Brooks, Model 5850e – Brooks Instrument 5850E User Manual
Page 50
4-18
Installation and Operation Manual
X-TMF-5850E-MFC-eng
Part Number: 541B102AAG
September, 2009
Section 4 Maitenance &
Troubleshooting
Brooks
®
Model 5850E
Q
GAS
x
Q
GAS
=
Desired flow rate of the gas (sccm)
P
NITROGEN
=
Density of Nitrogen at 70°F
P
GAS
=
Density of the gas (taken at customer temperature)
SG
GAS
=
Specific gravity of the gas (taken at customer
temperature)
Refer to Table 4-4 for specific gravities.
Example:
Q
gas
=
2,000 sccm
SG
gas
=
.269
SG
Nitrogen
SG
gas
Q
Nitrogen
=
SG
Nitrogen
=
2,000 x .269
=
538 sccm Nitrogen
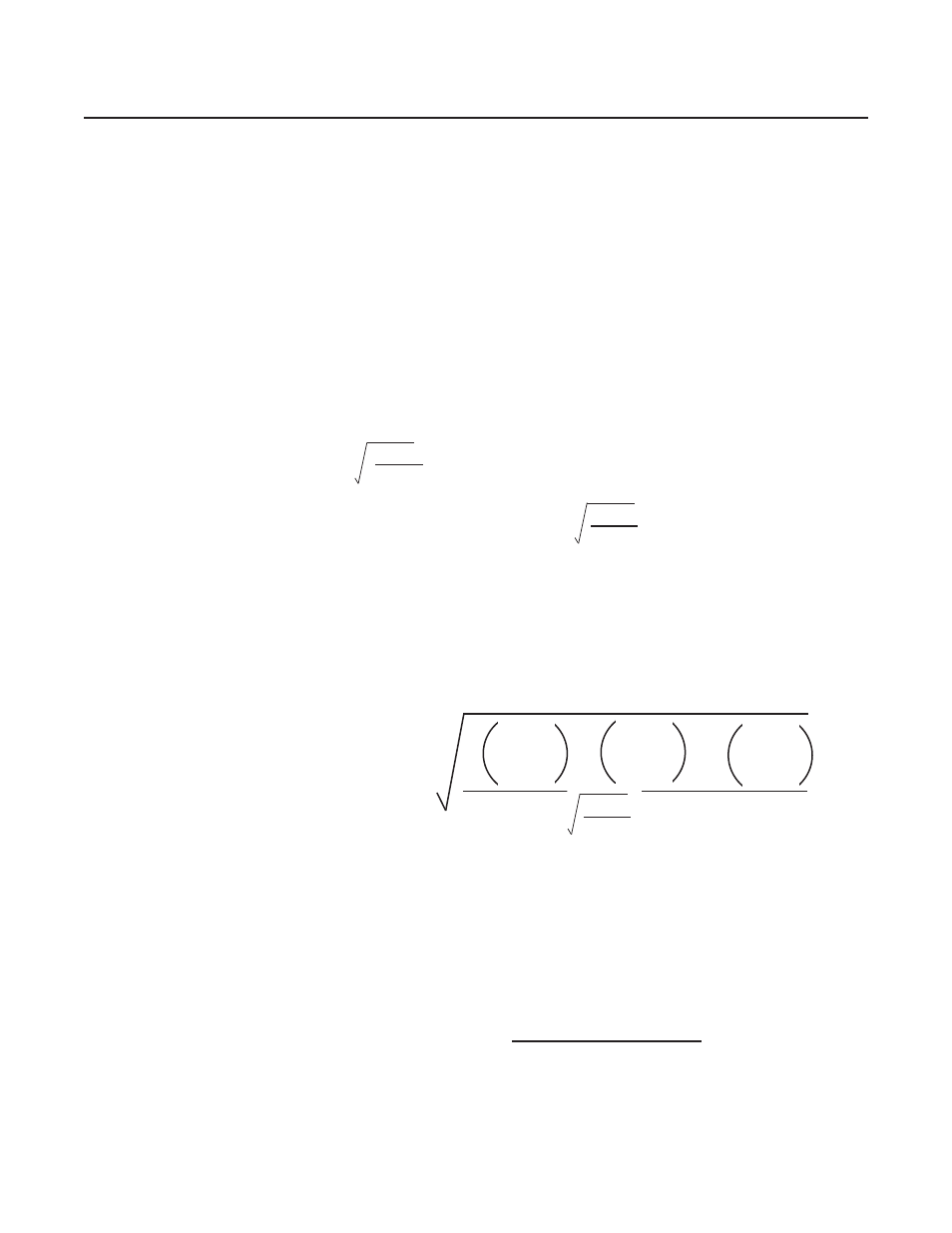
In order to calculate the orifice conversion factor when using a gas mixture,
the following formula must be used:
Orifice
Conversion
Factor 1
P
1
Orifice
Conversion =
Factor
Mixture
+ P
2
Orifice
Conversion
Factor 2
100
Orifice
Conversion
Factor n
+ P
n
Where
P
1
=
percentage by volume of gas 1
P
2
=
percentage by volume of gas 2
P
n
=
percentage by volume of gas n
Example: Find the Nitrogen equivalent for 20 slpm of a 20% Helium and
80% Chlorine gas mixture.
Orifice
Conversion
=
20(.378)
+
80(1.598)
Factor
100
Mixture
Q
Nitrogen
=
Q
gas
(orifice conversion factor)
=
20 x 1.439
=
28.78 slpm Nitrogen
Q
GAS
x
