HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 160
Description
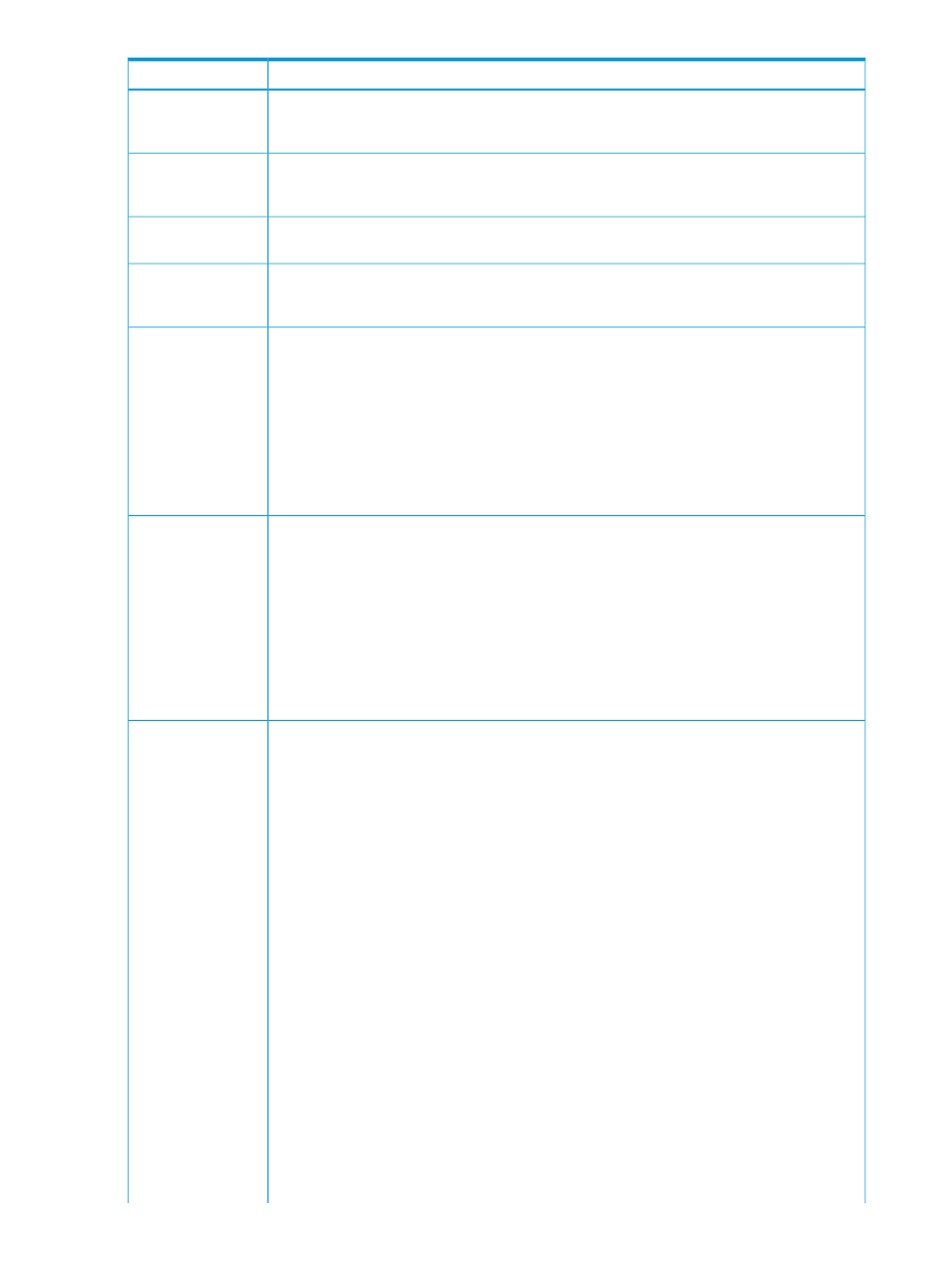
Item
The number of data volumes associated with the journal. When one journal uses multiple mirror
IDs, this field shows the number of data volumes in the journal whose mirror ID is other than
Hold, Holding, or Hold(Failure).
Data Volumes
The total capacity of all data volumes. When one journal uses multiple mirror IDs, this field
shows the total capacity of the data volumes in the journal whose mirror ID is other than Hold,
Holding, or Hold(Failure).
Data Capacity(GB)
The restrict inflow of update data to the journal volume. Yes restricts inflow, No does not restrict.
(slows delay response to hosts).
Inflow Control
Sets number of seconds for the system to monitor write data to the journal volume, after the
journal volume threshold (80%) is reached. Data Overflow Watch is blank when Inflow Control
is No. For additional information, see
“Changing options used by journals ” (page 81)
.
Data Overflow
Watch (sec)
Displays whether journal data in the restore journal can be stored in the cache.
Use of Cache
•
Used: Journal data will be stored in cache. When there is insufficient space in cache, journal
data is also stored in the journal volume.
This setting only takes effect on the journal volumes of RAID-5 or RAID-6. For external volumes,
or non RAID-5 or RAID-6 journal volumes Not Used is the only setting possible.
•
Not Used: Journal data is not stored in cache.
CAUTION:
This setting does not effect master journals unless the RAID Manager horctakeover
command is used to change a master journal to a restore journal.
Shows a list of registered journal volumes.
Journal Volumes
•
Parity Group: The parity group where a journal volume belongs.
•
LDKC:CU:LDEV: The LDKC number, the CU number and the LDEV number of a journal volume.
•
Capacity: The capacity of a journal volume in gigabytes.
•
Emulation: The emulation type of a journal volume.
•
CLPR: The number and the name of the CLPR where the journal volume belongs. Journal
volumes and data volumes in the same journal can belong to different CLPRs. Journal volumes
must belong to the same CLPR. A primary journal and the corresponding secondary journal
need not belong to the same CLPR.
Shows a list of mirrors. Information of four mirrors are displayed. If four mirrors include the
mirror used by Cnt Ac-J pairs or unused mirrors, information of those mirrors are also displayed.
Mirrors
•
Mirror ID: indicates a mirror ID.
•
Attribute: indicates the attribute of a mirror ID.
Master indicates a mirror to which P-VOLs of local system are registered. Restore indicates
a mirror to which S-VOLs of local system are registered. Initial indicates that no data volumes
are registered in the journals of local system.
•
Status: The status of a mirror in the local system. For detailed information about the statuses,
see
“Monitoring journal (mirror) status” (page 77)
.
•
CTG: The number of a consistency group to which the mirror belongs. This column is blank
if there is no consistency group. A consistency group number shown as 001 indicates that
the multiple primary and secondary system share the consistency group.
•
S/N(LDKC): The serial number of the remote system and the LDKC number.
This column is blank if the attribute of the mirror is Initial.
•
ID: Path group ID registered at DKC registration.
•
Pair JNL: The number of a journal in the remote system.
This column is blank if the attribute of the mirror is Initial.
•
Controller ID: The controller ID, which indicates the remote storage system model. Note the
following controller IDs: P9500 = 6. XP24000/XP20000 Disk Array = 5, XP12000 Disk
Array/XP10000 Disk Array = 4. The column is blank if the attribute of the mirror is Initial
•
Path Watch Time: The time for monitoring blockade of paths to the remote system. If the
status of the mirror in the restore attribute is Hold, this column is blank.
160 GUI reference
