GE Industrial Solutions Entelliguard TU, MicroVersaTrip Plus and PM Conversion Kits User Manual
Page 19
19
disconnecting the breaker from all power sources,
perform the following procedure:
1. Check that all phase sensors are the same type
(current range).
2. Verify that the tap settings on all three phase sen-
sors are identical.
3. Verify that the wiring harness connections to the
sensors have the proper polarity (white lead to
common, black lead to tap), as shown in the
cabling diagram in Figure 21.
4. On ground fault breakers serving four-wire loads,
check that the neutral sensor is properly
connected, as indicated in Figure 21. In particular,
check the following:
a. Verify that the neutral sensor has the same
rating and tap setting as the phase sensors.
b. Verify continuity between the neutral sensor
and its equipment-mounted secondary
disconnect block. Also check for continuity
from the breaker-mounted neutral secondary
disconnect block through to the trip unit wiring
harness connector.
c. If the breaker’s lower studs connect to the
power source, then the neutral sensor must
have its load end connected to the source.
d. Verify that the neutral conductor is carrying
only the neutral current associated with the
breaker’s load current (the neutral is not shared
with other loads).
5. If the preceding steps fail to identify the problem,
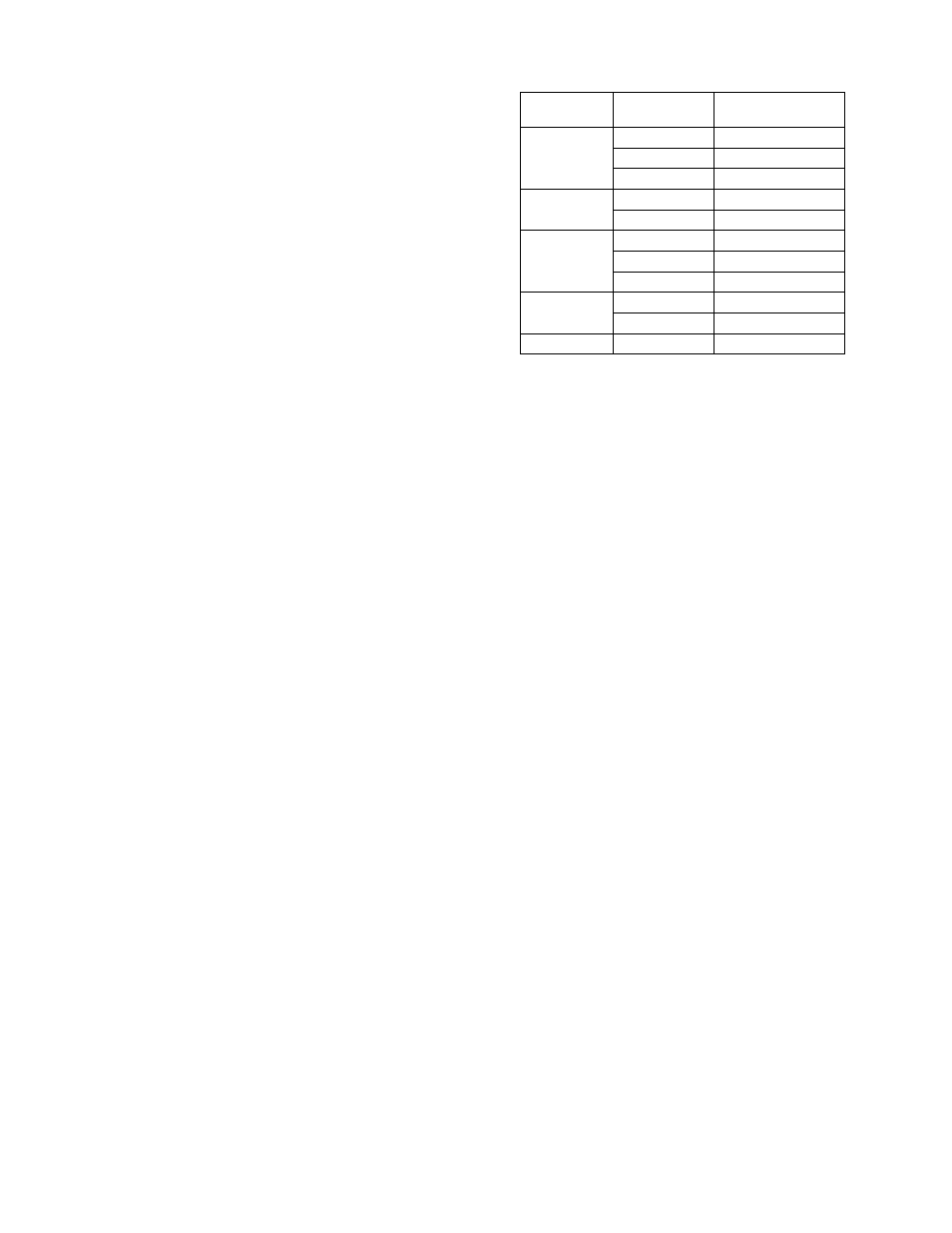
then measure the sensor resistances. The appro-
priate values are listed in Table 1. Since the phase
and neutral sensors are electrically identical, their
resistances should agree closely.
Breaker
CT Rating, A
Resistance,
ohms
150 10.1–15.2
225 14.5–22
LA-600
600 4–58
800 54–81
LA-1600
1600 110–166
150 10.1–15.2
400 27–41
RL-800
800 51–77
800 54–81
RL-1600
1600 110–166
RL-2000 2000
20.4
Table 1. CT resistance values.
