Ss pin functionality – Rainbow Electronics AT90S8515 User Manual
Page 48
48
AT90S8515
0841G–09/01
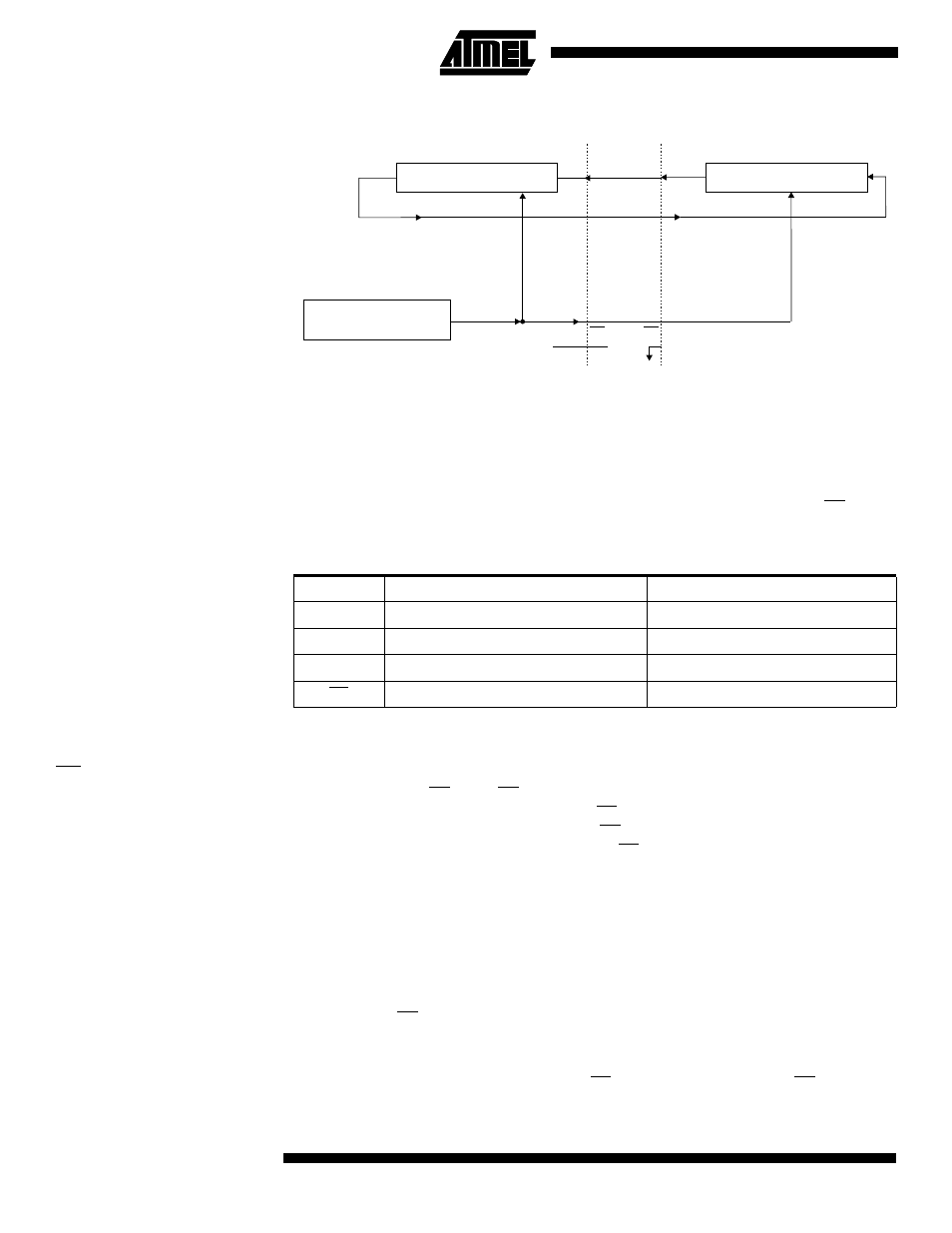
Figure 35. SPI Master-slave Interconnection
The system is single-buffered in the transmit direction and double-buffered in the
receive direction. This means that bytes to be transmitted cannot be written to the SPI
Data Register before the entire shift cycle is completed. When receiving data, however,
a received byte must be read from the SPI Data Register before the next byte has been
completely shifted in. Otherwise, the first byte is lost.
When the SPI is enabled, the data direction of the MOSI, MISO, SCK and SS pins is
overridden according to Table 15.
Note:
See “Alternate Functions of Port B” on page 66 for a detailed description of how to define
the direction of the user-defined SPI pins.
SS Pin Functionality
When the SPI is configured as a master (MSTR in SPCR is set), the user can determine
the direction of the SS pin. If SS is configured as an output, the pin is a general output
pin, which does not affect the SPI system. If SS is configured as an input, it must be held
high to ensure master SPI operation. If the SS pin is driven low by peripheral circuitry
when the SPI is configured as master with the SS pin defined as an input, the SPI sys-
tem interprets this as another master selecting the SPI as a slave and starts to send
data to it. To avoid bus contention, the SPI system takes the following actions:
1.
The MSTR bit in SPCR is cleared and the SPI system becomes a slave. As a
result of the SPI becoming a slave, the MOSI and SCK pins become inputs.
2.
The SPIF flag in SPSR is set, and if the SPI interrupt is enabled and the I-bit in
SREG is set, the interrupt routine will be executed.
Thus, when interrupt-driven SPI transmittal is used in Master Mode and there exists a
possibility that SS is driven low, the interrupt should always check that the MSTR bit is
still set. Once the MSTR bit has been cleared by a slave select, it must be set by the
user to re-enable SPI Master Mode.
When the SPI is configured as a slave, the SS pin is always input. When SS is held low,
the SPI is activated and MISO becomes an output if configured so by the user. All other
Table 15. SPI Pin Overrides
Pin
Direction, Master SPI
Direction, Slave SPI
MOSI
User Defined
Input
MISO
Input
User Defined
SCK
User Defined
Input
SS
User Defined
Input
MSB
MSB
MASTER
LSB
LSB
SLAVE
SPI
CLOCK GENERATOR
8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER
8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER
MISO MISO
MOSI MOSI
SCK
SCK
SS
SS
V
CC
