Power spectrum, Fft options – GE Industrial Solutions Control System Toolbox For Configuring the Trend Recorder User Manual
Page 37
GEH-6408A Trend Recorder
Chapter 5 Viewing Trends
•
29
Power Spectrum
The Trend Recorder can perform a spectral analysis on plots of real-time data and
display the power spectrum of the recorded data. The Trend Recorder uses a Fast
Fourier Transform (FFT) to convert the data from the time domain to the frequency
domain. Power spectrum plots may be obtained from any trend but are most reliable
with data obtained using a block-collected trend. Power spectra of data collected
using real-time trending, especially of data coming across networks, should be
regarded as unreliable.
À
To create a Power Spectrum plot
1.
Obtain a plot of data using any of the types of collecting data.
Best results will be obtained when data is collected using block-collected trends
with the capture block configured to collect a number of samples that is a power
of 2 (512, 1024, 2048, etc.). The more samples collected, the better the
resolution of the power spectrum.
2.
From the
View
menu, choose
Power Spectrum
.
The
FFT Options
dialog box displays.
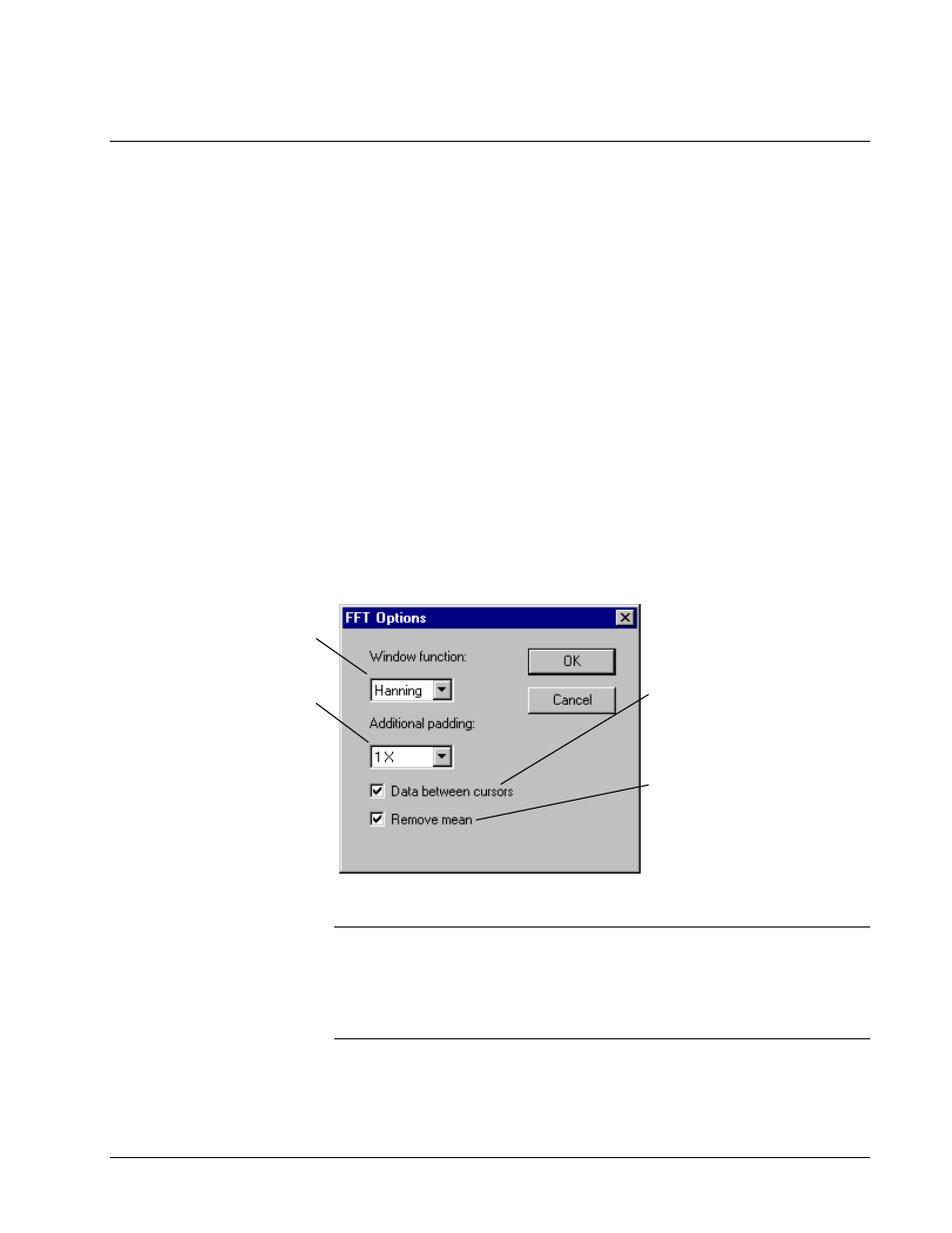
FFT Options
Select the window function to
use with the data. (Refer to the
note below.)
Select how many additional
powers of 2 the data is padded
with 0 values.
The Fast Fourier Transform
algorithm requires a data set
where the number of samples
is a power of 2. Increasing the
padding beyond the nearest
power of 2 increases the
apparent resolution of the
power spectrum.
Check for the power
spectra analysis to be
performed on the data
between the two cursors,
instead of on the entire
set of data contained in
the current event being
trended.
Check to remove any
DC component of the
power spectrum that
could distort the
appearance of the
spectrum near 0 Hz.
Note
A variety of windowing functions (such as Hanning, Hamming, Bartlet,
Welch, and others) are available to minimize phenomena associated with the discrete
time-window nature of the collected data. Refer to other signal processing theory
textbooks for explanations of the theory of operation of Fast Fourier Transforms,
such as Introduction to Communication Systems, Ferrel G. Stremler; Electrical
Noise, W. R. Bennett; Circuits and Systems: A Modern Approach, A. Papoulis.
