Pin descriptions and pinouts – Rainbow Electronics AT25DF081A User Manual
Page 3
3
8715C–SFLSH–11/2012
AT25DF081A
2.
Pin Descriptions and Pinouts
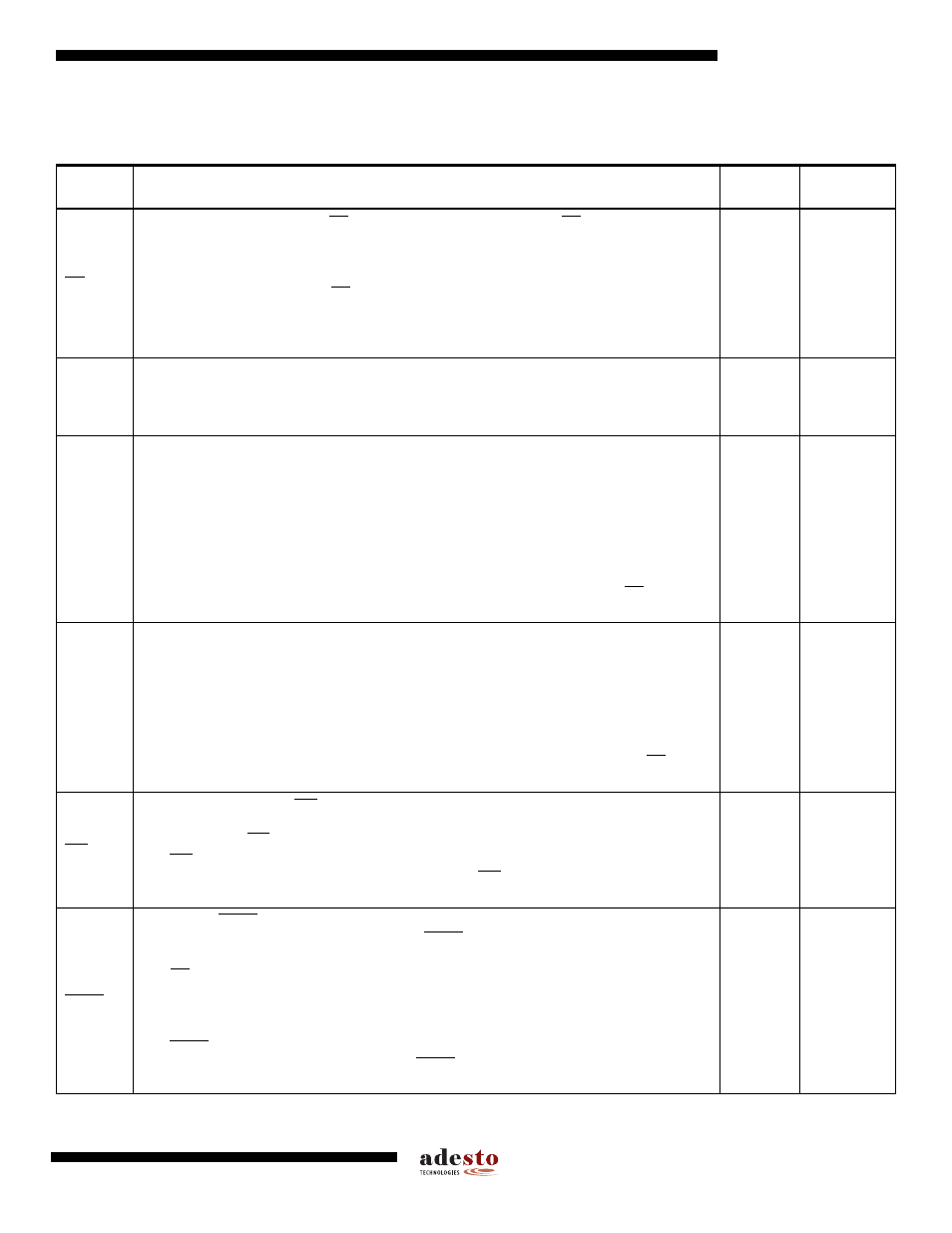
Table 2-1.
Pin Descriptions
Symbol
Name and Function
Asserted
State
Type
CS
CHIP SELECT: Asserting the CS pin selects the device. When the CS pin is deasserted,
the device will be deselected and normally be placed in standby mode (not Deep Power-
Down mode), and the SO pin will be in a high-impedance state. When the device is
deselected, data will not be accepted on the SI pin.
A high-to-low transition on the CS pin is required to start an operation, and a low-to-high
transition is required to end an operation. When ending an internally self-timed operation
such as a program or erase cycle, the device will not enter the standby mode until the
completion of the operation.
Low
Input
SCK
SERIAL CLOCK: This pin is used to provide a clock to the device and is used to control the
flow of data to and from the device. Command, address, and input data present on the SI pin
is always latched in on the rising edge of SCK, while output data on the SO pin is always
clocked out on the falling edge of SCK.
-
Input
SI (SIO)
SERIAL INPUT (SERIAL INPUT/OUTPUT): The SI pin is used to shift data into the device.
The SI pin is used for all data input including command and address sequences. Data on the
SI pin is always latched in on the rising edge of SCK.
With the Dual-Output Read Array command, the SI pin becomes an output pin (SIO) to allow
two bits of data (on the SO and SIO pins) to be clocked out on every falling edge of SCK. To
maintain consistency with SPI nomenclature, the SIO pin will be referenced as SI throughout
the document with exception to sections dealing with the Dual-Output Read Array command
in which it will be referenced as SIO.
Data present on the SI pin will be ignored whenever the device is deselected (CS is
deasserted).
-
Input/Output
SO (SOI)
SERIAL OUTPUT (SERIAL OUTPUT/INPUT): The SO pin is used to shift data out from the
device. Data on the SO pin is always clocked out on the falling edge of SCK.
With the Dual-Input Byte/Page Program command, the SO pin becomes an input pin (SOI) to
allow two bits of data (on the SOI and SI pins) to be clocked in on every rising edge of SCK.
To maintain consistency with SPI nomenclature, the SOI pin will be referenced as SO
throughout the document with exception to sections dealing with the Dual-Input Byte/Page
Program command in which it will be referenced as SOI.
The SO pin will be in a high-impedance state whenever the device is deselected (CS is
deasserted).
-
Output/Input
WP
WRITE PROTECT: The WP pin controls the hardware locking feature of the device. Please
refer to
“Protection Commands and Features” on page 17
for more details on protection
features and the WP pin.
The WP pin is internally pulled-high and may be left floating if hardware controlled protection
will not be used. However, it is recommended that the WP pin also be externally connected
to V
CC
whenever possible.
Low
Input
HOLD
HOLD: The HOLD pin is used to temporarily pause serial communication without
deselecting or resetting the device. While the HOLD pin is asserted, transitions on the SCK
pin and data on the SI pin will be ignored, and the SO pin will be in a high-impedance state.
The CS pin must be asserted, and the SCK pin must be in the low state in order for a Hold
condition to start. A Hold condition pauses serial communication only and does not have an
effect on internally self-timed operations such as a program or erase cycle. Please refer to
for additional details on the Hold operation.
The HOLD pin is internally pulled-high and may be left floating if the Hold function will not be
used. However, it is recommended that the HOLD pin also be externally connected to V
CC
whenever possible.
Low
Input
