FUTEK IPM500 (D500) Digital Display User Manual
Page 52
- 52 -
23. GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Adaptive Filter Threshold
A threshold which causes an adaptive moving average filter to be reset to the
latest reading when the accumulated difference between individual readings
and the filtered reading exceeds that threshold. Adaptive moving average
filtering allows a meter to respond rapidly to actual changes in signal while
filtering out normal noise. The accumulated difference is also reset to zero
when the latest reading has a different polarity than the filtered reading. A low
adaptive filter threshold is normally selected. A high filter threshold should be
selected if the signal has large transients.
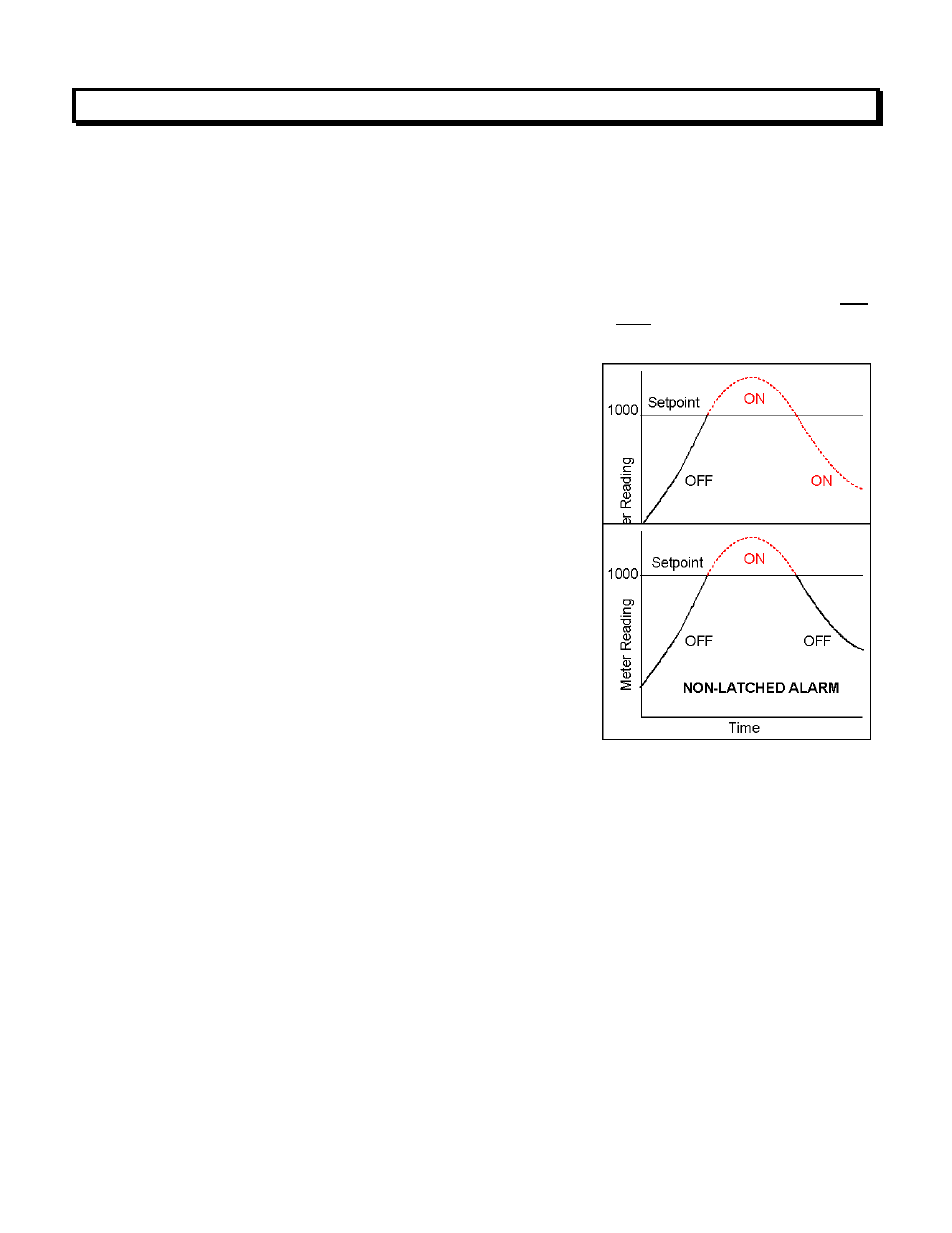
Alarm, Latched
An alarm which stays actuated until reset.
Latched alarms can shut down machinery or
a process when an operating limit has been
exceeded, or maintain an alarm condition
until acknowledged by an operator.
Alarm, Non-latched
An alarm which changes state automatically
when the reading rises above a specified limit
and changes back automatically when the
reading falls below a limit.
Autofilter
A selectable digital filter mode which auto-
matically selects an appropriate moving aver-
age filter time constant from 0.08 sec to 9.6
sec for the encountered noise condition.
Auto-tare
A selectable meter operating mode, where
the first reading following power-on or meter reset is used to zero the display.
Further readings are then relative to this new zero.
Batch Average Filter
A digital filter mode which averages 16 readings and then displays the average.
Readings are taken at 60/sec with 60 Hz power and 50/sec with 50 Hz power.
Counts
The reading displayed on the panel meter ignoring the decimal point.
Custom ASCII Protocol
A simplified, short protocol for use with these panel meters. It allows 31 digital
addresses. Not an industry-standard protocol, like the more complex Modbus
protocol
, which is also offered with the meters.
Deviation Band
A band in counts which controls relay action symmetrically around a setpoint.
The relay actuates when the reading falls within the deviation band, and de-
actuates when the reading falls outside. A limit (e.g., 50 counts) is set up
around both sides of the setpoint to create a deviation band (e.g., 100 counts).
Setting up a passband around a setpoint is often used for component testing.
