Node, Repeater hub, Ring – Cirrus Logic CobraNet User Manual
Page 144: Run length, Single mode fiber, Repeater, Or a
144
©
Copyright 2006 Cirrus Logic, Inc.
DS651PM25
CobraNet Programmer’s Reference
Glossary of Terms
NIC
A NIC or Network Interface Card is an expansion board inserted into a computer in order
to connect the computer to a network. Typically, NICs are designed for a particular type of
network and media, although some can serve multiple networks.
Node
A processing location. A node can be a computer, a switch, a CobraNet device, or any
other device that has a unique network address.
Repeater Hub
An Ethernet multi-port repeater. A data signal arriving in any port is electrically
regenerated and reproduced out all other ports on the hub. A repeater hub does not
buffer or interpret the data passing through it. An Ethernet network is typically wired in a
star configuration and the hub is at the center. Hubs are available with port counts from 4
to 24. There are two grades of Fast Ethernet hubs: Class I and Class II. Class II hubs
deliver higher performance than the Class I hubs. Most hubs shipping today are of the
Class II variety. The use of hubs require that all devices on the network run in half duplex
mode.
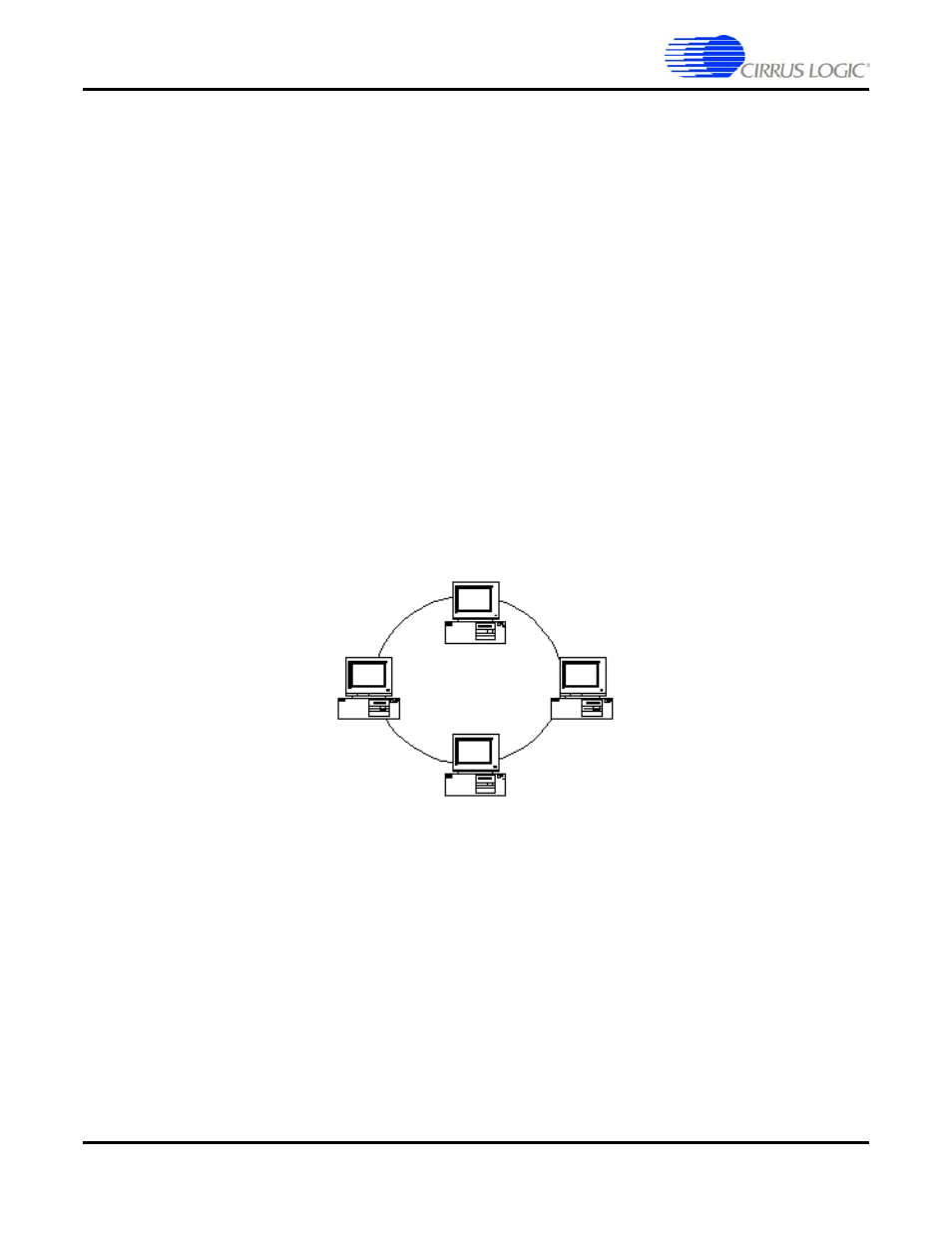
Ring
A network topology in which all nodes are connected in a closed loop.
Run Length
Each type of media has a limitation in the length of a point-to-point run between two
devices. When maximum run length guidelines are exceeded it may not be possible to
establish a valid network connection or data may be corrupted. Longer distances can be
achieved by upgrading the media or using multiple runs in series.
Single Mode Fiber
A fiber optic cable built from a single type of glass. Data is carried over single mode fiber
in the coherent light produced by a laser. While the single mode fiber cable cost
approximately the same as a multimode cable, the cost of the optical transmitters and
receivers is significantly more for a single mode installation than multimode. However,
single mode fiber systems are able to achieve much greater transmission distance than
multimode. There is no official standard for carrying Ethernet over single mode fiber.
