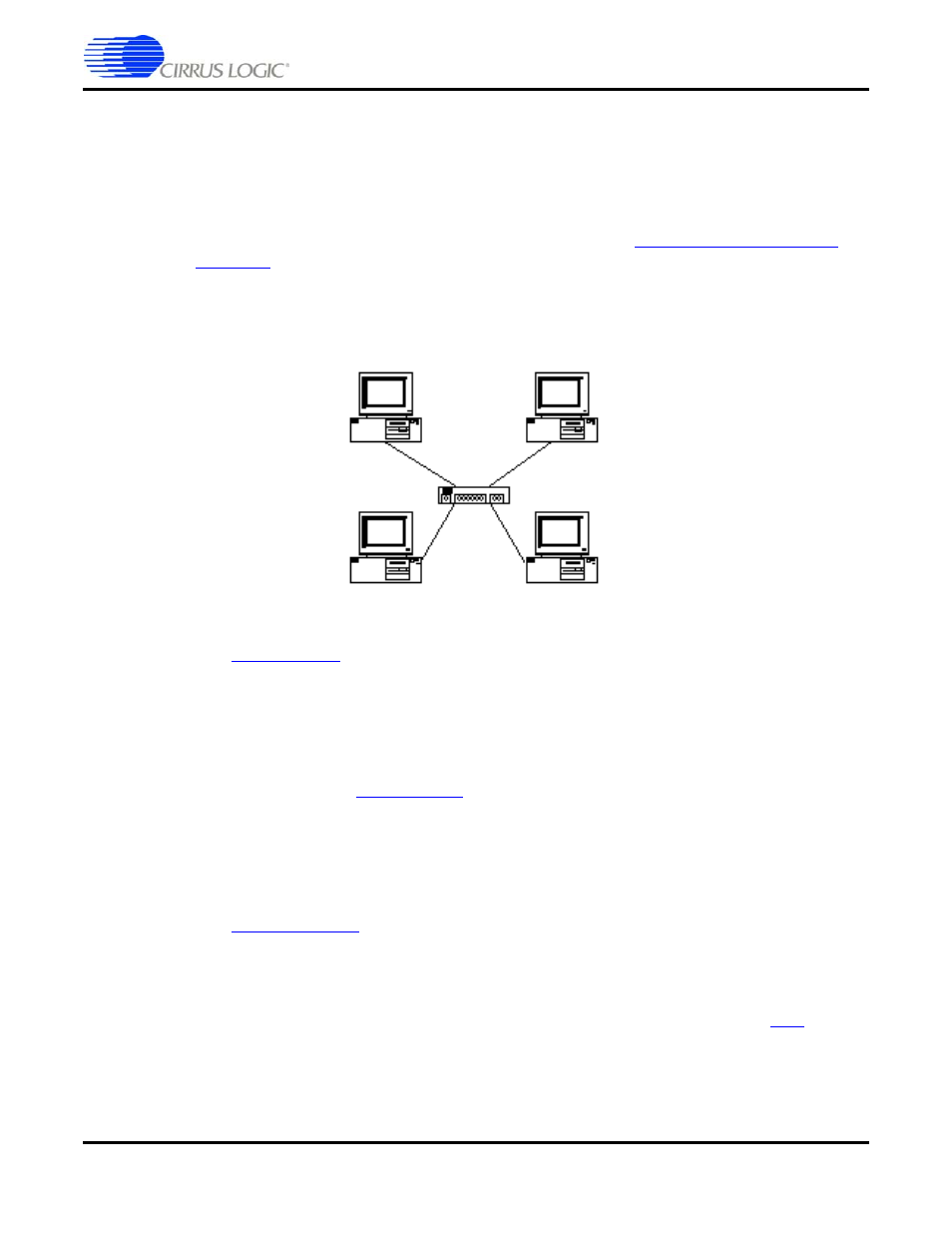
Star
A network topology in which all nodes are connected to a central network device such as
a hub or switch.
Switch
See
below.
Switching Hub
A Switching Hub, or simply "Switch", examines addressing fields on data arriving at each
port and attempts to direct the data out the port or ports to which the data is addressed.
Data may be buffered within the Switching Hub to avoid the collision condition
experienced within a
. A network utilizing Switching Hubs realizes higher
overall bandwidth capacity as data may be received through multiple ports simultaneously
without conflict. Switches are full-duplex devices. A network utilizing switches to connect
network segments is referred to as a switched network.
Trunking
See
Unicast Addressing
Data which is unicast is addressed to a specific DTE. A switching hub may examine the
unicast address field of the data and determine on which port the addressed
resides
and direct the data out only that port. Delivery of an e-mail message is an example of
unicast data addressing.
