Table 4-4. ieee 488 (gpib) bus data mode messages, 1 serial interface, 2 rs 232 implementation – KEPCO BIT 4886 Operator Manual User Manual
Page 45: Serial interface -11, Rs 232 implementation -11, Ieee 488 (gpib) bus data mode messages -11, 4 de
BIT 4886 120413
4-11
4.5.1
SERIAL INTERFACE
The serial interface behaves like the GPIB interface in that the command is parsed after receiv-
ing a control character of either a Line Feed or Carriage Return. The serial interface supports six
special control characters. The six special control characters are:
Escape (1B
H
)
Causes the input buffer to be cleared. This character is used to ensure
that the buffer is empty when the host powers on since it is possible
that the Interface Card was previously powered on and received some
characters prior to the initialization of the host computer.
Backspace (08
H
)
Causes the last character in the input buffer to be removed from the
input buffer queue.
Carriage Return (0D
H
)
Causes the input buffer to be parsed by the BOP.
Line Feed (0A
H
)
Causes the input buffer to be parsed by the BOP.
4.5.2
RS 232 IMPLEMENTATION
The following paragraphs are provided to help the user understand how the RS 232 serial inter-
face is implemented in the BIT 4886. Since the RS 232 protocol does not use a parity bit, the
echo mode is the default method used to ensure reliable communication between the command
originator (computer) and the BIT 4886, thus avoiding a more complex “handshake” protocol.
When the BIT 4886 is in the RS 232 echo mode it returns all data sent to the host controller. The
BIT 4886 provides one additional option that allows handshake communication: the XON XOFF
method. In standard echo mode the controller must verify that each character is echoed back by
the BIT 4886. As shown in Figure 4-4, there are times when the BIT 4886 does not echo back
the character from the controller, requiring that the controller resend the character. By using the
handshake option (XON XOFF) the host controller can ensure that serial data interrupts occur-
ring after parsing of the incoming message do not result in lost data.
Figure 4-4 illustrates the default echo mode and the XON XOFF method described in the follow-
ing paragraphs.
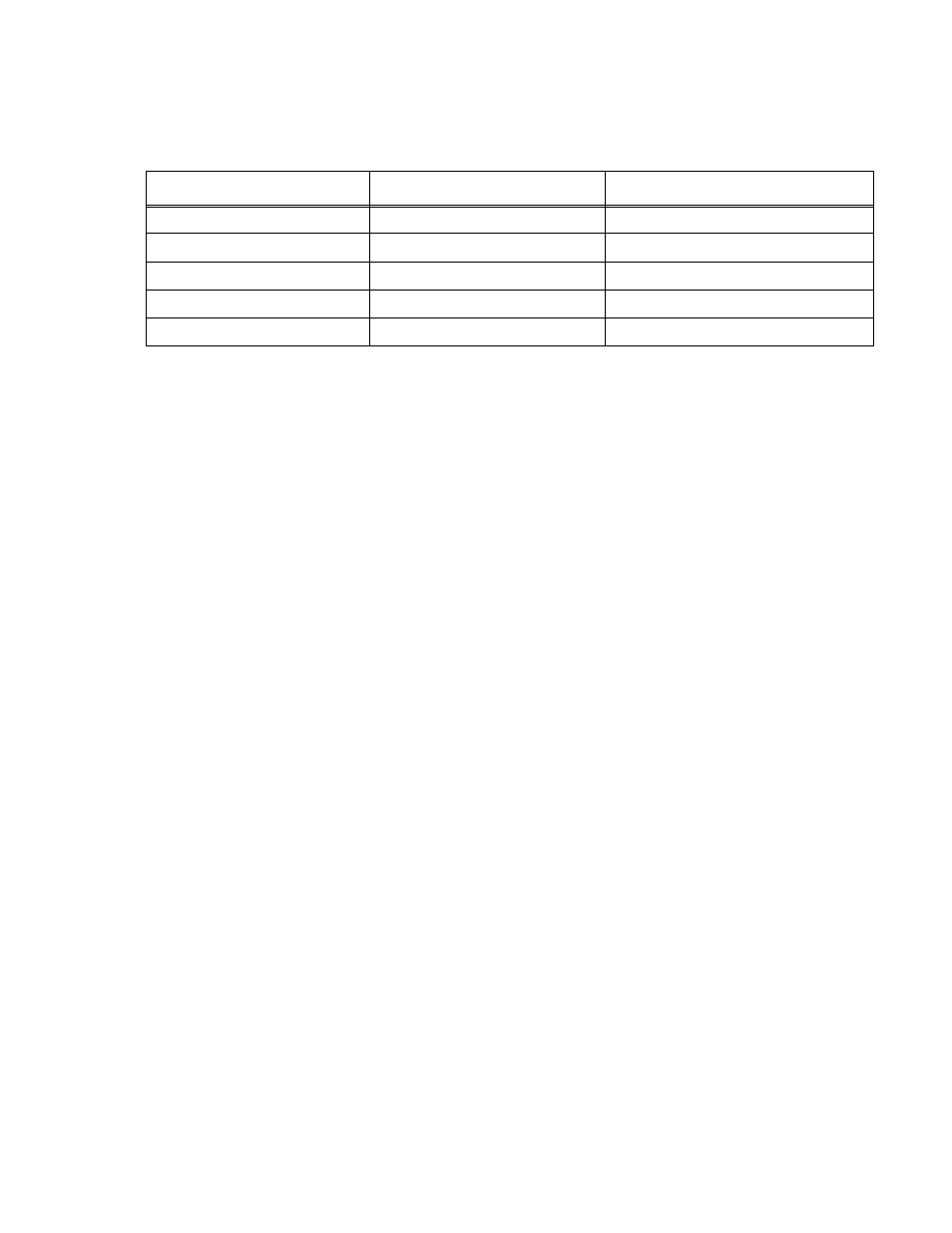
TABLE 4-4. IEEE 488 (GPIB) BUS DATA MODE MESSAGES
MNEMONIC
MESSAGE DESCRIPTION
COMMENTS
DAB
Data Byte
Received or Sent
END
End
Received or Sent
EOS
End of String
Received or Sent
RQS
Request Service
Sent
STB
Status Byte
Sent
